Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are chronic skin diseases that cannot be completely cured by currently known methods. These dermatoses have become the most common chronic skin diseases. It was once believed that psoriasis and atopic dermatitis have completely different bases.
Read about the latest research in the field of immunological causes of development, approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, read on estet-portal.com
- atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: impaired epithelial immunity
- factors in the development of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
- approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: impaired epithelial immunity
Modern scientific findings in the field of genetics, epidemiology and pathogenetic factors of both diseases have significantly enriched our knowledge of the complex mechanisms underlying atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Follow us on Instagram!
According to modern scientific concepts, both diseases are based on a genetically determined predisposition, which can manifest itself under the influence of provoking factors. Several specific chromosome loci are considered potential causes of this tendency.
A number of these genetic regions of chromosomes are common to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Genetic studies have established chromosome loci 1q21, 3q21, 20p12 that are common to atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Not all genes from these loci have yet been identified, but it has been observed that certain factors, caused by individual genes or groups of genes , have a general effect on epithelial immunity.
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis development factors
Chromosome 1q21, which is associated with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, also carries the genetic information of the epidermal differentiation complex. The genes of this complex are expressed during the maturation of epidermal cells. They are now considered as the most likely factor causing the polymorphism that leads to the onset of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Read also: What determines the course of atopic dermatitis
These findings indicate that the common genetic regions for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis contain polymorphic genes with the same effect of developing inflammation and compromising skin immunity. The pathological process, which began under the influence of provoking factors, is maintained and regulated both in atopic dermatitis and in psoriasis due to complex immunological mechanisms, the central link of which is the activation of T-lymphocytes and their migration into the skin.
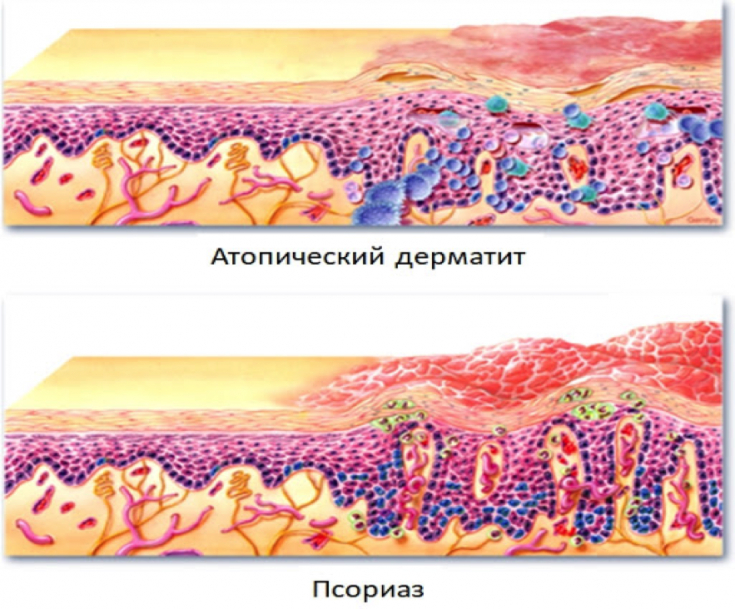
The clinical picture in most cases makes it easy to differentiate atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but sometimes this can cause difficulties, for example, in the case of a papular rash with severe infiltration in atopic dermatitis, erythroderma, etc. .
Even histopathological studies may not always be useful in the differential diagnosis of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Thus, the rash in the acute phase of atopic dermatitis differs much less from that in psoriasis. During the histological examination of material from chronic foci of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis from patients with a clearly established diagnosis, many common factors of keratinization disorders are found.
Read also: Impaired immune function of the skin with vitamin deficiency D
In more than 50% of cases, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis cannot be clearly distinguished on the basis of histological findings alone. Cell proliferation, acanthosis, and the number of keratinocyte layers may also not differ in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Even the expression of the recognized marker of keratinocyte activation during hyperproliferation - CK16, according to the literature, may not differ in patients with atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Follow our news on Facebook!
An increased tendency to colonize the skin with bacterial, fungal and viral agents is also well known in patients with atopic dermatitis. Despite the significantly lower propensity of psoriasis patients to microbial colonization of the skin, it has been proven that in both psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, colonization of the skin by strains of Malassezia exceeds normal values.
Approaches to the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
The common mechanisms underlying both diseases determine the similarity of the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis, but there are certain differences. Phototherapy is more commonly used to treat patients with psoriasis. A group of American scientists attempted to summarize the data available in the world scientific literature on the use of phototherapy in atopic dermatitis and concluded that during exacerbations it is better to use medium doses of UVA 1, and UVB is more beneficial for patients with chronic rashes.
Read also: What vitamins does your skin lack
Calcineurin inhibitors are a common treatment for patients with atopic dermatitis. Shortly after its creation, a systemic treatment for psoriasis was proposed, but according to scientific data, the concentration of the drug in topical dosage forms was insufficient to achieve a good clinical effect in psoriasis, and systemic use often led to nephropathy and hypertension.
More useful information on our YouTube-channel:







Add a comment