It is no coincidence that vitamin D is called the "vitamin of the sun", because, unlike other vitamins, it is practically not found in food, but it is produced to the maximum when our skin is exposed to light and heat. But only a couple of hot months cannot fill the body with enough vitamin in the human body.
In the material estet-portal.com you will find out what are the signs of vitamin D deficiency, what threatens its lack and how to fill it. We offer to sort it out right now.
Vitamin D: what role does this "sunshine vitamin" play
Thanks to numerous studies, scientists have been able to prove that diseases begin to progress much faster if the body contains low levels of vitamin D. A sufficient amount of it helps fight existing diseases and reduces the risk of new ones.
Follow us on Instagram!
Also "sunshine vitamin" plays a very important role in maintaining healthy bones, reduces the risk of diabetes, certain types of cancer and heart disease.
He is also:
• Helps maintain a healthy body weight;
• Preserves brain functions during aging;
• Reduces the risk of developing multiple sclerosis;
• Reduces the severity of asthma symptoms and their frequency;
• Reduces the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in women.
Vitamin D deficiency: five main signs
It's not easy to detect vitamin D deficiency based on symptoms. Often it can be: general weakness, fatigue, frequent diseases, bone pain. But most of the population may not experience these symptoms if they are deficient in the vitamin. To be 100% sure of this problem, only blood tests in the laboratory to determine the level of vitamin D will help.
If the result is less than 30 ng/ml – this is not enough vitamin D, and a result of 10 ng/ml indicates a critical deficiency. The optimal concentration of vitamin D in the blood is 40 & ndash; 70 ng / ml.
Let's take a look at the five main signs of vitamin D deficiency:
1.Frequent infections.
Vitamin D is essential for the normal functioning of the immune system, because without sufficient vitamins, our immune cells will not be able to properly respond to a threat. As a result, the body will be more susceptible to infections.
Vitamin D also affects the quality of both innate and adaptive immunity.
2. Lack of mood
Doctors say that vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining healthy levels of serotonin in the brain. Thanks to a study published in Medical Hypotheses, it was possible to establish a link between vitamin D deficiency and seasonal depression.
Read also: Best vitamins for skin
3. Constant fatigue.
The sunshine vitamin is also needed by the body to convert food into energy. If a person constantly feels tired, it may indicate that the body is not absorbing nutrients from food, which can be triggered by a vitamin D deficiency. But this can be corrected in a week with vitamin D supplements.
4. Weak bones.
Vitamin D is also needed to regulate the levels of phosphate and calcium in the body. This is beneficial for the health of teeth and bones. Adequate vitamin levels help prevent bone softening and osteoporosis in adulthood.
5. Muscle pain.
If your muscles are constantly aching for no particular reason, then you should also think about a possible vitamin D deficiency in your body. When vitamin D enters the muscle tissue cells, it increases the frequency of muscle contractions, thus helping the muscles to remain strong and elastic. This protects them from tearing and minor damage, especially during training.
Read also: B vitamins: effects on the skin and body
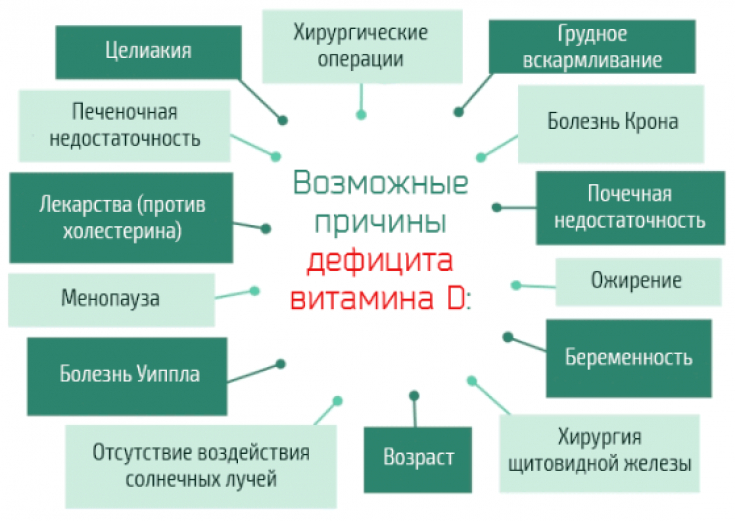
Causes that can cause vitamin D deficiency
First reason – if you don't get enough sun.
Second – you are not using the vitamin as a dietary supplement or have been using it below the recommended dose for a long time.

Third - The kidneys cannot convert 25(OH)D to its active form, absorption of vitamin D from the digestive tract is insufficient.
Fourth – if you are pregnant or overweight, you need a lot of vitamin D
Fifth – you are on a vitamin D deficient diet (milk allergy, lactose intolerance, vegetarian).
Scientists say that more than 50% of the world's population is deficient in vitamin D. It is stated both in Africa and Asia, and in Europe, especially in the elderly.
The most at risk are: children, pregnant women, residents of the Northern Hemisphere, people over 65 years of age, and people who are very overweight (when BMI is more than 34).
It is also worth remembering that a number of chronic diseases are exacerbated by vitamin D deficiency. Among them: asthma, migraine, osteoporosis, infertility, hypertension, autism, Alzheimer's disease, cancer, cystic fibrosis, dementia, depression, diabetes (types 1 and 2), hearing loss, psoriasis, eczema, inflammatory bowel disease, insomnia, macular degeneration eyes, multiple sclerosis, Crohn's disease, muscle pain, obesity, rheumatoid arthritis, schizophrenia, seizures, periodontal disease (periodontitis, tooth loss), hemorrhagic septicemia, tuberculosis.
How to get vitamin D
The best source of vitamin D is the ultraviolet rays of the sun. To do this, you need to be in the sun for 15-20 minutes daily. The optimal time for this — period from 11:00 to 15:00.
The second source is high-quality nutritional supplements – vitamin D3. It should be taken from October to April when the sunlight is not strong enough in our climate.
Third source – food. Recommended foods include salmon, mackerel, tuna, fish oil, cheese, dairy products, yogurt, mushrooms and eggs.
Therefore, be sure to make sure that these products are present in your diet in autumn and winter, and also try to spend more time outdoors in warm weather.






Add a comment