Acne is one of the most common skin diseases that causes comedones, papules, pustules, cysts, nodules, scars, which reduces the quality of human life. Three main pathogenic factors play an important role in the development of acne: excessive secretion of sebum, hyperkeratinization of follicular keratinocytes, colonization of Propionibacterium acnes (P.acnes).
Currently, there are many systemic and local approaches in the treatment of acne, but the effectiveness and safety some funds are still questionable. Acids, especially salicylic acid, are very popular both in salon procedures and in home use. In this article on estet-portal.com, you will learn about the effectiveness of salicylic acid in patients with acne.
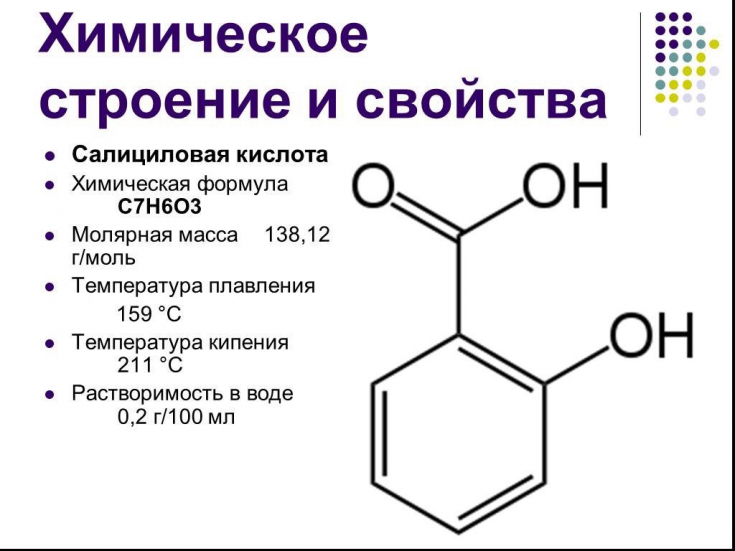
- Salicylic Acid Characteristics
- The effect of salicylic acid on lipid production
- Salicylic acid, effect on inflammation
- Conclusion
Salicylic Acid Characteristics
Salicylic acid is a typical exfoliator. It is a beta hydroxy acid extracted from natural plant sources and can also be synthesized artificially. Salicylic acid can soften the stratum corneum and rapidly dissolve desmosomes, resulting in decreased adhesion of corneocytes and flaking of corneocyte sheets. As a result, salicylic acid has comedolytic properties and promotes cell renewal.
Due to its lipotropic effect, salicylic acid easily penetrates into the sebaceous glands and counteracts hyperseborrhea, providing an additional therapeutic effect.
Anti-inflammatory activity is another important property of salicylic acid, which reduces facial erythema.
Salicylic acid is widely used in the treatment of acne as a chemical peeling agent.
Read also: Etiological factors of acne.
In vitro experimental results initially confirmed that salicylic acid mainly targets two of the three pathological processes in acne, including excessive sebum production and inflammation.
Previous research has mainly focused on its exfoliating properties and comedolytic mechanism. There have been only a few clinical studies that have reported its sebosuppressive and anti-inflammatory activity. However, the detailed mechanisms behind these two actions have not been fully understood.
The effect of salicylic acid on lipid production
Salicylic acid significantly reduced lipid levels by 27.9% and 41.2% at 50 and 100 µmol/L treatment, respectively. Notably, the lipid content decreased as the concentration of salicylic acid increased.
The main features of salicylic acid.
At the transcriptional level, quantitative real-time PCR showed that salicylic acid reduced mRNA levels of styrene protein isoforms by 40%. Salicylic acid also inhibited synthesis of fatty acids and acetyl-CoA carboxylase, the main downstream targets of styrene series proteins. Moreover, salicylic acid has been found to significantly inhibit COX-2 expression. Thus, lipogenesis was inhibited by suppression of the MAPK/SREBP-1 pathway after treatment with salicylic acid.
Salicylic acid, effect on the inflammatory process
The MAPK (mitogen-activated protein kinase) and NFκB pathways have been identified as pathways involved in the inflammatory process. Salicylic acid suppresses the P. acnes inflammatory response by inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway in sebocytes.
To confirm this finding, mRNA expression of several pro-inflammatory cytokines from P. acnes-treated inactivated sebocytes was tested by qPCR. Expression of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, oncostatin-M, and oncostatin-M receptor was similar to microarray expression, supporting the hypothesis that the NF-βB pathway was activated in sebocytes stimulated with heat-inactivated P .acne.
Features of peeling with salicylic acid.
Enzyme immunoassay confirmed that salicylic acid significantly reduced the expression of IL-1.beta., IL-6, TNF-.alpha. in a dose-dependent manner.
Thus, in a dose dependent manner, salicylic acid reduced cytokine expression in human SEB-1 sebocytes.
It is generally understood that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and sterol response element binding proteins (SREBP) play a vital role in inducing sebum suppression due to salicylic acid. Research results strongly support the anti-inflammatory properties of salicylic acid.
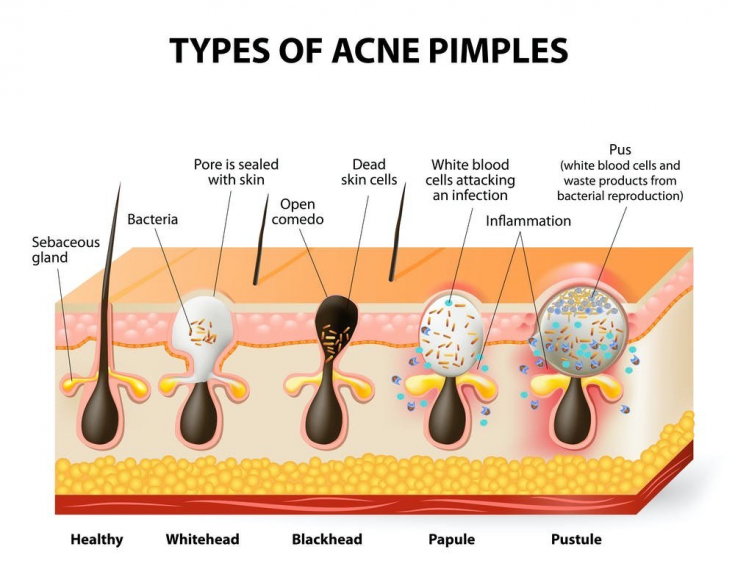
Salicylic acid reduces the viability of SEB-1 sebocytes by increasing apoptosis via signaling pathways. After salicylic acid treatment of the skin, the number of cells in the process of apoptosis increased, since the concentration of salicylic acid increased from 3% to 16%. In addition, salicylic acid causes a significant reduction in cell growth not only in SEB-1 sebocytes, but also in SZ95
sebocytes.
Conclusion
Understanding the mechanisms of action makes it easier to choose one or another acid for different patients. The use of salicylic acid is a successful and, most importantly, safe therapeutic strategy in the treatment of acne and hyperseborrhea. Patients experience no discomfort during salicylic acid cosmetic procedures and can also use salicylic acid products at home.







Add a comment