The understanding that skin barrier dysfunction influences the activity of atopic dermatitis has led to increased interest and emphasis on treatments that improve skin barrier function.
Moisturizers are the primary treatment for atopic dermatitis. Moisturizers that improve barrier function (protective cream) have been shown to reduce the incidence of atopic dermatitis recurrence when used regularly.
On estet-portal.com, read what are the levels of treatment for atopic dermatitis, and why moisturizing is at the forefront of the treatment of this disease.
- Moisturizers for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis
- Bathing for atopic dermatitis – it is an important element of treatment
- Peculiarities of treatment of moderate and severe atopic dermatitis Moisturizers for the treatment and prevention of atopic dermatitis Moisturizer ingredients that are helpful for atopic dermatitis include:
(e.g. ceramides, cholesterol) – they restore the composition of lipid bilayers in the stratum corneum and reduce the permeability of the skin;
Physiological humectants (urea, glycerin) that do not participate in the metabolic process of the skin, but prevent excessive water loss and keep the stratum corneum hydrated;
- Anti-itch (e.g. glycerin) that block the release of histamine and allow the stratum corneum to start repairing;
- Dexpanthenol – stimulates lipid synthesis and epidermal differentiation;
- Occlusive agents (e.g. petroleum jelly) that reduce water evaporation;
- Emollients that soften the skin (such as cream with sorboline and glycerin).
- Lifestyles to choose for atopic dermatitis
Restoration of the barrier function of the skin can actively prevent the development or progression of atopic dermatitis, as shown in randomized control trials of newborns at risk of 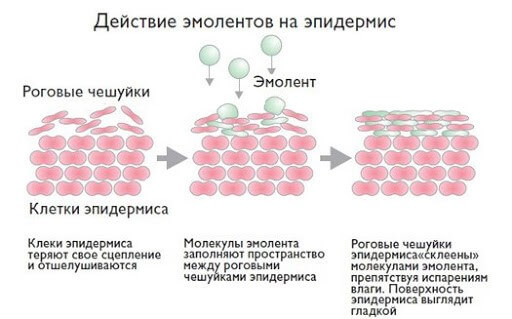 daily moisturizing skin
daily moisturizing skin
It is recommended to apply moisturizer shortly after bathing. Non-soapy, hypoallergenic, low pH cleansers are recommended as soap substitutes, as they cause less damage to the stratum corneum and acid mantle of the skin.
Bathing will help to remove irritants, allergens and scales in atopic dermatitis, allowing the skin barrier to repair more quickly.
Using the
"soak and smear" technique

New options for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults
Bleaching agents have been shown to be useful in reducing the clinical severity of atopic dermatitis due to their antibacterial, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties.
Whitening baths – this is diluting household bleach with bath water. The concentration of chlorine is similar to that in a swimming pool. It has an antimicrobial effect.
Althoughsodium hypochlorite (bleach) normally has an alkaline pH (pH 11–13), when dissolved in water it releases hypochlorous acid (pH 2–7.5). It is possible that this acidity helps to maintain the normal
skin barrier function
and also acts as an antiseptic.Peculiarities of treatment of moderate and severe atopic dermatitis
Other treatments that are sometimes needed for atopic dermatitis include other topical anti-inflammatory drugs such as: Topical calcineurin inhibitors; Wet wraps;
Antibiotics to treat secondary infections;
Oral antihistamines to relieve symptoms.
- Read the most interesting articles in
- Telegram !
severe atopic dermatitis, recommended treatments include: Phototherapy; Oral corticosteroids; Non-steroidal immunomodulators or immunosuppressants;
New biological agents, such as dupilumab.
Severe atopic dermatitis requires- a strict diet, intensive moisturizing of healthy skin and effective treatment of affected areas
- . Accomplishment of a daily care ritual can avoid exacerbation of atopic dermatitis, or endure it in a mild form. More useful and interesting information on our channel on
- YouTube
:







Add a comment