Measles epidemic news is the most frightening to date. Morbillivirus – measles virus – extremely contagious, it is quickly transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person by airborne droplets.
Virus outbreaks are cyclical and occur every 5-6 years. The main reason for outbreaks – low vaccination coverage.
Measles – one of the leading causes of child mortality in the world. According to WHO, every year in the world 30-40 million children suffer from measles, more than 800 thousand die from the infection itself and complications. However, the infection can also affect unvaccinated adults in a more severe form.
Read on estet-portal.com about the characteristic signs of measles, the periods of the course and the features of measles vaccination.
Signs of measles: stages in the development of an infectious disease
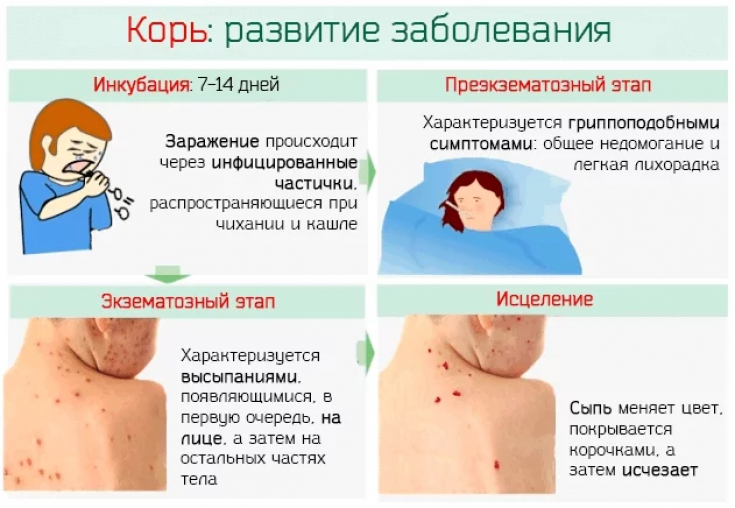
Measles has three periods of flow: incubation, prodrome, rash and convalescence. The incubation period for measles is 8 to 17 days. The prodromal period lasts from 3 to 8 days and is characterized by the appearance of fever, runny nose, conjunctivitis and cough. Conjunctivitis may be accompanied by photophobia or lacrimation.
A characteristic feature of this period is the appearance of whitish spots on the oral mucosa near the molars – Koplik spots.
During the period of rashes, the state of health deteriorates significantly. A rash appears: first behind the ears, on the scalp, face, neck and chest. The next day the rash spreads to the trunk, arms and thighs.
On the 3rd day, papules and spots pass to the shins and feet, and on the face they begin to turn pale. During the recovery period, drowsiness, asthenia and cough are characteristic. The rashes disappear in the same sequence as they appeared.
Follow us on Instagram
Many-faced disease: clinical forms of atypical measles
A measles epidemic usually follows a typical course of the disease. However, there is atypical measles, which has an erased clinical picture and is divided into abortive, mitigated, asymptomatic and erased forms.
The abortive form is characterized by a typical onset, but after the appearance of a rash, the course of the disease stops.
The rash appears against the background of subfebrile temperature, which usually lasts for 1 day.
Mitigated measles develops after passive immunization with immunoglobulin or after administration of blood and plasma preparations during the incubation period.
This variant is characterized by a longer incubation period and mild intoxication syndrome.
Staging of rashes and the presence of Koplik's spots are also not typical. The erased form lasts 3-4 days, without a rash. There is mild malaise and slight nasal congestion.
Signs of measles are not characteristic of the asymptomatic form, which is detected only by laboratory analysis.
You may also be interested in: Night dry cough: causes and remedies treatment
Measles Prevention: Answers to Common Questions about Vaccines
A measles epidemic poses a risk to children and adults who have not been vaccinated. Vaccination forms specific immunity, as a result of which a person becomes immune to the disease for life. scheduled revaccination.
If you are not sure that you yourself have been vaccinated against measles, you need to take tests to determine antibodies to the measles virus, and, if necessary, get vaccinated.
Vaccination is contraindicated by the presence of HIV infection, pregnancy, allergy to egg white, neoplasms, blood diseases, heart defects, acute diseases, as well as exacerbation of any chronic diseases.
4 childhood diseases that are dangerous for adults
After the MMR vaccine or the measles monovaccine, some reactions of local and widespread nature are observed in the period from 5-14 days. These include:
• increase in temperature (often no more than 39 C);
• pain and swelling at the injection site;
• swollen lymph nodes;
• catarrhal phenomena (cough, conjunctivitis);
• slight morbilliform rash (rare).

Side effects are allergic reactions (urticaria) that occur in a few percent of cases. A severe consequence of the MMR vaccine can be anaphylactic shock, which occurs once in a million doses. Extremely rare among the adverse effects of vaccination are convulsions and lesions of the central nervous system (panencephalitis).






Add a comment