Statistical data from countries around the world indicate an increase in cases of latent syphilis.
This situation increases the risk of infection of healthy people, including infection of children during pregnancy.
Congenital syphilis – an insidious venereal disease that affects the unborn child.
Closely half of these pregnancies end in abortion or early death of the baby. Children who manage to survive may have serious consequences for their health in the future.
On estet-portal.com read about what happens to an infected fetus, as well as about the main signs of early and late congenital syphilis.
How does infection with syphilis pathogens occur and manifest?
In the etiology of congenital syphilis, attention must be paid to the fact that the transmission of syphilis occurs transplacentally from a sick mother.
Pale treponemas cross the placental barrier, penetrating the fetus through the umbilical vein and lymphatic vessels from the 10th week of pregnancy.
However, pathological changes in the fetus occur only at 4-5 months of gestation.
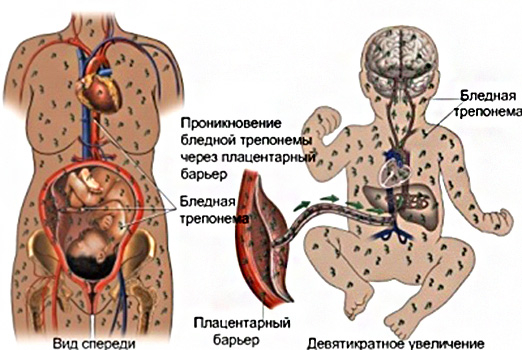
In pregnant women with a history of secondary syphilis, infection of the fetus occurs in almost 100% of cases, less often intrauterine infection occurs in patients with late forms of syphilis and extremely rarely – in patients with primary syphilis.
Typical specific changes in the fetus include: enlargement and hardening of organs, as well as diffuse inflammatory infiltration and proliferation of connective tissue.
The lungs suffer most («white pneumonia») due to specific infiltration, hyperplasia and desquamation of the epithelium of the alveoli.
The phenomena of osteochondrosis and periostitis are also characteristic, which are already detected on x-rays at 5-6 months.
Early congenital syphilis: reliable signs of congenital pathology
Early congenital syphilis is considered the period from the moment of fetal formation to 2 years of a child's life. In some cases, early syphilis can be hidden – without any clinical signs, but with positive serological reactions.
Early congenital syphilis includes:
• fetal syphilis;
• syphilis in infants;
• syphilis of early childhood (1-2 years).
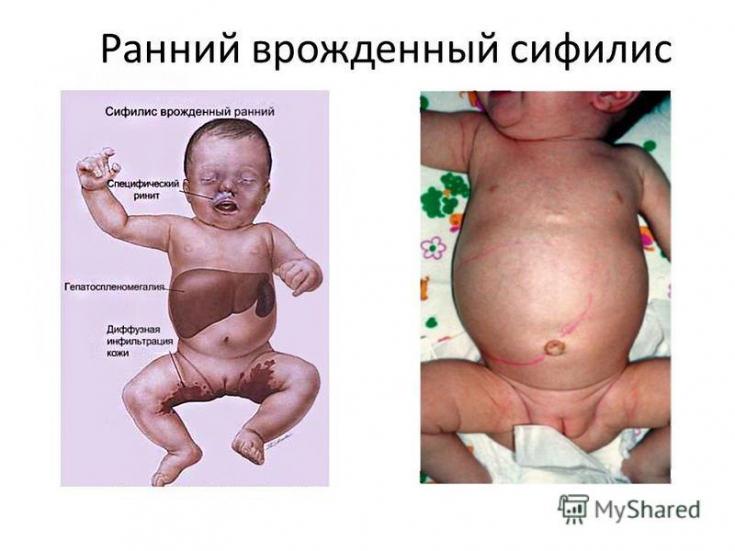
For a newborn, the characteristic classic look – malnutrition, hydrocephalus and maceration of the skin.The characteristic signs of early congenital syphilis are: syphilitic pemphigus, osteochondritis, lesions of internal organs and the nervous system.
Also, early congenital syphilis is manifested by specific rhinitis, which is manifested by severe mucosal edema, profuse discharge and difficulty in nasal breathing.
Often, infiltrative changes in the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity lead to deformities and the formation of a saddle nose.
Late congenital syphilis: Hutchinson's triad and other features
The symptoms of late congenital syphilis are similar to those of the tertiary period.
The absolute signs (Hatchinson's triad) of late syphilis are:
1.
2. specific labyrinthitis (bilateral lesion of the labyrinth and degenerative processes in the auditory nerve);
3. parenchymal keratitis (clouding of the cornea with subsequent loss of vision).
This period is also characterized by the appearance of gummas or tuberculous syphilis, which appear on the face, trunk, limbs, nasal mucosa and hard palate.Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Venerology" section. You may also be interested in:
Secondary syphilis: a dangerous enemy in the guise of other diseases







Add a comment