When planning of aesthetic correction gender differences should be taken into account in terms of anatomy, histology of hard and soft tissues, facial skin relief.
It is also important to understand what changes occur during aging with the male and female face, which features require special attention during correction.
Knowing the multilevel model of aging of the face gives the beautician the opportunity to more delicately and personalize the therapy needed for the patient.
At estet-portal.com read about gender differences in facial anatomy and histology that , unequivocally, influence the tactics of working with the patient.
- Gender differences in the skeletal skeleton of the face
- How women skin differs from men
- Musculature of the face in women and men
- Features of the soft tissues of the face of women and men
Gender differences in the skeletal skeleton of the face
In the early stages of development, all individuals are phenotypically "female" prototype, regardless of biological sex.
As a man approaches puberty, a more masculine appearance will take on a more masculine appearance due to changes that are caused by the influence of testosterone, including:
- adaptation of the skeleton shape;
- subcutaneous fat distribution;
- skin physiology.
The ratio of the height and width of the face determines its general type: in men, this ratio is usually 1.35: 1, and in women 1.31: 1. In women, the upper, middle and lower thirds of the face are usually equal, in men, the lower a third of the face predominates.
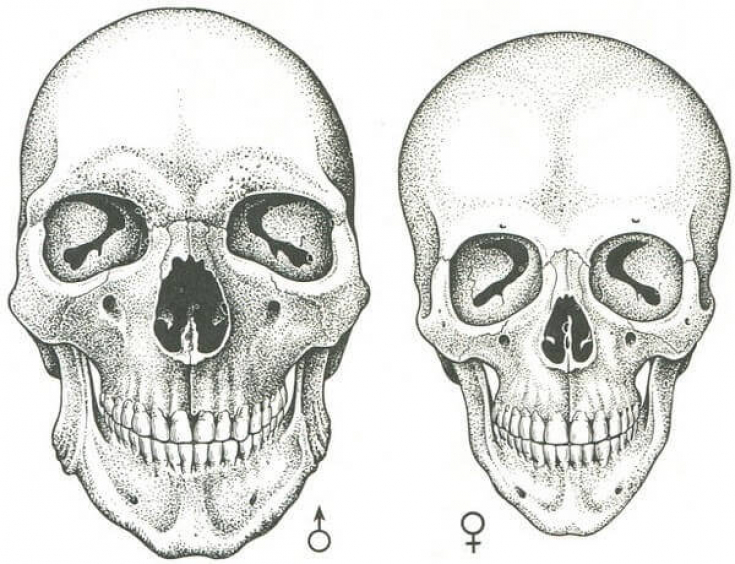
At the skeletal level, the female facial skull is more oval and v-shaped, compared to the male skeleton, which is typically more angular and square in shape.
Facial anatomy for beauticians: how to bypass danger zones
The male mandible has a more pronounced curve, which is reflected in a stronger, wider and forward protruding chin, a sharper jawline.
How women skin differs from men
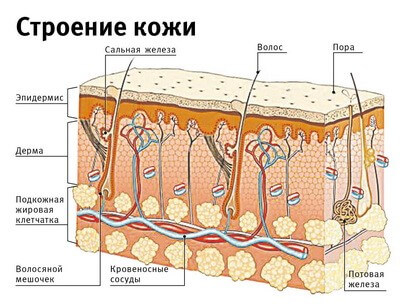
The skin plays a key role in perception of the beauty of the face.
Knowing the physiological and chemical differences between male and female skin can help clinicians develop customized treatment plans for optimal cosmetic results.
Studies have shown that men's skin has larger pores and produces more sebum, making it more prone to acne in preteen years.
In post-teen groups – acne is more common in women.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!
Skin pigmentation and thickness of its cross section are much higher in men. Men's skin also has a higher collagen content and shows higher levels of lactic acid production.
As for the facial hypodermis, in women it is more pronounced.
Musculature of the face in women and men
As for the muscles of the face, in men and women it differs both in anatomical size and in dynamic functions.
ABC of the skin for a cosmetologist: the structure of the epidermis
Women's muscle mass, including facial muscle mass, has been documented to be significantly lower than men's.
In one study using 3D analysis techniques, rates of wrinkle formation were found to be significantly higher in men compared to women.
In the lower third of the face, for example, the average thickness of the masticatory muscle in women is 13 mm +/- 1.8 mm, and in men it is 15.1 mm +/- 1.9 mm.
The kinetic energy generated by these muscles is comparatively greater in men than in women, resulting in more pronounced mimic activity.
Features of the soft tissues of the face of women and men
When examining the soft tissues of the lower face, anatomical studies have shown that women's chin and jaw are narrower and less prominent than men's.
Assessment of faces in profile shows that the chin in women is most often located slightly behind the lower lip, while in men they are on the same line.
Men tend to have larger mouths (intercommissural distance) and at the same time thinner lips.
At the same time, the thickness of the vessels in the representatives of the stronger sex is somewhat larger than in women, which should be taken into account when performing injection correction of this area.







Add a comment