Today, many people are exposed to recession risk factors. Gum recession – dental pathology, in which the neck and root of the teeth are exposed due to the lowering of the gums.
The causes of this disease are poor oral hygiene or intensive brushing of the teeth. Anatomical features, pathological bite, bad habits and other factors also play an important role in the exposure of teeth.
In addition to unpleasant aesthetic phenomena, gum recession can lead to various complications, such as periodontitis and advanced tooth loss. On estet-portal.com read about the causes, symptoms, prevention and treatment of gum recession.
Causes of recession: what provokes exposure of the neck and root of the tooth
The development of the disease is based on pathological resorption, which occurs as a result of increased activity of osteo- and odontoblasts.
Distinguish between internal and external resorption. It is believed that internal resorption is associated with chronic simple pulpitis.
External can in turn be called:
• inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues (gingivitis, periodontitis);
• tooth trauma (root fracture);
• the presence of stones and plaque with insufficient oral hygiene;
• improper brushing of teeth (brush damage);
• anatomical features of the oral cavity (too short frenulum of the lip);
• occlusion anomalies (deep bite, protrusions, crowding);
• bad habits (use of toothpicks, pen-nibbling habit);
• wrong orthodontic treatment.
Recession can occur at any age, but most often the pathology develops in people over fifty.
Recession symptoms: how to detect receding gums in time
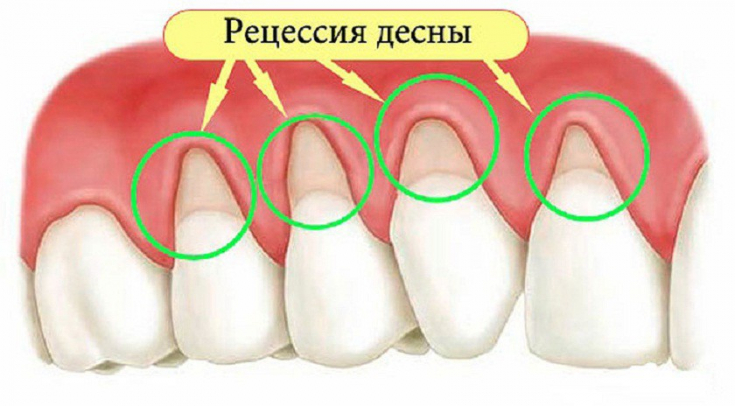 Diagnostic criteria for gingival recession include:
Diagnostic criteria for gingival recession include:
1. reducing the level of the gums and exposing the neck of the tooth;
2. inflammation, bleeding, discoloration of the gums;
3. Increased tooth sensitivity;
4. caries in the cervical region; 5. presence of wedge-shaped defects;
6. formation of periodontal pockets.
There are several types of recessions, which include: local, generalized, traumatic, symptomatic and physiological recessions.
You may also be interested in:Inflammation of the root teeth: what are the causes and how to treat
Diagnosis of dental pathology: what to do first
If you are experiencing signs of gum recession, you should contact your periodontist or your dentist.
After the visual examination, a panoramic or targeted x-ray is taken to assess the condition of the bone tissue.
The condition of various parts of the gums is also assessed, a series of tests are performed if an inflammatory process is suspected, including with the help of special markers that determine the amount and localization of periodontal deposits.
The width and depth of the recession, the filling of the interdental spaces, the width of the keratinized gingiva and its attachment zone, the biotype of the periodontium are evaluated.
Differential diagnostics are also carried out, with the help of which the type of recession is determined and a rehabilitation plan is drawn up.
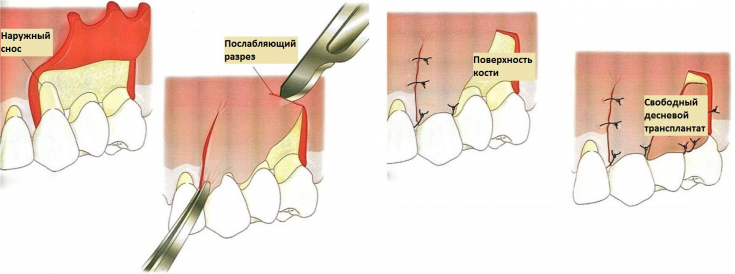 The choice of treatment regimen for receding gums is carried out taking into account the severity of the pathological process, as well as the causes of the development of the disease.
The choice of treatment regimen for receding gums is carried out taking into account the severity of the pathological process, as well as the causes of the development of the disease.
In the inflammatory nature of the lesion of the gums, anti-inflammatory and antiseptic agents are used, plaque and stone are removed.Surgical treatment is used in the later stages. Several options are used: lateral flap, moving free gingival flaps, or moving a gingival trapezoidal flap coronally to the defect area.
Restoration of the gums is also carried out by implanting a rigid membrane into them. This method reduces the likelihood of recurrence, does not require damage to the donor site, as with transfer, and also minimizes the risk of soft tissue edema. However, this technique is much more likely to result in rejection of the foreign plate.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dentistry" section. You may also be interested in: Gummy smile: how to get rid of an aesthetic defect






Add a comment