Wisdom teeth – controversial topic. If only because they don’t “make happy” someone; by its appearance (and, as luck would have it, it is always unexpected and unpleasant – completely out of place and out of time), and someone suffers with painful teething of such teeth so much that the light does not seem pretty. In addition to the fact that wisdom teeth grow painfully, their removal is also difficult.
Why did nature give people such a punishment? In what cases wisdom teeth must be removed, and in what – can't they be touched? How to take care of the oral cavity in case of wisdom tooth extraction? Look for answers to all these questions in the article estet-portal.com.
Whether to remove a wisdom tooth: arguments for and against
To decide whether to remove a wisdom tooth, first you need to find out where the third molars come from in our body (this is the scientific name of wisdom teeth).
Molars are considered a vestige, and therefore grow only in half of the world's population. Ten thousand years ago, wisdom teeth grew in every adult on the planet. However, in the process of evolution, the structure of the human jaw changed, so only 32 teeth began to have enough space. Over the past century, our jaw has narrowed by ten centimeters, as we began to eat softer food (incomparable to the tough, half-cooked mammoth meat), which does not require thorough intensive chewing. Considering that our food continues to become more and more refined, it is possible that the evolutionary process of narrowing the jaw (and, as a result, the dentition) will continue.
If a person has healthy chewing teeth, then the "eights" do not perform important functions. Unless they can serve as a backup option if, with age, a person loses his main chewing teeth. Molars also have secondary positive functions: they hold back adjacent chewing teeth when loosened and can serve as a support for bridge prosthetics.
In rare cases, the wisdom tooth has an antagonist – "mirror" a tooth that is located opposite and closes with a molar. In this case, the entire “couple” is usually removed (if there are indications for removal), since if you leave the second tooth alone, then without support it will bend over time. Only an experienced dentist can objectively assess all the risks and make an informed decision.
So if the teething of the "eights" did not cause you any special complications, then there is no point in removing them. However, not all patients of dentists can boast of this.
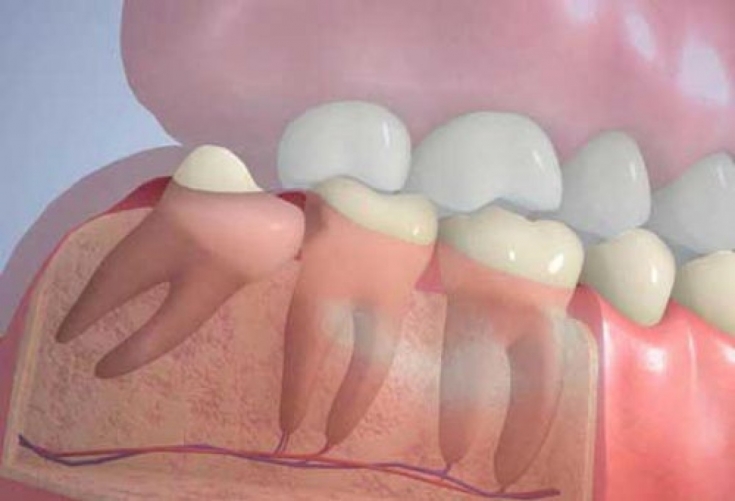
In what cases are wisdom teeth removed?
1. The tooth grows at an angle, in the wrong direction.
If a molar leans to the side, like the Leaning Tower of Pisa, then it loses even secondary positive functions (you can’t chew with such a tooth and you can’t install a prosthetic bridge on it), and at the same time it still carries many additional risks: it injures the mucous membrane and gradually deforms neighboring teeth.
2. For physiological reasons for the "eight" there is not enough space in the jaw.
This factor depends on the individual physiological structure of individual patients. If the jaw is naturally too narrow, then teething will cause hellish suffering to a person with strong pressure on adjacent teeth. Or (even worse) the third molar will not be able to make its way up at all and will remain in the gum, which can lead to additional complications.
3. When installing braces.
If a patient plans to wear braces to correct an overbite, then in the vast majority of cases, the G-8s will be removed before installing the braces; (regardless of their problematic or problem-free) to make room for the main teeth, which will gradually change their location.
4. Severe caries.
If the wisdom tooth is already destroyed by caries almost to the ground, then there is no point in treating it (and treating the "eight" is much more difficult than a regular tooth) – easier to remove.
5. & nbsp; Obstruction of the G-8 root canals.
If the wisdom tooth needs treatment, and its root canals cannot be cleaned and sealed due to their obstruction (the canals of the third molars are very curved), then only tooth extraction remains.
6. Pericoronitis.
This disease is characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the gums, which leads to external swelling. At the same time, the wisdom tooth is practically covered with an overhanging swollen gum. In the resulting "hood" a place appears where the remnants of food accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
6. Pericoronitis.
This disease is characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the gums, which leads to external swelling. At the same time, the wisdom tooth is practically covered with an overhanging swollen gum. In the resulting "hood" a place appears where the remnants of food accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".xxxx>If a wisdom tooth needs treatment, and its root canals cannot be cleaned and sealed due to their obstruction (the canals of the third molars are very curved), then only the extraction of the tooth remains.6. Pericoronitis.
This disease is characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the gums, which leads to external swelling. At the same time, the wisdom tooth is practically covered with an overhanging swollen gum. In the resulting "hood" a place appears where the remnants of food accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
then only the extraction of the tooth remains.6. Pericoronitis.
This disease is characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the gums, which leads to external swelling. At the same time, the wisdom tooth is practically covered with an overhanging swollen gum. In the resulting "hood" a place appears where the remnants of food accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
then only the extraction of the tooth remains.
6. Pericoronitis.
This disease is characterized by the formation and accumulation of pus in the gums, which leads to external swelling. At the same time, the wisdom tooth is practically covered with an overhanging swollen gum. In the resulting "hood" a place appears where the remnants of food accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
where food remains accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
where food remains accumulate and bacteria and microbes begin to multiply intensively. In this case, it is also easier to remove the "eight".
Interestingly, in Western countries, wisdom teeth are usually removed as soon as they appear – to avoid possible complications. Domestic dentists are more balanced and careful about this, carrying out the removal only when complications or severe pain appear.
By the way, for pregnant women, the removal of a wisdom tooth is categorically not recommended due to the complexity of the procedure, difficulties with anesthesia (due to the risk to the fetus) and the risk of complications after the operation.
How to take care of the oral cavity at home after the removal of a wisdom tooth?
To avoid the risk of complications after wisdom tooth extraction, a number of recommendations must be carefully followed.1. Immediately after the operation, a swab – it should not be kept in the mouth for longer than 20-30 minutes, because after being heavily soaked with blood, it quickly becomes a breeding ground for germs.2. Since the operation is quite complicated, after its completion, a qualified doctor will definitely measure the pressure of the patient. It is important to ensure that the dentist does not neglect this measure. 3. To reduce pain and swelling after surgery, ice wrapped in a cloth can be applied to the cheek.4. If «eight» removed due to inflammation, the doctor prescribes an antibiotic to the patient to relieve inflammation. In no case do not neglect their reception! 5. When agreed with your doctor, it is useful to rinse your mouth with a solution of chlorhexidine or a decoction of special herbs (chamomile, oak bark, calendula), which will relieve pain, swelling and soothe the mucous membrane. However, this should not be done in the first few hours after the operation, while the wound is being healed! Also important: the solution should be warm, but in no case hot! 6. You can not rinse your mouth too intensively, as there is a risk of washing out a blood clot from the hole, which closes the wound from germs.7. Never heat the cheek on the side where the tooth was removed! Warm compresses, which some patients unknowingly prescribe to themselves to relieve pain, can lead to increased inflammation and even pus formation. Accordingly, it is also better to refuse hot baths and sauna visits in the first week after the removal of the G8. 8. You can not prescribe yourself painkillers and other medications! Strictly follow the list written for you by your doctor. You can not prescribe yourself painkillers and other medications! Strictly follow the list written for you by your doctor. You can not prescribe yourself painkillers and other medications! Strictly follow the list written for you by your doctor. As you can see, if there are indications for the removal of a wisdom tooth, then it is better not to delay this procedure. For all its trouble, it can save you from the formation of further much more serious pathologies. And in order to avoid the risk of complications after the operation to remove the "eight", it is enough to carefully follow the medical recommendations for caring for the oral cavity described above. Healthy teeth to you!





Add a comment