Most often, the course of dermatitis is of an erased character, inflammation is associated with an infectious agent, the identification of which is difficult.
Topical glucocorticoids are among the most widely used topical drugs in dermatological practice, due to the wide coverage of pathogenetic targets and the good knowledge of both positive and negative action vectors.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com all features of the use of topical glucocorticoids in dermatology.
Mechanism of action of topical glucocorticoids
According to the theory that arose in the 70s of the twentieth century, penetrating into the cell, glucocorticoids bind to cytosolic receptors, forming a complex that, moving into the nucleus, activates the expression of genes responsible for the synthesis of proteins with anti-inflammatory action.
Follow us on Instagram!
However, later scientists found that hormone-receptor complexes bind to transcription factors that are activated as a result of exposure to inflammatory mediators of free-radical oxidation products, toxins, viruses, resulting in a decrease in the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, enzymes, endolin- 1, adhesion molecules and the like.
What a dermatologist should know about hives in children
Recently, the ability of glucocorticoid and glucocorticosteroid receptors to interact with the formation of a heterodimer has been proven, which makes it possible for there to be various variations and biological effects of glucocorticosteroids depending on the ratio of their concentration in physiological and pathological conditions.
Biological effects of glucocorticoids
Glucocorticosteroid preparations effectively eliminate allergic and inflammatory reactions due to:
1) Vasoconstrictor effect, blocking the migration of lymphocytes and macrophages, as well as the release of cytokines and other inflammatory mediators;
2) The properties of glucocorticosteroids to block the metabolism of arachidonic acid − the starting product of a cascade of various enzymatic redox reactions;
3) Effect of glucocorticoids suppression of hyaluronidase activity, stabilization of lysosomal membranes of epidermal cells.
Main risk factors for melanoma

According to Miller & Munro, depending on the activity of the anti-inflammatory action of the drug, topical glucocorticosteroids (glucocorticoids + mineralocorticoids) can be divided into:
1. Glucocorticosteroids with low activity (class 1 − weak): hydrocortisone acetate, prednisolone, as well as combined preparations containing hydrocortisone and prednisolone;
2. Glucocorticosteroids with moderate activity (class 2 – moderately strong): triamcinolone acetonide, aclomethasone dipropionate, deoxymethasone, mazipredone, prednicarbate, etc.;
3. Active glucocorticosteroids (class 3 − strong): amcinonide, betamethasone valerate, betamethasone dipropionate, etc.;
4. Highly active glucocorticosteroids (class 4 − superstrong): halobetasol propionate, galcinonide, diflorazone diacetate, etc.
Differences in dosage forms of glucocorticoids
The effectiveness of the treatment of a patient with dermatitis depends on the adequacy of the selected medicinal substance and the form of the drug, taking into account the activity of the process, its depth and the individual characteristics of the patient. So, in case of exudative processes, it is recommended to use topical glucocorticoids of the 2nd class, of medium strength.
A new antibiotic in the treatment of pyoderma
However, dermatitis therapy should be started with the weakest ones, switching to more active glucocorticosteroid drugs after 2-3 weeks if there is no effect. For secondary infection, combined antimicrobial agents should be used.
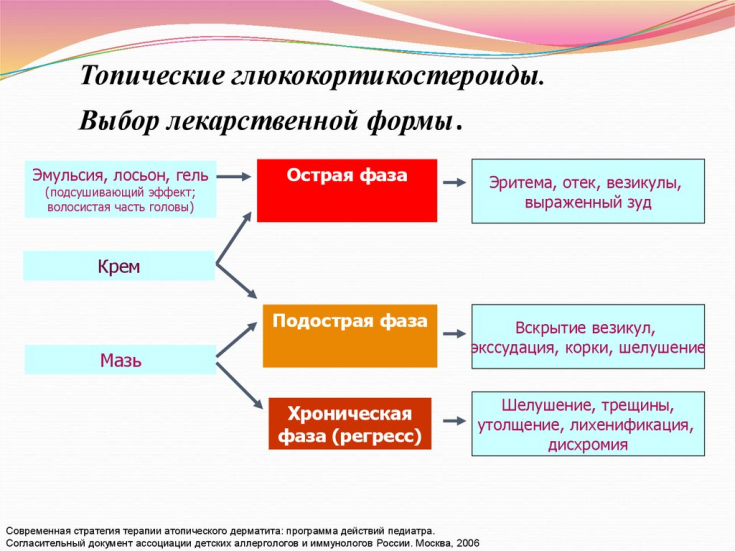
The application of the ointment ensures deep penetration of the drug, cream and lotion − more superficial. In chronic processes, the use of ointments, acute − cream, lotion, emulsion. With an excessive amount and frequency of use of the drug or the wrong method of application, the development of adverse reactions is possible. Therefore, it is important to explain in detail to the patient how to apply the drug, guiding him how to achieve the optimal dosage.
Therapeutic efficacy of histamine blockers in eczema
The use of ointments with topical glucocorticoids increases the risk of a common side effect of this group of drugs − accession of a secondary bacterial and fungal infection. At the same time, the combination of glucocorticosteroids with an antiseptic reduces the likelihood of complications. Unlike the combination of a glucocorticosteroid with an antibiotic, the combination of such a drug with an antiseptic has a wide spectrum of action.
Discoveries in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis
It has been noted that the use of traditional fat-based ointments in acute exudative processes can increase the severity of inflammation. The hydrophilic base with high osmolar activity does not cause a harmful effect on tissues, absorbing exudate and providing control over the depth of penetration of glucocorticoids, limiting their action in the lesion.
Immune function of the skin to guard the health and order of the body







Add a comment