Herpes simplex – This is an anthroponotic disease of a viral nature, which is accompanied by the appearance of painful blisters on the skin or mucous membranes and is prone to generalization. I would like to pay special attention to herpes of smooth skin. Cosmetologists are faced with the fact that patients take herpetic vesicles for ordinary pyoderma (pustules) and eliminate them mechanically. As a result, inflammation spreads at a high speed, and herpetic skin lesions become extremely dangerous.
The main forms of herpetic skin lesions
The occurrence of vesicular or erosive rashes on the skin and mucous membranes, severe subjective symptoms ( itching, burning, tingling, redness) allow doctors to visually diagnose herpes infection, start antiviral therapy in a timely manner and inform the patient about the infectious nature of the disease and the risk of infecting others.
But it is not always possible to make a diagnosis in the shortest possible time, as more and more often herpetic skin lesions occur in an atypical form.
Under the influence of ongoing therapy, typically occurring herpes can significantly change and acquire an abortive course. In this case, the elements in the lesion bypass separate stages of development.
In these cases, the lesion may be represented by a diffuse element (without a clear localization), an edematous spot on an erythematous background, an ulcerative or necrotic defect, as well as other manifestations. Clinical manifestations of herpetic lesions skin with an atypical course, read further on estet-portal.com. Help in making a diagnosis when a patient presents with an abortive herpetic skin lesion can be provided by a correctly collected anamnesis, in which there is an indication that the patient had rashes typical of herpes in the past.
Factors that contribute to the misdiagnosis of herpetic skin lesions:
- violation of the usual cycle of development of herpetic elements in the lesion;
- unusual localization of the focus and anatomical features of the underlying tissues;
- the predominance of subjective sensations in the focus.
Features of the course of herpetic skin lesions in atypical forms
Disseminated form of herpes – the appearance of two or more typical foci of herpetic skin lesions in areas of the skin that are distant from each other. At the same time, synchrony of clinical manifestations is noted.
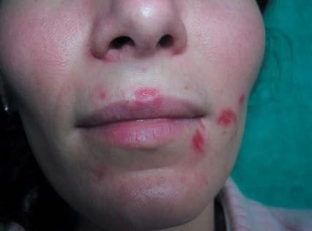
A migratory form of herpes, which is characterized by a change in the location of the rash with each new recurrence of the disease.
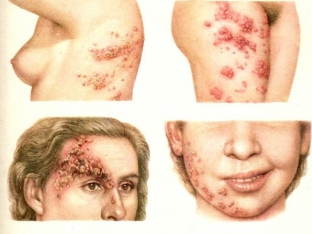
The abortive form proceeds without the formation of bubbles – vesicle. It appears as pink or pinkish-yellowish spots with indistinct borders of rounded or irregular outlines with slight swelling. Sometimes, at the site of the typical localization of herpes, there is a burning sensation, itching. However, it is characteristic that the rash does not appear. Subjective sensations disappear within a day.
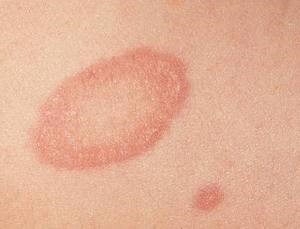
The edematous form of herpetic skin lesions is characterized by a sharp localized swelling of the tissues without the formation of vesicles. More often it develops in areas of the body rich in loose fiber: on eyelids, lips, scrotum. With the spread of edema deep into and along the periphery, elephantiasis (elephantiasis) may develop.
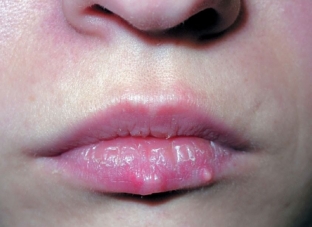
Zosteriform skin herpes is characterized by the location of the rash in the projection zone of a particular nerve. Typical localization – limbs, torso, face. The clinical picture of this form of herpetic skin lesions is characterized by pronounced symptoms of neuralgia and general intoxication (fever, headache and muscle pain).
Hemorrhagic-necrotic and erosive-ulcerative forms of the disease are the most severe. In the hemorrhagic-ulcerative form, on an edematous-hyperemic background, grouped vesicles with serous-purulent contents appear, which have a hemorrhagic character. In the process of reverse development, necrosis is noted at the site of hemorrhagic eruptions, followed by the formation of scars.
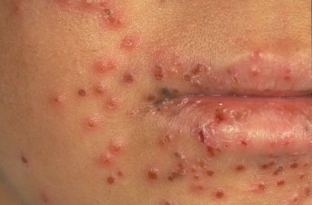
The main feature of erosive and ulcerative herpetic skin lesions – the presence of extensive, long-term non-healing ulcerative defects.
Kaposi's eczema herpetiformis is one of the most severe forms of herpes simplex. The disease develops in children suffering from simple childhood eczema or atopic dermatitis, 1-2 weeks after contact with a patient with herpes. The appearance of a rash in children is accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication up to impaired consciousness. Rashes with this form of herpetic skin lesions are always accompanied by itching, burning, soreness, regional lymphadenitis, lymphangitis. Often, the mucous membranes of the mouth, nasopharynx are involved in the pathological process. Possible damage to the eyes, central and peripheral nervous system, internal organs.
Summarizing, it can be noted that in atypical forms of herpetic skin lesions, any one of the stages of the development of the inflammatory process or one of the components of inflammation, or subjective symptoms, which give the appropriate name to the atypical form of herpetic skin lesions, predominates.







Add a comment