Botulinum toxin has long been used in many branches of medicine. It helps to treat blepharospasm in ophthalmology, muscle hyperactivity after a stroke and due to neurological injuries, eliminates mimic wrinkles, allows you to fight urinary incontinence due to overactive bladder, minimizes migraine symptoms and much more.
However, why would a toxin be even more valuable? By suppressing the pathological hyperactivity of the muscles, it eliminates pain by blocking the neuromuscular transmission, preventing the pain impulse from reaching the brain.
Moreover, recent studies have shown that botulinum toxin also has its own analgesic effect. Due to what the neurotoxin suppresses pain, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Mechanisms of pain suppression with botulinum toxin
When botulinum toxin is used to treat painful muscle hyperactivity disorders, patients often report significant pain relief. So far, this pain relief has been associated with a reduction in muscle hyperactivity. However, formalin-induced pain in animals can be reduced by the direct analgesic effect of botulinum toxin. It is likely that this effect of the neurotoxin is based on the effect on other neurotransmitters besides acetylcholine.
Botulinum toxin has an analgesic effect by blocking not only acetylcholine, but also other neurotransmitters.
Botulinum toxin interrupts the pathological chain, the nerve impulse that goes from the nociceptors to the brain, and thereby alleviates the pain and discomfort of the patient.
Botulinum toxin: a terrible poison or an invaluable medicine
Substance P: the effect of botulinum toxin on pain neuropeptide
Substance P, a neuropeptide involved in pain perception, vasodilation, and neurogenic inflammation, can be blocked by botulinum toxin along with acetylcholine in rabbit iris muscles as well as cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons.
This substance in humans is found in the brain and spinal cord, skin, muscles, intestinal nervous system, and thyroid gland. What does it mean that if you block this neuropeptide, you can suppress the pain impulse from almost anywhere in the body, and also indirectly fight inflammation in the future.
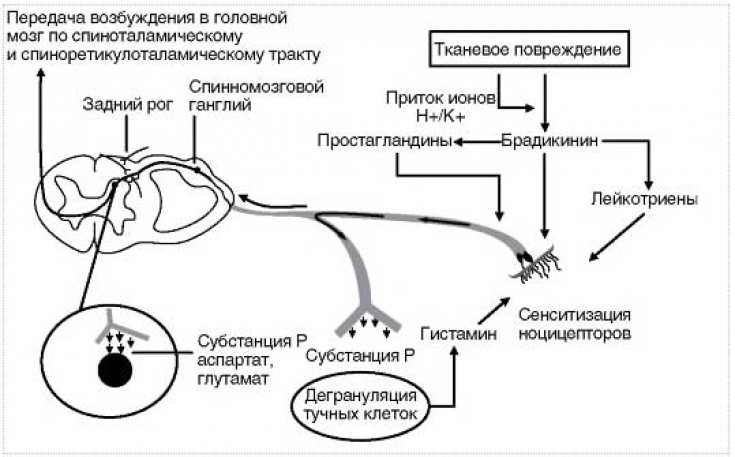
The association of substance P inhibition by botulinum toxin with the decrease in SNAP 25 suggests a direct effect of the toxin. Botulinum toxin-induced suppression of substance P can also be demonstrated in dorsal root ganglion neurons of rat embryos, suggesting that botulinum toxin may have similar effects in humans.
Read the latest articles in Telegram
Botulinum toxin and glutamic acid: suppression of nociception
Neurotoxin has also been shown to inhibit the release of glutamic acid – excitatory amino acid, another neurotransmitter involved in nociception, in the periphery and dorsal horn, confirming earlier findings of botulinum neurotoxin-induced inhibition of glutamic acid release from cerebrocortical synapses.
The binding of glutamic acid to specific receptors leads to the excitation of neurons. Therefore, by blocking it, botulinum toxin is able to suppress the nerve transmission of pain impulses.
Norepinephrine release in cells can also be reduced by botulinum toxin, suggesting additional possible mechanisms for the neuropeptide's effect on pain transmission.
Thus, botulinum toxin has great potential as an analgesic, and the day is not far off when it will be used even more widely than it is now.
BOTOX injections® in different age periods: when and what to correct







Add a comment