The human body is made up of trillions of different cells. Each organ in our body, each structure and square centimeter of tissue has billions of cells, the state of the whole organism depends on the correct functioning of which. The most important cells of the largest organ in the human body – skin are fibroblasts. They are called youth cells, since it is the active work of fibroblasts that helps maintain youthfulness and beauty of the skin. Today on estet-portal.com read important information about fibroblasts, which every aesthetic medicine specialist must have.
Skin fibroblasts: functions and structural features
Fibroblasts – These are the connective tissue cells of the body. Their precursors are stem cells of mesenchymal origin.
Fibroblasts can be found in two forms in the human body.
An active fibroblast is large, has processes, an oval nucleus, and many ribosomes. Such a cell can divide and intensively produce collagen. Inactive fibroblasts are also called fibrocytes. They are highly differentiated cells that are formed from fibroblasts, do not have the ability to divide, but take an active part in the synthesis of fibrous structures and wound healing. Inactive fibroblasts are slightly smaller than active fibroblasts and are spindle shaped.
Fibroblasts:
- structural-functional types of active fibroblasts;
- products of fibroblast synthesis – extracellular matrix components;
- The main functions of fibroblasts in the human body.
Structural and functional types of active fibroblasts
All active fibroblasts are divided into several structural and functional types, each of which performs certain functions:
- poorly differentiated fibroblasts have pronounced proliferative properties, that is, they actively multiply and grow;
- young fibroblasts – more differentiated cells, which are also capable of proliferation, but, unlike poorly differentiated ones, can synthesize collagen and acid glycosaminoglycans;
- Mature fibroblasts are formed from young forms, practically cannot multiply, and are divided into three subtypes:
- fibroclasts destroy collagen by phagocytosis and intracellular lysis;
- collagenoblasts synthesize collagen;
- myofibroblasts play a role in the contraction of fibrous tissue in wound healing.
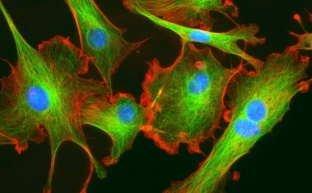
Fibroblast synthesis products – extracellular matrix components
Fibroblasts are located in the middle layer of human skin – in the dermis. There they produce an extracellular matrix, the components of which form a kind of skin frame. The main components of the extracellular matrix are glycoproteins, proteoglycans and hyaluronic acid. The widely known collagen, which is known not only to every specialist, but also to almost every patient, is the predominant glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix. In addition, fibroblasts also produce the proteins fibrin, elastin, tinascin, nidogen, and laminin, which are used as "building materials" for for the skin. Another product of fibroblast synthesis – these are cell growth factors which include:
- the main factor that enhances the growth of all skin cells;
- transforming factor that stimulates the production of elastin and collagen;
- an epidermal factor that accelerates cell division and keratinocyte movement;
- keratinocyte growth factor.
The main functions of fibroblasts in the human body
Knowing exactly what fibroblast cells produce in the dermis, one can understand a wide range of their functions, which include:
- synthesis of collagen, elastin, hyaluronic acid and other components of the extracellular matrix;
- vessel formation;
- intensification of cell growth processes;
- acceleration of tissue growth;
- healing of skin lesions;
- direction of cells of the immune system to bacteria and other foreign agents.
Thanks to the proper functioning of fibroblasts, human skin retains its fresh, toned and youthful appearance for many years.
Only by understanding the basic principles of these cells, a specialist can correctly understand anti-aging techniques. Read more interesting articles at estet-portal.com.







Add a comment