Disturbances in skin collagen metabolism caused by ultraviolet radiation are the main causes of skin photoaging.
Single exposure to ultraviolet radiation has been shown to decrease procollagen mRNA expression in the dermis, and chronic ultraviolet exposure has been shown to decrease collagen and cause wrinkling.
As you know, amino acids regulate protein metabolism, and by maintaining their level, you can slow down the degradation of collagen, and therefore preserve youth.
On estet-portal.com, read how amino acids support skin health and how to use them to keep you young.
- Amino combinations counteract photoaging
- The effect of various amino acids on the skin
- Mechanisms of Skin Rejuvenation with Amino Acidsfrom
Combinations of amino acids resist photoaging
Scientists have investigated the effects of ultraviolet radiation and various orally administered amino acids on the rate of collagen synthesis in the skin.
Branched-chain amino acids, arginine, glutamine, and proline did not increase the fractional rate of skin tropocollagen synthesis compared to distilled water as a control.
However, mixtures of essential amino acids significantly increased the rate of tropocollagen synthesis.
The result indicates that combinations of BCAAs and glutamine or proline are important in restoring UV-damaged collagen protein synthesisem.
Cosmetic use of collagen: does it really work
Effects of various amino acids on the skin
Amino acids are protein substrates and regulators of protein metabolism and are safe for humans.
An in vitro study found that glutamine increased procollagen mRNA levels and collagen content and suggested that de novo proline synthesis from glutamine is important for collagen synthesis.
Proline and its precursors, glutamate and pyrroline-5-carboxylate, enhance collagen synthesis in human fibroblasts.
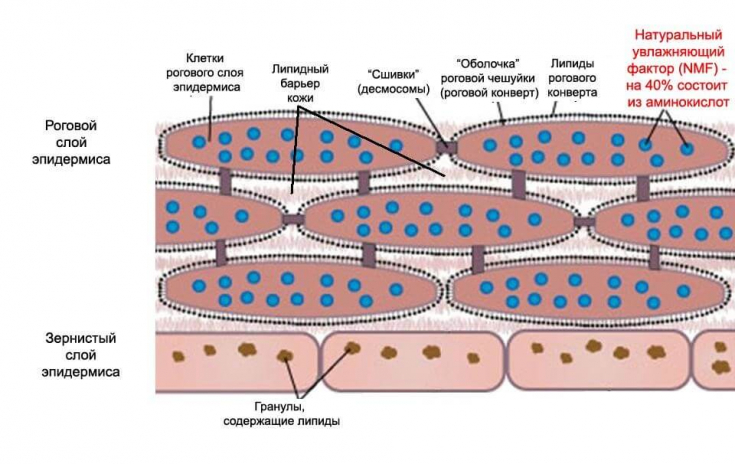
Some amino acids such as arginine and ornithine, as well as mixtures of amino acids, promote wound healing in rats.
However, little research has been done on the ability of amino acids to restore collagen synthesis in the skin after UV exposure.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Mechanisms of skin rejuvenation with amino acids
Collagen is a major component of the dermis and is essential for maintaining the structure of the skin, and exposure to excess ultraviolet radiation drastically reduces the amount of collagen in the skin, leading to skin aging or delayed wound healing.
Proline and its precursors, glutamate significantly increase collagen synthesis in human dermal fibroblasts.
While nitric oxide (NO) produced by dermal fibroblasts activates collagen synthesis, certain amino acids such as arginine, ornithine and amino acid blends accelerate wound healing by increasing the amount of dermal collagen produced by NO dependent mechanisms.
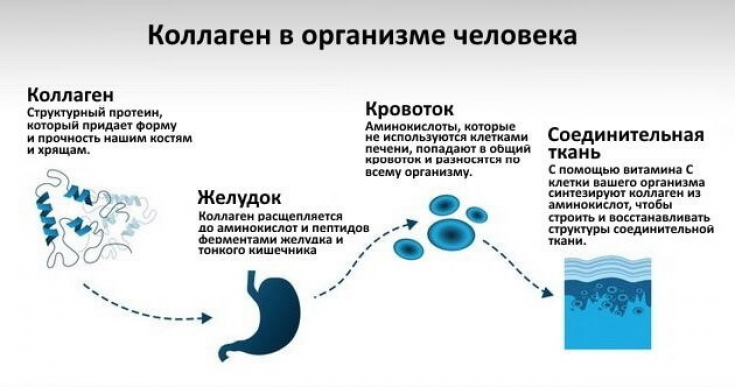
Moreover, recent studies show that the silk protein, sericin, improves epidermal hydration in parallel with elevated filaggrin levels in an animal model of atopic dermatitis.
These results indicate that amino acids not only protect the skin from damage caused by ultraviolet radiation, including skin aging and delayed wound healing, but may also be useful in the treatment of certain skin conditions such as atopic dermatitis.
Fibroblast stimulation and collagen synthesis – effective way of skin rejuvenation







Add a comment