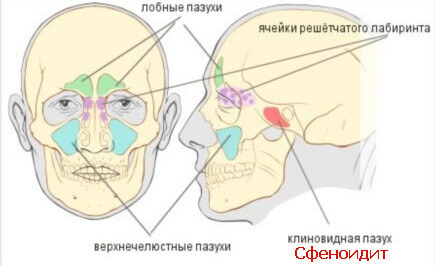
Sphenoiditis is an inflammation of one or more of the paranasal sinuses, often occurring during an upper respiratory tract infection when the infection in the nose spreads to the sinuses (sometimes stimulated by excessive blowing of the nose). It can also be a complication of a dental infection, allergies, or certain infectious diseases such as pneumonia and measles. There are many other causes, including air pollution, diving and snorkeling, sudden changes in temperature, and structural defects in the nose that interfere with breathing, such as a deviated septum.
Isolated sphenoiditis (IS ) is a relatively rare clinical event (1-2.7% of all sinus infections). Due to the important anatomical relationships of the sphenoid sinus, complications can be devastating.
The editors of estet-portal.com will tell about the symptoms, diagnosis and treatment of sphenoiditis.
- Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): symptoms and disease factors
- Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): diagnosis of the disease
- Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): treatment of disease
Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): symptoms and disease factors
When the mucous membranes of the sinuses become inflamed and swollen, the openings that lead from each sinus to the nasal passages become partially or completely blocked. The mucus that accumulates in the isolated sinus causes pressure on the sinus walls, causing discomfort, fever, pain, and difficulty breathing.
Follow our Facebook page! xxxx>
Factors predisposing to IS include severe water intrusion during swimming or diving, 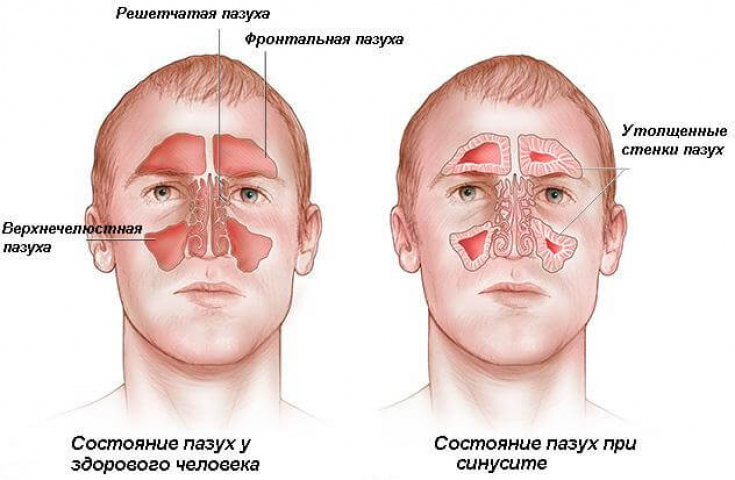 allergic
allergic
rhinitis, sinonasal canal polyps, bronchial asthma, septal deviation , anomalies in the middle/maxilla, radiation therapy, immunosuppression, diabetes mellitus, and cocaine abuse. Among the pathogens involved in IS, the most common are S.aureus, Streptococcus species, Peptostreptococcus, Fusobacterium, Klebsiella, P.aeruginosa, Aspergillus fumigatus and Aspergillus flavus.
The most common symptom is headache (50-60%) 1.2 with no characteristic distribution pattern. Patients may also experience eye involvement with VI or III cranial nerve palsy (diplopia in 40%) and blurred vision.
Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): diagnosis of the disease
Nasal endoscopy is useful for diagnosis. However, up to 60% of cases may have a normal endoscopic examination. Therefore, computed tomography is the only modality that can consistently detect IS. The role of MRI complements each other. Initial treatment for IS is conservative (amoxicillin-clavulanic acid and cephalosporins are typical choices). Response to conservative therapy, however, is often poor.13 body signals that contain secret messages from our body
An endoscopic transnasal approach is usually preferred. This can be done in two approaches: (1) through the middle passage after total ethmoidectomy and (2) direct approach over the choanium. The transnasal technique, using a direct approach, is the safest3. As an alternative to the use of an endoscope, the use of a 
Isolated sphenoiditis (IS): treatment of the disease
At the department of one of the American clinics, 2 patients with IS were recently treated: a 45-year-old woman and a 60-year-old woman who complained of severe occipital headache. Endoscopy revealed postnasal drip and purulent secrets on the left and right, respectively, of the sphenoid sinus. A CT scan showed complete occlusion of the left sphenoid sinus in the first patient, while an MRI of the brain (obtained earlier during the neurological evaluation) showed occlusion of the right sphenoid sinus in the second patient. Initial conservative therapy (ceftriaxone 2 g daily + clindamycin 600 mg IV IV + xylometazoline 0.1% nasal spray) was unsuccessful.
The patients were finally cleared for surgery. Sphenoidotomy via endoscopic transnasal approach was performed. The postoperative period was uneventful, and both patients were discharged 48 hours after surgery. Patients remain asymptomatic and the new sinus ostia remain wide open.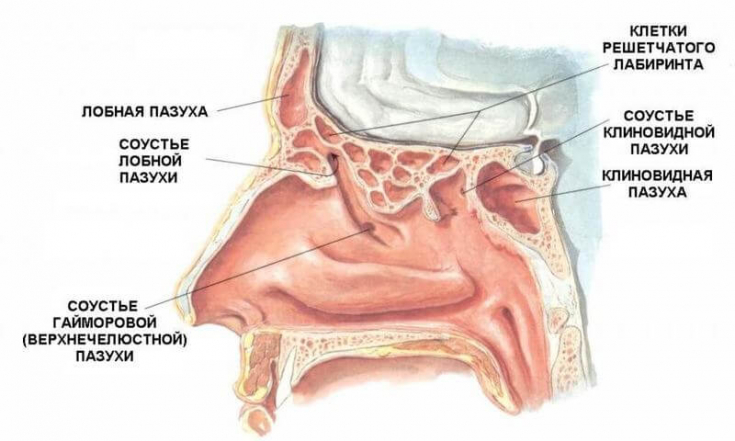
How to treat a runny nose
What conclusion should be drawn? In the event of periodic headaches, there is a possibility of sphenoiditis. If you also have bad breath
and haliotosis, rule out sinus infections and dental disease.
Watch us on YouTube:






Add a comment