According to modern ideas about the functioning of the female reproductive system, an important role is played by the vaginal microflora, which is a balanced ecosystem, the species and quantitative composition of which is regulated by the endocrine and immune systems of the female body.
Find out in this article on estet-portal.com how effective is the use of suppositories for restoration of microflora after antibiotic therapy for bacterial vaginosis.
- Vaginal microecosystem in bacterial vaginosis
- Principles of treatment of bacterial vaginosis
- Study of the need to restore the microflora after treatment of bacterial vaginalfor
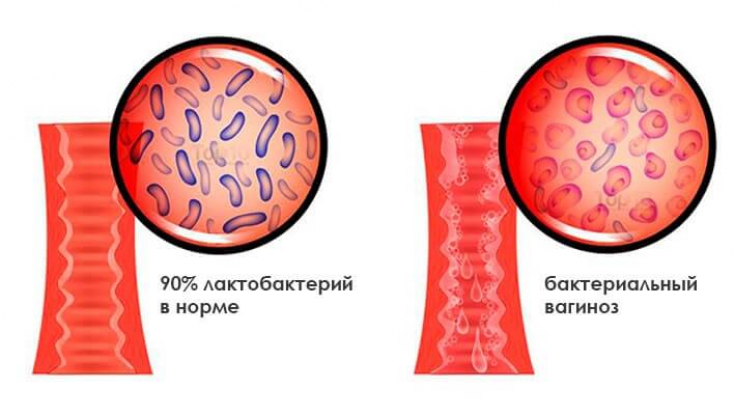
Vaginal microecosystem in bacterial vaginosis
The microecosystem of the vagina is the result of complex dynamic interactions of anatomical, histological, physiological and microbial factors (especially the vaginal epithelium and resident microflora), influenced by the homeostasis of the woman's body at different age periods of life, as well as exogenous factors.
Follow us on Instagram!
Violation of the microecology of the vagina leads to the development of bacterial vaginosis (BV) − non-inflammatory infectious syndrome caused by a dysbiotic state of the vaginal biotope, digestive tract and urinary system against the background of chronic immunodeficiency.
Vulvovaginal atrophy CO2 laser therapy
Today, the frequency of bacterial vaginosis in the structure of infectious diseases of the female genital area remains quite high and amounts to 60-80%.
The vaginal biotope contains both aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms, although lactobacilli dominate the vaginal microbial landscape. Their number reaches 106-109 CFU / ml and makes up to 95-98% of the entire vaginal microflora.
Critical periods in a woman's life: postpartum and perimenopause
The development of bacterial vaginosis is associated with a decrease in the number or replacement of the dominant forms of lactobacilli with opportunistic and pathogenic microorganisms, in particular obligate anaerobes − Prevotella spp., Bacteroides spp., Mobiluncus spp., Peptostreptococcus spp. etc.
It has been proven that lactobacilli are absent in 40-45% of patients with bacterial vaginosis, in 50-60% of cases their number is sharply reduced (less than 105 CFU / l).
The results of studies conducted in recent years indicate that, along with pathogenic pathogens, representatives of the normal microflora of the vagina can be the cause of infectious pathology in obstetric and gynecological practice. About 3-5% of the microbiocenosis of the vagina of healthy women are other microorganismswe, in particular − G. vaginalis is determined in 5.8-6.2% and even chlamydia in 1.4-6.4%.
Principles of treatment of bacterial vaginosis
The range of modern drugs used to treat bacterial vaginosis is quite wide. The principles of treatment for bacterial vaginosis are based on the use of two-stage therapy.
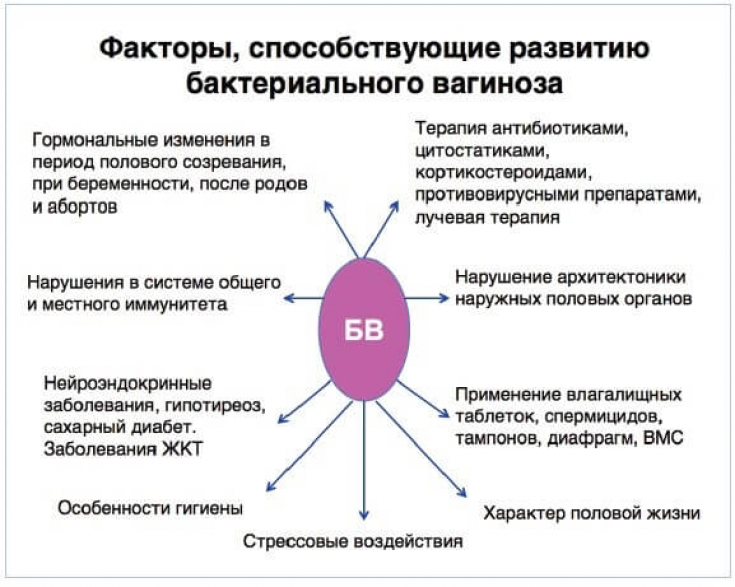
At the first stage, antibacterial drugs are prescribed to eliminate the vaginal biotope associated with bacterial vaginosis in combination with immunocorrection, and at the second − probiotics.
This concept is the basis for the restoration of the lactobacilli biotope and the immune defense of the vaginal microbiocenosis.
To date, a number of issues have not been finally resolved – is there an alternative to the two-stage treatment of bacterial vaginosis and what means are most effective in restoring the vaginal microflora, preventing recurrence of the disease and undesirable consequences.
One time caesarean section – always caesarean section: is it true?
The presented argument causes the need to search for new productive methods of treating bacterial vaginosis aimed at restoring and normalizing the vaginal biotope, preventingrelapses and possible complications.
Research on the need to restore microflora after treatment of bacterial vaginosis
This study was conducted to investigate the reduction in the frequency of relapses of bacterial vaginosis in women of reproductive age by prescribing complex dual therapy using vaginal suppositories.
The study involved 50 women with clinically diagnosed bacterial vaginosis. The patients were divided into 2 groups: the first 25 after antibiotic therapy for vaginosis received additional vaginal suppositories with a specially processed mass of lactic acid bacteria, in an optimal amount to maintain the balance of the vaginal microflora. The second group – 25 patients did not receive additional therapy after antibiotic therapy.
Studies show that the efficacy of vaginal suppositories in preventing the development of vaginal dysbiosis was 88%.
In the absence of measures aimed at normalizing the vaginal microbiocenosis after the main course of therapy, clinical and laboratory recovery was observed in 16 (64%) patients, recurrence of bacterial vaginosis was established in 9 (36%) cases.
It should be noted that no local or general allergic manifestations, side effects or adverse reactions have been recorded with the use of vaginal suppositories.
More interesting information on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment