Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by the development of a polymorphic itchy rash and a tendency to recur.
Eczema is treated with topical emollients and topical glucocorticosteroids. However, today there is no consensus on the effectiveness of the use of systemic antihistamines, in particular H1 receptor blockers, in eczema.
Only in our article on estet-portal.com read about the latest research on the use and effectiveness of H1-histamine blockers in the treatment of eczema.
Study of the effectiveness of histamine blockers in eczema
Scientists from the Institute of Medical Sociology, Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, University of Regensburg analyzed the results of 25 randomized controlled trials aimed at determining the effectiveness of the use of histamine H1 receptor blockers as an adjuvant to topical treatment of eczema therapy.
Follow us on Instagram!
Evaluation of randomized controlled trials
The authors analyzed the databases of patients diagnosed with eczema from the Cochrane Skin Group specialized registry, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), information databases MEDLINE, Embase, etc.
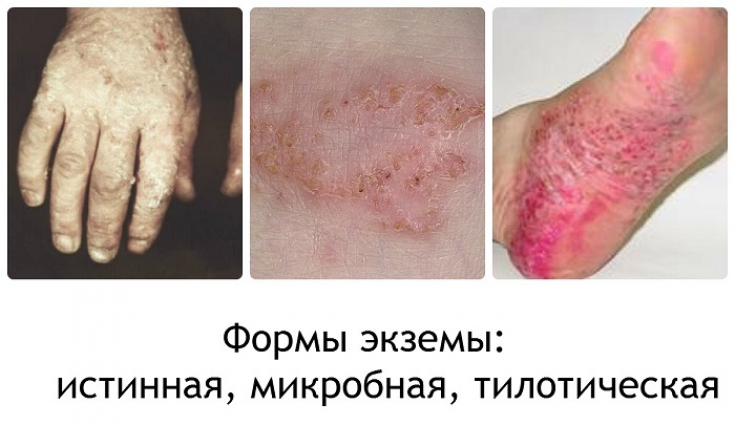
Twenty-five randomized controlled trials evaluated the efficacy of 17 systemic histamine blockers in reducing the symptoms and manifestations of eczema.
Mycosis fungoides: a trial of psoralen photochemotherapy
Due to the heterogeneity of the sample and the varying duration of use of systemic histamine blockers by participants (from 3 days to 18 months), scientists report the results of studies of only three oral histamine H1 receptor blockers: cetirizine, fexofenadine and loratadine. According to scientists, studies of the effectiveness of these three drugs are best suited for statistical analysis.
Efficacy of the histamine blocker cetirizine in eczema
The efficacy of the histamine blocker cetirizine was compared with placebo as adjuvant therapy for eczema in adults. Parameters such as changes in the intensity of itching and the severity of clinical manifestations of eczema according to the SCORAD scale (scoring of atopic dermatitis - scale of atopic dermatitis) were assessed against the background of the use of drugs.
What pathological conditions are often accompanied by chronic itching
The study involved 84 adult participants. The dose of cetirizine was 10 mg/day, the duration of treatment was 4 weeks. As a result of the study, it was found that the effectiveness of the histamine blocker cetirizine did not differ significantly from the effectiveness of placebo in the treatment of patients with eczema. The evidence for this comparison was rated as low.
Therapeutic effect of the histamine blocker fexofenadine in eczema
Fexofenadine 120mg/day for one week resulted in a slight improvement in eczema symptoms (particularly itching) compared with the placebo group.
According to the authors, the results of the studies may be clinically insignificant. The evidence for this comparison was rated as moderate.
Therapeutic efficacy of loratadine in eczema
The efficacy of the histamine blocker loratadine was compared with placebo as an adjuvant to topical treatment of eczema in adult patients. The study involved 28 adult participants. The dose of loratadine was 10 mg/day, the duration of treatment was 4 weeks.
Determining the severity of burns: protein analysis of the burn bladder fluid
We assessed such parameters as changes in the intensity of itching and the severity of clinical manifestations of eczema according to the SCORAD scale during the use of the drug. As a result of the study, it was found that the efficacy of loratadine did not differ significantly from the efficacy of placebo in the treatment of patients with eczema. The evidence for this comparison was rated as low.
Conclusion: Oral H1 blockers are not effective in treating eczema.
Thus, to date, there is no convincing evidence of the effectiveness of the use of systemic antihistamines (H1 receptor blockers) as an adjuvant to topical treatment in patients with eczema. Management of eczema is based on the use of local emollients aimed at restoring the epidermal barrier and an intermittent course of topical corticosteroids.
UV sensitivity in patients with Friedreich's ataxia: therapy







Add a comment