Vitamin B1 (thiamine) is involved in metabolic processes in the body. It ensures the normal functioning of cells, including nerve cells. With a deficiency of thiamine, the functions of the cardiovascular system are disrupted, endocrine problems arise, and resistance to infectious diseases decreases. Acute vitamin deficiency leads to neuroses, chronic fatigue, gradual destruction of the nervous system, and premature aging.
The editors of estet-portal.com offer to figure out how much vitamin B1 the body needs and from what products it can be obtained from
- What is Vitamin B1: Daily Value
- What threatens thiamine deficiency: 5 serious problems
- TOP 7 foods containing vitamin B1
- Highlights on thiamine and products which contain it contains
What is Vitamin B1: Daily Value
B1 — it is a non-toxic water-soluble substance that loses its structure when heated and exposed to an alkaline environment. At the same time, thiamine tolerates the effects of oxygen, acids, and ethyl alcohol well. Most of the vitamin B1 is found in foods of plant origin, but its amount can be significantly affected by the way you cook. For example, thiamine is destroyed when soda is added to food, and when cooked, it can turn into broths.
Follow us on Instagram
Minimum thiamine requirement for adults — 2-3mg per per day, and for — exact dose depends on features of the organism , the intensity of physical activity. Doctors recommend calculating the required amount of vitamin based on the formula: 0.5 mg B1 per 1000 calories of food consumed.
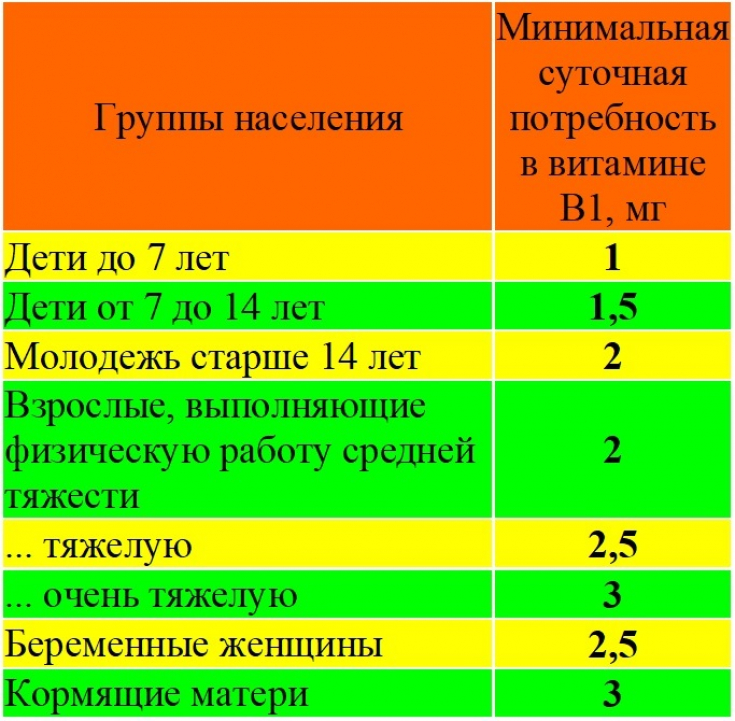
It should be taken into account that there are factors that worsen the absorption of the vitamin. Foods containing B vitamins should be consumed at every meal. This is the only way to provide the body with everything necessary for the normal work of all organs and systems.
What threatens thiamine deficiency: 5 serious problems
Thiamin deficiency can cause serious health problems:
-
Disturbance of carbohydrate metabolism. This leads to starvation of the brain: the cells receive little glucose, their protective layer becomes thinner. "Bare nerves" manifest themselves in the form of increased irritability of a person. Anxiety, nervousness arise.
-
Accumulation of lactic acid. Lactic and pyruvic acids are poorly excreted from the brain, liver, kidneys, myocardium, which leads to lethargy, loss of strength, drowsiness, and a feeling of chronic fatigue.
- Beriberi.
This disease occurs when there is a long-term deficiency of vitamin B1. Today, it has almost been forgotten about, but a century ago, people were dying en masse from take-take. Due to a lack of thiamine, the functions of the brain, heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, and musculoskeletal system are disrupted.
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome. Thiamine deficiency — this is just one of the factors of the onset of the disease, but important. In combination with drunkenness, a lack of a vitamin leads to partial paralysis, memory loss, vision problems. -
Childhood diseases: leucinosis, necrotizing encephalopathy, intermittent ataxia. These are infantile diseases directly related to B1 deficiency. Due to the lack of vitamin in newborns, the metabolism is disturbed, which can lead to serious problems in the functioning of the respiratory system, developmental delay, muscle weakness, various CNS disorders. -
Read also: Enriching your diet: 8 foods with folic acid
Thiamin deficiency in old age is thought to contribute to the development of Alzheimer's disease. So far, there are no reliable studies that would prove the connection of the disease with a lack of vitamins, but this cannot be ruled out, because B1 is really necessary for the normal
 function of brain cells.
function of brain cells.
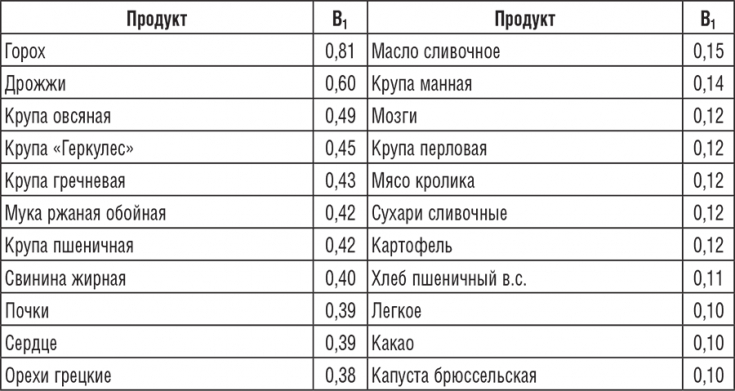
TOP-7 foods that contain vitamin B1 To provide the body with the necessary amount of thiamine, be sure to include the following foods in your diet:
Nuts.
- All types of nuts are useful, but pine — out of competition. 100 g contains about 33 mg of thiamine. In second place — pistachios, and on third — peanut. A handful of nuts for a snack will make up for the deficiency of B vitamins.
-
Pork. It's not the healthiest food from a nutritionist's point of view, but it is valuable due to its thiamine content (0.6 mg per 100 g of meat). -
Lentils. Include lentils in your diet and get a lot of benefits. 100 g of product contains 0.5 mg of vitamin B1. -
Cereals. The most useful are oatmeal, millet, buckwheat, barley groats. -
Liver. It is best to buy chicken liver (0.5 mg B1 per 100 g of product). Vitamin B1 is also found in pork liver, but in smaller amounts (0.3 mg per 100 g). -
Corn. It has more thiamine than pork liver: 0.38 mg per 100 g. -
Wheat. Wheat — good source of thiamine. So, in 100 g of pasta contains 0.25 mg of vitamin B1. Don't give them up. -
Read also: TOP 10 tasty and healthy foods containing potassium
There is a nuance. Some foods destroy vitamin B1. This should be taken into account. So, coffee lovers deprive themselves of up to & nbsp; 50% of thiamine coming from & nbsp; food. The amount of vitamin can be affected by tea bags, refined carbohydrates, high salt content. It should be borne in mind that in products that have undergone intensive heat treatment, there are few vitamins left, including
 and thiamine.
and thiamine.
The main thing about thiamine and the products that contain it
Remember that:Fatigue, nervousness, sleep disturbances can be associated not only with stress, but and with lack of thiamine.
-
Serious diseases associated with acute B1 deficiency are not frequent today, but they are possible.
-
The minimum daily dose of thiamine for children — 1-2 mg, a for adults — 2-3 mg.
-
The familiar foods contain enough B1, but it is also important to follow the way of food processing so that it retains all the necessary vitamins.
- Follow us on Telegram
What is the benefit of linseed oil for women and how to use it
You may be interested in: How to understand what the "chips" of your appearance are.






Add a comment