Botulinum toxins are among the most toxic poisons known to man, with a lethal dose of approximately 1 ng per kilogram of body weight. There are seven different serological botulinum toxins. Botulinum toxin A is the most potent serotype, with a toxicity one million times higher than cobra toxin and much higher than cyanide.
While botulinum toxin is generally considered safe in aesthetic medicine, its widespread use and ever-expanding indications raise safety concerns.
The purpose of this article on estet-portal.com is to review the complications of therapeutic and cosmetic use of botulinum toxin and ways to prevent them. dermatovenereologist, pediatric neurologist (Krivoy Rog) Ekaterina Avramenko helped to figure it out.
Botulinum therapy: features of a healing toxin

Botulinum neurotoxins are among the most toxic substances found in nature.
Their mechanism of action is based on the inhibition of acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction of striated muscles, resulting in chemical denervation and muscle paralysis.
The therapeutic use of botulinum toxin began about two centuries ago, and the indications for the use of botulinum toxin are constantly expanding.
Botulinum toxin type A injections have become the most common cosmetic procedure since 2002.
Despite the fact that BOTOX® of the Allergan company is one of the most studied and safe drugs, it is important for the doctor to follow the instructions of the drug and clearly follow all the rules for its recovery, storage and administration, in order to prevent any possible complications.
Toxin at gunpoint: how botulinum toxin works
Main side effects of botulinum toxin therapy
Systemic dissemination of toxins can lead to adverse events indicative of botulism, including muscle weakness or paralysis, dysarthria, dysphonia, dysphagia, and respiratory arrest.
Adverse events are more common after therapeutic use of botulinum toxin, but can also be seen after cosmetic use.
Botulinum toxin injections are generally well tolerated with few side effects. There may be mild pain on injection and local swelling, erythema, transient numbness, headache, malaise, or mild nausea. Approximately 1-3% of patients may experience temporary upper eyelid ptosis or drooping eyebrows. This is due to the diffusion of botulinum toxin into the levator muscle palpebrae superioris.
For more interesting articles visit Facebook!
How to avoid complications of botulinum toxin therapy
Patients are often asked to remain upright for three to four hours after injection and not to touch the injection site to avoid diffusion of the toxin into adjacent muscles.
Active contraction of the treated muscles may increase the uptake of botulinum toxin and reduce its diffusion.
Bruising may occur after botulinum therapy, especially if the patient is taking aspirin, vitamin E, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Ideally, patients should stop taking these medications two weeks before the procedure.
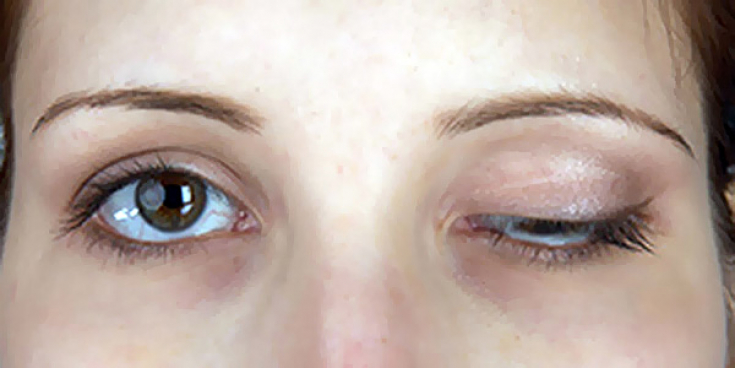
Headaches may also occur after injections, however this is most likely due to the injury from the injection rather than the toxin.
Proper storage of BOTOX®, choosing the correct dose, and correct reconstitution of the drug will help prevent any side effects.
Original drugs of the Allergan company You can only purchase from an authorized distributor.
Botulinum toxin recovery: important aspects of the use of the drug







Add a comment