is most often diagnosed in young women, many of whom want to become pregnant. Therefore, it is important that the issue of pregnancy planning is actively discussed when choosing methods of treating the disease.
The relatively modest efficacy of modifying drugs, as well as limited evidence of their safety during pregnancy, has previously led many women to delay therapy until after the planning and actual pregnancy period.
On the other hand, early treatment
has been shown to reduce/delay disability. Read the article on
estet-portal.com about modern approaches to the treatment and management of pregnancy with a history of multiple sclerosis.
- Categories of drugs for the treatment of multiple sclerosis in pregnancy
- Peculiarities of prescribing therapy for the treatment of multiple sclerosis
- Symptoms of multiple sclerosis during pregnancyand Categories of drugs for the treatment of multiple sclerosis during pregnancy
Early treatment causes a dilemma: what to do when women with multiple sclerosis want to get pregnant while on medication?
Follow us onInstagram! Most of the drugs used in multiple sclerosis are classified
Cby the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Category C drugs are recommended for use during pregnancy, but a risk to the fetus cannot be ruled out.
There are no studies of these drugs in humans, and the potential benefit of the drugs may be a reason for their use in pregnant women.
It is also a problem that safety data in the context of pregnancy and risk to the fetus is limited
. The exception is glatiramer acetate, which is FDA Category B.
Peculiarities of prescribing therapy for the treatment of multiple sclerosis
It is very important to reduce the recurrence of the disease not to delay the use of modifying drugs, given the desire to have children in the future.
when a woman becomes pregnant (with the exception of certain medications).
But, a woman, upon registration, should see a doctor as soon as possible for a consultation.
On a question regarding nutritional supplements, women with multiple sclerosis should receive 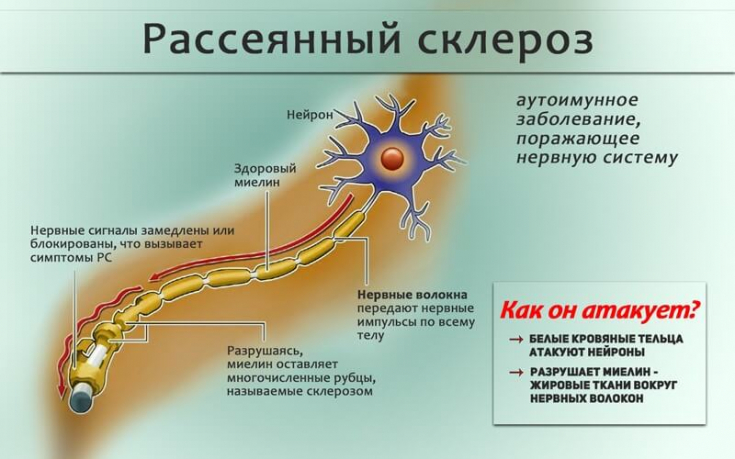 vitamin supplements
vitamin supplements
. The results of the study showed that although recurrence rates decrease during pregnancy, approximately ¼ women will relapse within the first 3 months postpartum.
Within a year (9 months of pregnancy and 3 months postpartum), the risk of recurrence is the same as that of a woman with multiple sclerosis who has not been pregnant. It is important to note that
corticosteroids.
May be increased Risk of relapse after use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists to promote conception
July. Hormonal contraception: features of oral contraceptive prescription
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis during pregnancy Many women find that MS symptoms improve during pregnancy.
But some symptoms may worsen, such as
fatigue,
imbalanceand bladder symptoms, especially in the later stages of pregnancy. Bell's palsy and
compression neuropathies, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, are more common late in pregnancy and may cause new symptoms to be distinguished from recurrent MS .
Any woman with relapsed MS should be offered  methylprednisolone
methylprednisolone
For severe relapses that do not respond to corticosteroids, plasmapheresis.
Medicated treatment of postpartum haemorrhage
Magnetic resonance imaging is not necessarily contraindicated during pregnancy, but
contrast agent (gadolinium) should be avoided. If a pregnant woman with multiple sclerosis has problems with muscle spasticity or severe weakness, she should be referred to a neurologist early in pregnancy to optimize the start of pregnancy and delivery.
Consequences of pyelonephritis during pregnancy
There is increasing evidence that delaying initiation and/or routine discontinuation of modifying drugs in pregnant women or unintended pregnancy in multiple sclerosis is associated with increased relapse rates. This affects the loss of performance in women with MS.
Women of childbearing potential should be considered for the possibility of pregnancy when prescribing treatment: counseling should take place until the woman stops using contraceptives.






