Nevus is a malformation of the skin, which is characterized by the appearance on it, less often on the mucous membranes, conjunctiva and in the choroid of the eyeball, spots or formations consisting of nevus cells. Nevi arise due to disorders that developed in the embryonic period. Different types of nevi are many people of different age groups. They are congenital and acquired, occur in childhood and persist into old age. All nevi may enlarge and become more pigmented at puberty or during pregnancy.
Provocative transformation factors in different types of nevi
Provoking factors for the transformation of certain types of nevi into melanoma are various injuries – mechanical, chemical, radiation. Therefore, biopsy of a suspicious pigmented skin formation or its partial cosmetic treatment (electrocoagulation, cryotherapy, exposure to chemical and other factors) without prior diagnosis is absolutely contraindicated.
A significant proportion of patients with melanoma of the skin (20-70%) indicate a previous injury in the area of the existing nevus.
On the other hand, surgical removal of such nevi within healthy tissue has never been associated with the development of melanoma.
The following types of nevi are clinically distinguished:
- melanocytic nevus;
- congenital melanocytic nevus;
- dysplastic nevus;
- Dubrel's melanosis;
- vascular nevus;
- nevus of connective tissue.
Characteristic features and pathohistology of dysplastic nevus
Dysplastic nevus (Clark's nevus, atypical birthmark) – this is an acquired pigment formation.
Dysplastic nevus occurs in 5% of the white population. It is detected in almost all patients with familial melanoma and in 30-50% of patients with sporadic melanoma, notes estet-portal.com. Men and women get sick with the same frequency. A dysplastic nevus occurs on unaffected skin or as a component of a complex neocellular nevus.
These types of nevi appear during life. Clinically, they are manifested by uneven pigmentation of the skin from black-brown to pink-red with a darker area in the center of the neoplasm. Nevus has indistinct borders, irregular shape, more often localized on the back, lower extremities, scalp, chest, buttocks, genitals.
Pathological examination of a dysplastic nevus reveals a disordered proliferation of polymorphic atypical melanocytes.
This type of nevus is diagnosed on the basis of the clinical picture in combination with epiluminescence microscopy and histological examination results. Surgical removal indicated.
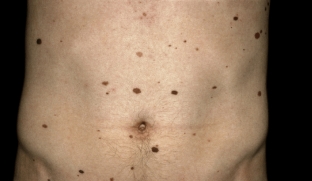
Nevus of connective tissue – type of nevus with probable malignant degeneration
Nevus of connective tissue (collagenoma, elastoma, “shagreen plaques”, disseminated lenticular dermatofibrosis) – it is a cutaneous hamartoma that is predominantly composed of collagen, elastin, or both. More common in older men.
Clinically, a connective tissue nevus is manifested by the presence of asymptomatic papules or plaques. They are localized around the genitals, on the palms, the nail bed, mucous membranes, the color is flesh or yellowish.
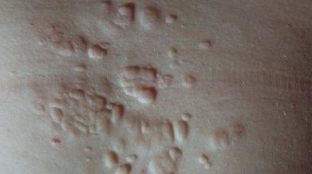
Pathological examination reveals dense conglomerates of collagen and elastin fibers. The diagnosis is made on the basis of clinical manifestations and data from instrumental and histological studies. Connective tissue nevus should be differentiated from scleroderma, dermatofibroma, xanthoma.
With this type of nevus, surgical removal or observation is indicated. The prognosis is favorable, but in some cases malignant degeneration is possible.
With what pathologies should vascular types of nevi be differentiated
Vascular nevi (congenital vascular skin lesions, vascular malformations, Unna's nevus, flaming nevus, port wine stain) – congenital malformations of blood or lymphatic vessels of a permanent nature (with the exception of Unna's nevus). They can be combined with malformations of the vessels of the eye and meninges. They occur in 0.3% of newborns. The cause of the appearance of vascular nevi & nbsp; not definitively clarified. On their development may affect the pathological course of pregnancy, phenotypic features and environmental factors. Nevi are pink-red or purple in color.
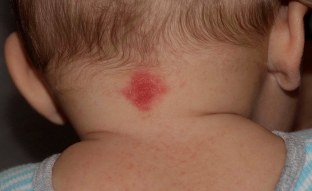
Pathological examination of vascular nevi reveals primary neurodystrophy and secondary angiopathy. Diagnosis of this type of nevus is carried out on the basis of clinical manifestations and data from instrumental and histological studies. Vascular malformations must be differentiated from hemangioma, angiokeratoma, lupus erythematosus, lymphohemangioma.
The main methods of therapy for vascular nevi are: cryodestruction, electrocoagulation, sclerosing, selective phytothermolysis. The prognosis is favorable.
For all types of nevi, constant monitoring is necessary.







Add a comment