We all love to treat ourselves to sweets, but we rarely think about the harmful effects of sugar not only on weight, but also on skin condition.
It turns out that there is not only chrono- and photoaging. In the modern beauty industry, the term "sugar face" is often used. —the result of skin glycoaging.
Is it really necessary now to give up all the sweets in the world? Of course not! But excessive consumption of sugar in any form will take its toll on your face very soon.
Read on estet-portal.com an article on the effect of sugar on skin quality and glycoaging on the recommendations of Andrey Beloveshkin, a doctor, candidate of medical sciences, seminar and master class leader.
The effect of sugar on the face: typical symptoms of skin glycoaging
The glycation process consists in the interaction of sugars with proteins, resulting in the formation of glycosylation end products (AGEs, aka AGE products).
Accumulating in huge quantities, the end products negatively affect the tissues of the body.
One of the "targets" glycation products – skin that undergoes premature aging.
The process of glycoaging is noticeable after 30-35 years, when it starts together with chrono- and photoaging.
AGE-products are firmly "glued" with collagen and elastin, which impairs blood circulation and the proliferation of new cells.
The skin loses elasticity, changes its color and becomes wrinkled.
The harmful effects of sugar are visible on the face: symptoms of glycation include:
• thinning and flabbiness of the skin;
• loss of elasticity;
• appearance of wrinkles and dark circles under the eyes;
• dim color;
• breakouts.
This is why it is important to start the fight against glycation as early as possible to prevent damage to the underlying tissues that protect the skin, as well as a decrease in its elasticity and firmness.
Follow us on Facebook

AGE products: the role of collagen and glucose in glycation processes
Collagen – one of the main proteins of the skin, as well as tendons, ligaments and bones, accounting for 20-30% of body weight.
In the normal state, there are cross-links (covalent bonds) between collagen molecules that give the collagen fibers the necessary mechanical properties.
However, with age, the number of crosslinks between units increases. This process, which takes place with the participation of glucose, occurs more intensively in patients with diabetes mellitus.
Maillard's theory states that collagen crosslinks are formed as a result of the damaging action of monosaccharides.
It begins with reversible glycation — reduced sugar (glucose, fructose, etc.) is attached to the terminal α-amino group of the protein. As a result, a rather diverse group of substances is formed, which received the general name Advanced Glycosylation End-products (AGE). AGEs slowly accumulate in tissues and have many negative effects, in particular, they promote the formation of crosslinks between collagen fibers. And this is fraught with inflammatory reactions, oxidative stress and vascular sclerosis.
Foods with a high content of CNG: what to avoid
CNG can get into our body by exogenous route – with food. By choosing foods low in glycosylation end products, we protect ourselves not only from the development of diabetes and vascular pathologies, but also prevent skin aging. The influence of sugar on the development of cardiovascular and dental pathologies should not be underestimated.
AGE products other than refined sugar and fructose include:
1. semi-finished products;
2. fried meat;
3. fast food;
4. animal fats.Cooking method is of great importance: roasting and grilling increase the content of AGEs in food.
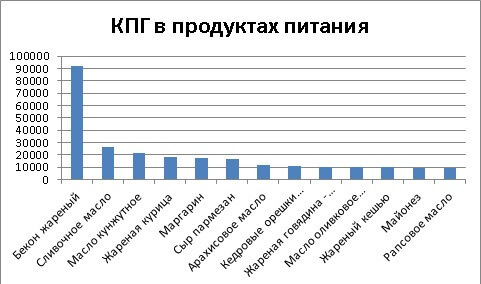 Try to limit your intake of these foods and instead opt for fresh, whole foods or steamed foods that will keep your skin healthy and youthful longer.
Try to limit your intake of these foods and instead opt for fresh, whole foods or steamed foods that will keep your skin healthy and youthful longer.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Beauty and Health" section. You may also be interested in:






Add a comment