If the oral mucosa is often injured in the same place, oral fibroma may develop. Scientists suggest a hereditary predisposition to this disease, most often trauma to the mucosa and the formation of fibroids occurs & nbsp; in children and adolescents. This tumor formation is usually formed from connective tissue, has a benign course and very slow growth. But with constant traumatic effects on the formed fibroma, its malignant degeneration is likely.
Signs and causes of oral fibroma
Usually oral fibroma is located on the tongue, gums, inner surface of the cheeks & nbsp; or mucous membrane of the lips – that is, in those places that are most often injured. Mucosal injury occurs in children and adolescents – from foreign objects that they take into their mouths, and from frequent biting of their lips or cheeks, in elderly patients – from poorly fitting dentures. The cause of injury can be a sharp edge of the tooth, a poor-quality filling or a dental crown.
Chronic inflammatory processes can provoke the development of oral fibroma – such as stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis.
Fibroma of the oral cavity looks like a rounded dense nodule of connective tissue fibers. This formation is smooth, dense to the touch and painless, covered with a mucous membrane, has a leg or a wide base. Fibroma grows slowly, sometimes ulcerates and becomes inflamed. If it is constantly injured, the fibroma degenerates into a cancerous tumor.
Types of oral fibroma:
- dense – happens on the gums and hard ribs;
- soft – is formed on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and tongue;
- irritation fibroma – develops in response to irritation in the form of a pink papule, with repeated injury becomes bumpy and covered with ulcers;
- symmetrical – gingival growths in the area of the upper third painters, are bean-shaped and firm in texture;
- lobulated – occurs due to trauma to the mucosa with a denture, is localized on the gum and has a bumpy structure;
- fibrous epulis – dense and slowly growing formation on the gum.
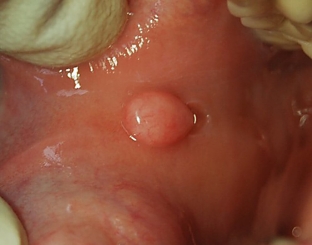
Diagnosis and treatment of oral fibroma
The dentist usually makes a diagnosis on the basis of examination and palpation of the oral fibroma, if necessary, a histological examination of the formation, ultrasound diagnostics is performed so as not to confuse it with a lipoma, tumors of the tongue.
Fibroma of the oral cavity is treated by surgical removal. The most effective – removal by laser or radio wave method. The excision is carried out together with a leg or an arcuate incision – together with the base.







Add a comment