The predominance of muscle mass in the human body has a beneficial effect on the metabolic rate and the process of burning fat, since it is muscle tissue that actively uses the energy produced by cells. Because an increase in muscle mass – the goal is not only bodybuilders, but also any person who does not want to acquire unnecessary body fat. The mechanisms of muscle growth estet-portal.com will describe in this article, and also tell why women, contrary to popular belief, do not gain a large amount of muscle mass during strength training.
Skeletal Musculature and Muscle Growth – highlights
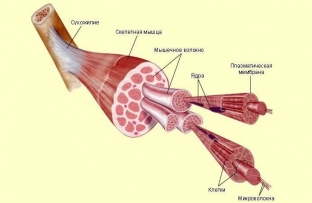
Today we will consider the basic mechanisms and principles of growth of skeletal muscles, which consist of thread-like myofibrils, which in turn consist of sarcomeres (their composition is represented by myosin and actin protein filaments – filaments).
About 650 skeletal muscles in the human body contract when they receive signals from motor neurons that cause the muscles to contract. And the better these contraction signals, the more power we can develop.
If a person is able to lift a very heavy load, despite not looking very muscular, that means that their motor neurons are sufficiently activated to cause stronger muscle contraction. Therefore, powerlifters can look less pumped up than bodybuilders, but still be stronger. Most of the initial growth in strength occurs in the early stages of strength training. Muscle growth stabilizes after this period as muscle activation occurs more easily.
We'll look at:
- physiology of muscle growth;
- mechanisms of muscle growth activation;
- the effect of hormones on muscle growth;
- impact of rest on muscle growth;
- why rapid muscle growth is unlikely.
Physiology of Muscle Growth: How Muscles Grow
After training, the body begins to repair or replace damaged muscle fibers through a cellular “adhesion” process; muscle fibers to form new myofibrils. Such myofibrils increase in thickness and number to promote muscle hypertrophy (muscle growth). Muscle grows when the rate of muscle protein synthesis exceeds the rate of protein breakdown.
Muscles grow when the rate of muscle protein synthesis exceeds the rate of protein breakdown.
However, this adaptation does not occur directly during heavy lifting, but during rest.
How do muscles grow? Myosatellites (they are also myosatellocytes and satellite muscle cells) act as stem cells for our muscles. During activation, they contribute to the division and maturation of muscle tissue cells and therefore are directly involved in the growth of myofibrils.
The degree of myosatellite activation has been shown to affect skeletal muscle growth. Therefore, in order to build muscle, you need to activate satellite cells. How to do it?
3 mechanisms of muscle growth activation: tension, damage, stress
The natural growth of muscles is provided by the ability to constantly load them. Such a load is the main component of the growth of muscle tissue, which disrupts the homeostasis of the body.
Mechanism one – muscle tension
In order for muscles to grow, it is necessary to provide them with a load to which they have not adapted before. Therefore, a logical step for those who want to build muscle is to gradually increase the weight of the weights being lifted. Additional muscle tension helps trigger changes in the chemical processes in the muscle, which allows you to activate growth factors (including mTOR) and satellite cells, which estet-portal.com spoke about above.
Muscle tension also affects the connection of motor units in muscle cells.
Mechanism of the second – muscle damage
Local muscle damage during exercise is the cause of muscle pain after exercise. Such local damage promotes the release of inflammatory molecules and immune cells that activate myosatellites. True, pain – optional companion of this process.
Third mechanism – metabolic stress
Metabolic stress causes swelling of muscle cells, which helps muscle growth without directly increasing the size of the cells themselves. This effect is observed as a result of an increase in the level of muscle glycogen, which gives the muscles volume and ensures the growth of connective tissue. This growth is called sarcoplasmic hypertrophy – it provides visually pronounced muscles without increasing their strength.

How do hormones affect muscle growth?
Hormones – another important factor that significantly affects muscle growth and recovery, since hormones regulate the activity of myosatellites. Insulin-like growth factor IGF-1, in particular mechanical growth factor (MGF) and testosterone – the main mechanisms for activating muscle growth.
Testosterone increases protein synthesis, suppresses their destruction, activates myosatellites and stimulates other anabolic hormones. The vast majority of this hormone in the body is not available for use (up to 98%), but during strength training not only testosterone is released, but also the sensitivity of muscle cells to it increases. Testosterone also stimulates the growth hormone response by increasing the presence of neurotransmitters at the sites of damaged muscle fibers, which also helps promote muscle growth.
Insulin-Like Growth Factor regulates the growth of muscle mass by stimulating protein synthesis, promoting glucose uptake and redistribution of amino acid uptake (the building blocks of protein) in skeletal muscle, as well as activating satellite cells to enhance muscle growth.
Why is rest necessary for muscle growth?
If you don't provide the body with proper rest or nutrition, you can reverse the anabolic process and put the body into a catabolic state (a state of destruction). Muscle protein metabolism responds to strength training within 24-48 hours after exercise. Thus, the interaction between protein metabolism and food ingested during this period determines the effect of nutrition on muscle hypertrophy.
Age, gender and genetic predisposition – factors affecting the growth of muscle tissue.
It is important to understand that the degree of muscle growth depends on the age, gender and genetic predisposition of the person. For example, males have more testosterone than females, which allows men to build larger, stronger muscles.
Why is rapid muscle growth unlikely?
Muscle hypertrophy takes time – this process is relatively slow in most people. As a rule, visible muscle growth is not observed for several weeks or even months after the start of strength training.
A number of genetic features, hormonal background, type and number of muscle fibers, degree of satellite cell activation – all these factors affect muscle growth.
In order for muscles to grow, it is necessary to ensure the predominance of protein synthesis over its breakdown. This requires eating enough protein and essential amino acids, as well as carbohydrates, to activate cellular processes to repair destroyed muscle tissue.
Thus, in order for muscle to be damaged and grow, it is necessary to force the muscle tissue to adapt to loads that exceed the loads that your body is used to. After completing a workout for muscle growth, it is necessary to ensure proper rest and nutrition so that the muscles can recover and grow.






Add a comment