Toothache is never under any circumstances pleasant. But it becomes especially painful when it accompanies any other illness.
This refers to the phenomenon of cold teeth. She is often mentioned in colloquial — this term describes a bursting dull pain in the teeth, which occurs against the background of acute respiratory infections or flu.
But what is a condition from a medical point of view, and how can it be dealt with?
- Cold teeth: why what causes it to develop
- Inflammation of the airways
- Enamel microdamages
- Gum inflammation
- Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
- Cold teeth: how to relieve the pain
Cold teeth: why what causes it to develop
In fact, the mechanisms of development of this symptom are very diverse. Among the most common are the following.
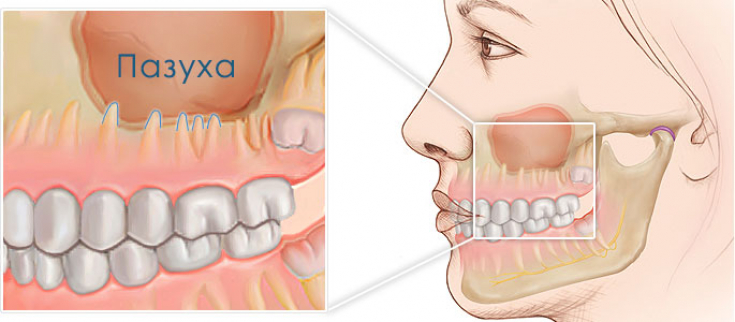
Inflammation of the airways
This condition is accompanied by nasal congestion — mucosal edema, which blocks the outlet openings of the maxillary sinuses. As a result, ventilation and outflow of fluid are disturbed in the sinuses, and pressure increases, which creates increased loads on the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw. As a rule, after the restoration of nasal breathing, the problem is solved by itself. But if the disease is advanced or turned into a chronic course, periodontitis, periodontal abscess and other complications often develop in the upper jaw.
Enamel microdamage
During a cold and flu, we often drink tea with lemon, currant, cranberry, or pharmacy preparations for preparing hot drinks that contain ascorbic and / or acetylsalicylic acid. Considering the fact that it is recommended to drink as much as possible during an illness, tooth enamel is almost constantly exposed to acids, as a result of which microdamages form in it. As a result, the teeth become extremely sensitive to any stress, and even relatively soft foods can cause teeth to ache when chewed.
Read also: Increased tooth sensitivity: getting rid of at home
Gum inflammation
With ARVI and influenza, the oral mucosa often becomes painful and sensitive. Against this background, "lost" symptoms of gingivitis, which very often develops against a background of a viral infection. The gums become loose and reddened, and plaque and bacteria quickly accumulate between them and the teeth. In in this case, the pain in the teeth is in the nature of a reflected — soreness in inflamed gums is "transmitted" on teeth.
Read also: Tips for care of the oral cavity: only natural products
Inflammation of the trigeminal nerve
Influenza and other infectious diseases may be accompanied by inflammation of the facial nerve. This condition is usually easy to recognize — the pain increases sharply with any muscle contraction (when smiling, chewing food) and when touching the side of the face where the nerve has become inflamed. But sometimes this condition proceeds atypically — along the entire length of the trigeminal nerve, there are no particularly unpleasant sensations, and the nerve transmits pain only to the areas in which it ends. Accordingly, if the branch of the trigeminal nerve that leads to the teeth is inflamed, severe and inexplicable toothache is guaranteed.

Cold teeth: how to relieve the pain
If a toothache during during a cold has already developed — try the following tips:
-
Rinse your mouth every hour with a solution of baking soda (1 tsp. baking soda dissolved in 200 ml water at room temperature).
-
Drink sour-tasting teas and drinks through a cocktail straw, then rinse your mouth thoroughly with clean water.
-
Use vasoconstrictor nasal drops or sprays that relieve nasal congestion — they will help restore the outflow of fluid from the maxillary sinuses and relieve pressure on teeth.
-
For redness and swelling of the gums, use a solution of chlorhexidine, a decoction of sage, pharmacy chamomile or calendula to rinse your mouth (4-5 times times day).
-
Don't neglect your dental hygiene — during a cold or flu, you should brush your teeth no less thoroughly than usual.
-
Avoid consumption of highly heated or chilled drinks and food — too high or low temperatures increase toothache, and negatively affect health in general if you have SARS.
-
Make sure that the area of the face does not overcool and overheat — with inflammation of the trigeminal nerve, this can dramatically increase pain and worsen health.
If within a few days after recovery, the toothache does not go away or, all the more, it gets worse — it means that the problem with the teeth lies in the teeth themselves, and the viral infection only provoked a more rapid course of caries or another disease.
In this case, only a visit to stomatologist and appropriate treatment will help you get rid of the pain, and prevent it reappearance.
Read also: Tooth hurts after filling: what cause and when to go to stomatologist
You might be interested in: How to place a filling.






Add a comment