The first signs of aging that patients often turn to aesthetic medicine specialists include vasodilation in the cheeks and nose, dyspigmentation or the presence of age spots on the face, shallow wrinkles around the mouth and eyes, decrease in tone and deterioration of skin texture. Seborrheic and actinic keratoses – problems affecting older patients more often.
The above symptoms appear primarily on the face, but these changes are also observed on other parts of the body: dyspigmentation on the neck and trunk (especially on the back) and limbs (more often on the arms); dilated vessels and hyper- or hypopigmentation on the chest and neck.
To reverse the signs of aging described above, which are mostly caused by photodamage to the skin, photorejuvenation is often used, which Dr. Christine Dierickx discusses in this article.
Photorejuvenation procedure to eliminate pigmentation and age-related changes
Therapy of the above described skin defects can be carried out using various devices that act on tissues with energy.
Follow us on Instagram!
The principle of operation of most of them is based on the principle of selective photothermolysis, or selective absorption of light energy by skin chromophores. As a result of the conversion of energy into heat, the structure containing the chromophore is destroyed with minimal impact on the surrounding tissues.
Because the skin is exposed to heat damage during the procedure, a wound healing reaction is triggered after the laser treatment:
•
• remodeling into more structured type I collagen over the next three–six months.
The principle of operation of most of them is based on the principle of selective photothermolysis, or selective absorption of light energy by skin chromophores.
Photorejuvenation of the face: stages and nuances of working with different skin types
To work with most patients, the author uses a multiplatform device (Nordlys, Candela, USA).
For all procedures, the author chooses the energy that will ensure the effectiveness of the procedure and the comfort of the patient.
The above device, based on the patient's skin type and degree of tanning, allows you to use preset settings. However, they need to be adjusted according to the patient's skin reaction (darkening, bluish appearance) and sensitivity.
The energy must also be reduced (by 1–1.5 J/cm2) before exposure to thin skin or work directly on bone structures.
For optimal results, it is important to work with the chromophores in the correct order. Most often, patients with Fitzpatrick skin types I and II have vascular lesions, while patients with skin types III and IV are more prone to dyspigmentation or both problems.
Stage 1: Target – remove epidermal pigment. Parameters:
• wavelength – 555 – 950 nm;
• impulse – 2.5ms;
• delay – 10ms;
• sequence of pulses – 2.5 ms.
If the patient does not have dyspigmentation, the author uses a wavelength of 530-750 nm with a similar pulse sequence. Since this wave is much better absorbed by melanin and hemoglobin, the author uses it when working with Fitzpatrick I–III skin types with a low level of tanning.
Stage 2: Target – eliminate diffuse redness after stage 1
The 530-750nm wavelength is often used to treat small areas of individual visible vessels, however, for patients with a high degree of skin photodamage, this procedure can be delayed for 1 month.
Step 3: Target – work with individual vessels
If they are located on the cheeks, the author uses a wavelength of 530 & ndash; 750 nm. The device allows you to choose one of four options for the length of the pulse in accordance with the size of the target vessel, but most often the author works with a pulse of 1.5 ms. Deeper vessels or vessels located in hard-to-reach places are processed in Nd:YAG mode.
Step 4 (optional): combined application of 530–750nm or 555–950nm radiation with 1550nm fractional laser to smooth out fine lines and wrinkles.
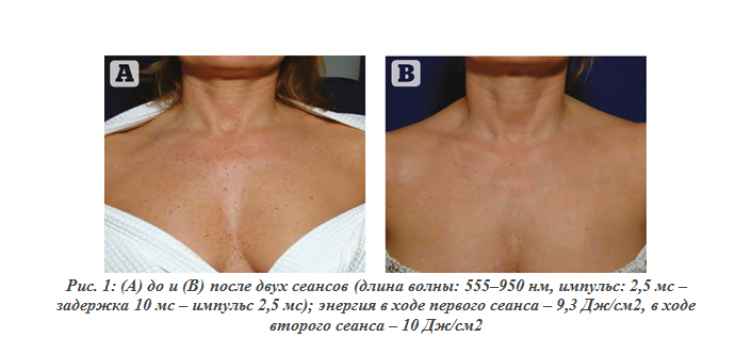
Photorejuvenation of the body: work with the neck, chest, shoulders, back and limbs
Photorejuvenation can be performed on any part of the body damaged by the sun:
Neck
This area is characterized by dyspigmentation and diffuse redness, as well as Civatt's poikiloderma. In order to treat the above changes, you can use a standard sequence of pulses with an energy of 1 J less than for the face. And the remaining small vessels can be removed after a month with a 1.5 ms pulse.
Chest
The most common problem in this area, – dyspigmentation, however, small areas of diffuse redness and single visible vessels also occur in the chest area. When working with them, you should be guided by the tere-step process described above, and during the treatment of the skin over the collarbone, sternum and ribs, it is necessary to reduce the level of energy supplied.
Peculiarities of the modern use of laser treatment
Shoulders and Back
Decrease your energy levels when passing over your shoulder blades, ribs and spine.
Hands
Dispigmentation in the area of the hands – a common occurrence that responds well to therapy. Working with this zone, you can lightly press on age spots or treat certain spots twice. Before the procedure, it is important to stretch the patient's skin, and in order to avoid the effect of "white gloves"; it is necessary to gradually reduce the energy, approaching the border of the uncultivated zone.
Decrease the energy level when passing over the shoulder blades, ribs and spine.
Legs
Telangiectasias are common in the legs, but photorejuvenation for such patients is associated with the risk of side effects and is ineffective, except in cases of progressive disseminated telangiectasia. Therefore, it is better to limit yourself to areas of dispigmentation or to postpone the procedure until the elimination of problematic vessels with the help of sclerotherapy or laser exposure.
According to Prime magazine







Add a comment