Tumor – result of abnormal cell division. With such a pathological process, the genetic apparatus of cells changes, which leads to a violation of their maturity and growth. But not all neoplasms are "cancer" disease. And not all of them carry danger and a mortal threat. There are benign and malignant tumors. Cancer – the general name for a huge group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell division. Over time, they spread throughout the body, affecting every organ. More than 100 types of the disease are known, 10 varieties are most common, 8 – affect organs, 2 – circulatory and lymphatic systems.
estet-portal.com will tell you
- Benign and malignant tumors – their types
- 5 differences between benign and malignant tumors
- Top 5 important facts about cancer Benign and malignant tumors – their types
Most often, the disease is given a name based on the organ in which it is located. For example, a tumor in the breast in women is called breast cancer. Cancer subtypes determine what the disease has developed from, this is important when choosing a method of treatment. Education in the bodies – solid, their cells form a tumor mass. Malignant diseases of the lymphatic and hematopoietic systems originate from the cells of one organ and circulate throughout the body.
Subscribe to our page on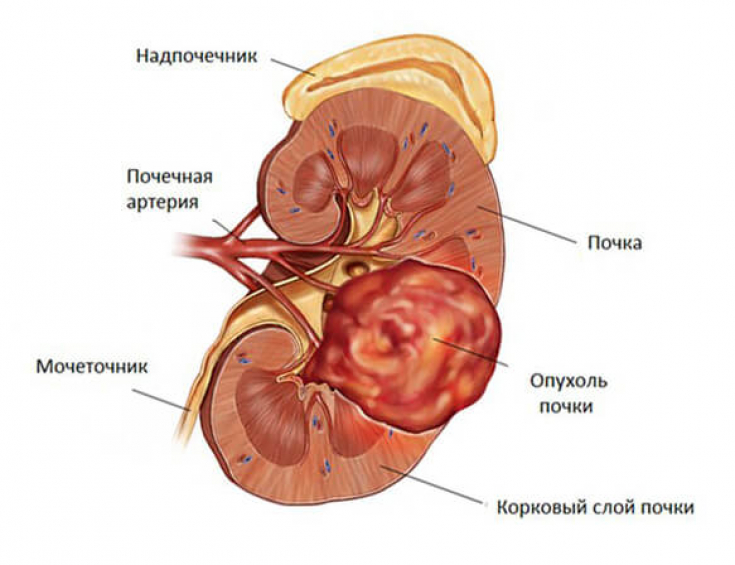
Cancer is the name given to these types of tumors:
• leukemia and myeloma – primary brain tumor;
• lymphoma – originates from the peripheral organs of the immune system;
• melanoma – its growth is triggered by melanocytes, cells that protect the skin from UV, are found in moles;
• neuroendocrine – differ in hormonal activity.
Instagram page!
Benign tumors
can become malignant over time. It is very difficult to suspect cancer, the symptoms are not pronounced. They are so common in other diseases and conditions of the body that it is impossible to suspect something was wrong.
Modern methods of diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer

There are varieties of "bad" Tumors:
• fibroma – grows from connective tissue;
• lipoma – formed from adipose tissue, inconspicuous;
• myoma – based on muscle tissue;
• hemangioma – congenital pathology with dilated capillaries;
• cyst – has a liquid inside, is characterized by
rapid growth.
1. Degree of maturity.
The cells of non-dangerous tumors are characterized by a normal structure, with minimal difference from healthy ones. Malignant – differ significantly in function and structure.
2. Growth.
Benign – grow slowly, gradually squeezing nearby organs. Dangerous tumors penetrate the surrounding tissues, grow in tissues, blood vessels and nerves.
3. Metastases.
These are secondary growths that have sprouted from the parent tumor. Thus, cancer is carried throughout the body with blood and lymph. Formations that do not carry a mortal threat are distinguished by the absence of metastasis.
4. Relapses.
Characteristic only for malignant diseases. Occur after the removal of benign formations with a "leg", for example, polyps.
5. Impact on the body.
Benign and malignant tumors affect a person differently. The first – appear locally, squeezing neighboring organs, tissues and vessels. Second – lead to intoxication of the body, the tumor grows actively, absorbing nutrients.
Skin lymphoma: causes, types and treatment The development of a tumor that does not pose a threat to humans takes a long time, sometimes tens of years. At the first stage, the DNA of the cells is mutated, at the second – cell division, which takes several years. On the next – rapid growth and compression of surrounding tissues.
For the development of cancer is characterized by the presence of the zero stage – the tumor has not gone beyond the area of education, has not spread to tissues and blood vessels, a cure is possible in 100% of cases. At the first stage, it turns into a lesion, enlarged in size. On the 2nd and 3rd – deeply grows into neighboring tissues and spreads only to the lymph nodes. On the 4th – cancer cells have penetrated all
organs and systems. Top 5 important facts about cancer
1. Name.
Initially, the disease was identified by Hippocrates, it was a tumor of the mammary gland. He saw a figure resembling a crab in the tumor. Later, a Roman physician translated his interpretation as "cancer" from Latin. Cancer statistics have been maintained since 1950
2. Is cancer contagious?
If we are talking about the transmission of the disease by airborne droplets, sexual contact, then no. There are viruses and bacteria that increase the risk of cancer. These are HPV, HIV, hepatitis B and C, the Epstein-Barr virus and the bacterium Helicobacter pylori.
3. Genetic predisposition.
The disease cannot be inherited, but an inherited mutation increases the risk of cancer. If your family had oncology before the age of 50, several relatives in the same line, or oncology without possible risk factors, then you should always be on the lookout.
4. Diagnosis.
Many people wonder if it is possible to take one test, which will show the presence or absence of malignant tumors in the body. There is no such analysis, screening is carried out for the presence of 4 types of cancer – cervical poppies, colorectal cancer, breast and lung.
5. Cancer in infants.
Very rarely, on ultrasound, oncology is detected in the fetus, at the birth of a baby. Most often we are talking about neuroblastomas – nerve tumors. There are cases
Only a complete diagnosis will help distinguish between benign and malignant tumors
. Sometimes doctors are not able to distinguish the nature of education even with the help of CT, MRI, biopsy, laboratory tests. Then surgical intervention is applied.
See more important and useful information on our YouTube:







Add a comment