The frequency of caesarean section (CS) as a tool for positively influencing perinatal mortality (PS) and neonatal morbidity in many countries exceeds reasonable limits.
Due to the liberalization of indications at the end of the 20th century, the weight of caesarean section in human birth has increased so much that abdominal delivery has become the most common operation in modern clinical medicine.
About what changes in the reproductive system a woman can expect after a caesarean section and what ways to resolve subsequent pregnancies, read on estet-portal.com
- Caesarean section: statistics
- One time caesarean section − always caesarean section
- Counseling a woman with a history of caesarean sectionze
Caesarean section: statistics
According to the WHO, around 18,500,000 caesarean sections are performed every year in the world today, and every minute − 50. As a result, in the 21st century, almost every third child in the world is not born naturally, but is removed during surgery.
Follow us on Instagram!
At the same time, the actual results of the global increase in the rate of caesarean sections prompt experts and specialists to make disappointing predictions.
It has been proven that "the CS epidemic" is not accompanied by a proportional decrease in the number of perinatal losses, however, it is costly for the medical service system and, no less important, it becomes one of the factors of deterioration in the health of women of reproductive age.
How to recognize an abdominal pregnancy? Tactics of diagnosis and treatment
Also, some negative consequences for the health of children taken by caesarean section in the short and long term have also become apparent recently, which is also alarming and motivates to curb further growth in the frequency of operative birthsov.
One time caesarean section − always caesarean section
Declaration "once caesarean section" minus; always caesarean section,” proclaimed by Edwin Craigin in 1916, was revised in the 1980s in many countries, and attempted delivery in women with a history of caesarean section was proposed as one of the ways to reduce the overall level of operations.
This was facilitated by the fact that operation in the lower segment of the uterus replaced the traditional CS.
However, an increase in the incidence of uterine rupture associated with a scar cast doubt on the choice of vaginal delivery in this cohort of women.
Since then, at different times, the frequency of caesarean section due to uterine scar in many countries has periodically increased and decreaseds.
Counseling a woman with a history of caesarean section
Counseling a woman with a history of CS regarding an attempted natural birth requires a thorough examination of her health, the availability of comprehensive information from the doctor in relation to the previous delivery.
The success of a physiological birth attempt at level II-B evidence is influenced by the following factors:
- Section type.
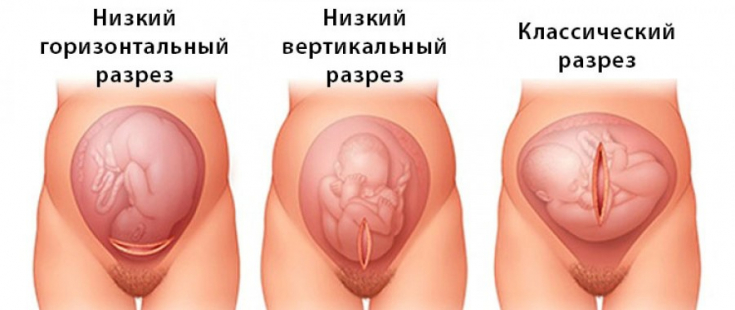
The transverse incision and the vertical in the lower segment have a negligible risk of uterine rupture, while the classic vertical or T-incision increases the risk of rupture, and therefore − should be considered a contraindication to attempting self-delivery.
The frequency of uterine rupture in the classic version or T-shaped incision ranges from 4-9%, with a low vertical − within 1-7%, low transverse − at the level of 0.2-1.5%.
Strategy for managing pregnancy in multiple sclerosis
3. Option to restore the integrity of the uterus.
Today, there is no consensus on the risk of uterine rupture when applying single or double-row sutures to close the wound of the uterus during a previous operation.
But in any case, data on the nature of the uterine suture must be recorded. Recently, there are more supporters of the two-row seam, with the first line of a continuous.
4. Maternal Health Characteristics − obesity and age over 30.
5. Interval after previous CS.
Short interval increases risk. When comparing data at intervals of 24 months, 18 months, 15 months after CS, the minimum interval for subsequent fertilization, because at a shorter interval the risk of uterine rupture increases.
This factor is the same as "ability" scar , which depends primarily on hemodynamic processes in the lower segment and isthmus after surgery. The formation of the architectonics of the vascular bed is completed 10-12 months after the operation, which probably justifies the high risk of pregnancy, which occurs earlier.

6. Start of labor.
Induction of labor, especially with prostaglandins E2, E1, correlates with an increased risk of uterine rupture.
7. Number of surgeries performed. However, multiple caesarean sections, if all performed with a transverse incision in the lower segment, slightly increase the risk of uterine rupture during trial labor compared to a single operation in the past.
Medicated treatment of postpartum haemorrhage
The combination of the above risk factors, constructed in the Shipp et al.
More useful and interesting information on our channel on YouTube:







Add a comment