The middle third of the face is the main target of anti-aging medicine, because it is in this area that the changes that become the basis of all aging occur.
Hypotrophy, hypertrophy and migration of fat compartments of the middle third lead to the formation of wrinkles, folds, blemishes, etc.
In this regard, contour plastic of the middle third of the face plays a key role in its rejuvenation.
At estet-portal.com a detailed protocol for working with this zone is presented, indicating the points of filler injection and drug injection techniques.
- Anatomy of the middle third of the face: structure of the fat compartments
- Aging of buccal fat compartments
- Planning midface correction
- Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 1 patients
- Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 2 patients
- Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 3 patients
- Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 4 patients
- Buccal area correction in patients with different types of agingi
Anatomy of the middle third of the face: structure of the fat compartments
Fat deposits of the middle zone of the face are classified as either superficial or deep.
The superficial fat compartments are located between the skin and the plane of the superficial muscular aponeurotic system (SMAS).
SMAS is a continuous and organized fibrous network connecting the periosteum and facial muscles to the dermis.
SMAS – it is a three-dimensional structure that consists of collagen, elastic and muscle fibers, as well as fat cells. The adipose tissue of the superficial sections is located within this fibrous network.

Under the SMAS plane and under the muscles of the face are deep fat compartments that reach and adjoint to the periosteal plane.

Buccal fat compartment aging
- Aging of superficial buccal fat compartments
Aging of the medial group of superficial fat compartments is characterized by downward migration (ptosis) and hypertrophy.
Only the lateral temporo-cheek fat is hypotrophic, and because it is located above the parotid fascia, it does not tend to migrate downward.
Clinical case: correction of the area around the eyes
- Aging of deep buccal fat compartments
Aging of the deep jaw fat compartments (lateral and medial SOOF and deep medial buccal fat) is mainly characterized by hypotrophy and little or absent downward migration .
Buccal expansion of buccal fat can also undergo hypotrophy resulting in a lack of support for the medial and lateral cheek fat pads, causing them to undergo ptosisy.
Planning midface correction
Knowledge of the anatomical changes associated with the aging process can suggest which fat compartments need to be filled with filler.
This step is critical, as selecting the wrong correction will likely result in little or no improvement in the patient's appearance.
Proper planning for correction will produce a satisfactory result.
To facilitate the choice of treatment, it is recommended to apply the Classification according to the type of aging of the middle third of the face, which simplifies the planning of correction tactics for a particular patient.
Classification of the types of aging of the middle part of the face:
Type 1. Hypotrophic
Hypotrophy of all fat pads upper jaw, predominantly deep sections: medial and lateral SOOF and DMCF.
The area appears flat or concave throughout.
Nasolabial fold is caused by "pseudoptosis" skin that is no longer supported by the underlying soft tissues is redundant and sagging.
concave due to hypotrophy of the middle buccal fat pad.
Type 2. Hypotrophic / PtoticHypotrophy predominates in
deep fat compartments(medial and lateral SOOF, DMCF). This area appears concave
in the suborbital region, while the region near the nasolabial fold is slightly convex due to ptosis of the nasolabial compartment.
Nasolabial fold defined by "pseudoptosis" skin, but appears more pronounced due to ptosis of the nasolabial fat pad.
Chemical blepharoplasty: correction of the periorbital region with peeling
The adipose tissue of the upper jaw is shifted downward due to the omission of the
superficial fat compartments. The infraorbital region appears flat or slightly concave due to hypotrophy of the medial SOOF and drooping of the medial cheek compartment.
The nasolabial fold is caused by sagging of ptotic and hypertrophied nasolabial fat.
The cheek is convex due to ptosis and hypertrophy of the middle buccal fat.
Type 4 Hypertrophic/Ptotic
The adipose tissue of the upper jaw is hypertrophied and shifted downward due to ptosis of the
superficial fat compartments. The area appears to be concave only in in the nasolabial groove, while the
central partand nasolabial region are clearly convex. The nasolabial fold is defined by sagging of the ptotic superficial fat compartment and is exacerbated by
hypertrophy. Read the most interesting articles in
Telegram! Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 1 patients
In patients 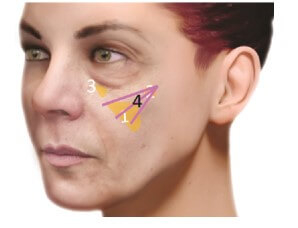 1st type
1st type
First, it is a reduction in deep medial buccal fat (DMCF);
Second, loss of lateral SOOF volume.- Therefore, in order to reduce adipose tissue hypotrophy, you first need to
- increase the volume of DMCF (Zone 1).
With this step, we achieve both volumizing and lifting the soft tissues of the cheek. By
Lateral SOOFcorrection (Zone 2), we improve the projection of the cheekbone and further increase the lifting of the soft tissues of the cheek.
Finally, we proceed to treatment of the medial SOOF (Zone 3) to correct the infraorbital depression.
The injection technique used in this type of patient is a bolus injection through a needle or cannula.
Suggested filler – YVOIRE Contour presented by
Academy of Scientific Beauty. In type 1 patients, it is useful to additionally correction the superficial medial fat pad and
nasolabial compartment(Zone 4) to complete the volume increase that began after the DMCF injection. Correction is performed with YVOIRE Volume filler in fan technique using cannulas
and. Practical case: correction of facial lipoatrophy with fillers
Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 2 patients
In patients 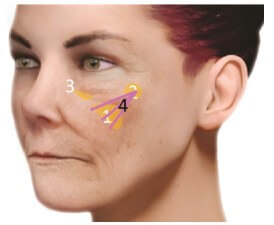 type 2
type 2
(Zone 1) and then Side SOOF (Zone 2). It will be advantageous to increase the amount of filler injected into the lateral SOOF as this will result in a greater lifting effect that type 2 patients require. The third step will be to
correction of the medial SOOF(Zone 3) to correct the infraorbital dimple.
The injection technique used in this type of patient is a bolus injection using a needle or cannula.
The optimal filler for this procedure – YVOIRE Contour.
For type 2 patients, we then correct the superficial medial buccal fat pad (Zone 4) to avoid increasing the initial nasolabial fat ptosis.
Filler YVOIRE Volume is inserted using the fan technique using cannulas
and. 3-Stage Lip Correction: An Anatomical Approach to Lip Contouring
Chygomatico-jaw area correction in type 3 patients
In patients 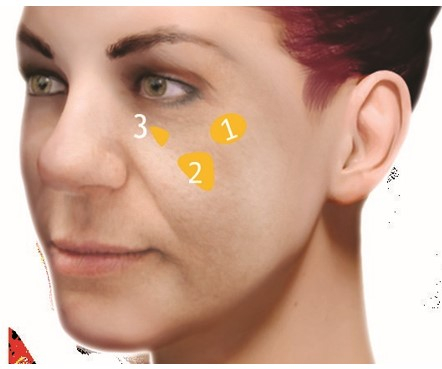 type 3
type 3
In this case, we must lift the ptotic fat compartments. We can only do this by
increasing the volume of the lateral SOOF(Zone 1).
Volume restoration of this compartment will increase cheekbone prominence and lift superficial fat. Only after assessing the degree of lifting, it will be possible to
increase the volume of DMCF(Zone 2).
Be very careful not to introduce too much filler into the DMCF because in this type of patient the lower jaw region is already hypertrophied and over-volumed. In type 3 patients, it will be necessary to
correct the medial SOOF(Zone 3) to eliminate the infraorbital cavity.
The injection technique used in this type of patient is a bolus injection with a needle or cannula.
Suggested filler – YVOIRE Contou
r.Facebook! Chygomatico-maxillary area correction in type 4 patients
In patients 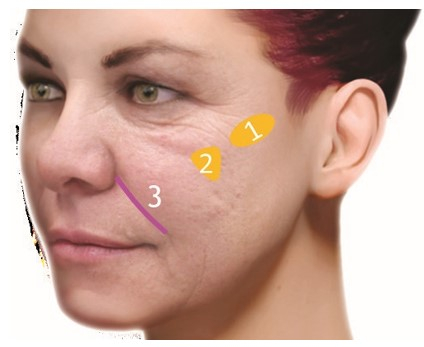 type 4
type 4
In this case, we can only balance the volumes between the upper and lower midface and lift the ptotic fat deposits by increasing the volume of the lateral SOOF (Zone 1).
In type 4 patients, the volume of the lateral SOOF is increased to lift the cheek soft tissue and balance it with the excess volume in the lower jaw region.
DMCF(Zone 2) correction is usually done only at the boundary with sideways SOOF.
The injection technique used in this type of patient is a bolus injection with a needle or cannula.
Suggested filler - YVOIRE Contour.
The nasolabial fold (Zone 3) can be corrected with a linear needle injection.
In this case, the suggested filler is YVOIRE Volum
e. Fundaro Salvatore: Anatomical Approach to Facial Correction
Buccal correction in patients with different types of aging In
Type 1 patients, buccal expansion of the buccal fat pad and medial buccal fat (MCF) wasting may create excessive concavity in the central cheek.
In this case, it is necessary to restore the volume of the MCF (Zone 5).
The injection technique used in this type of patient is cannula injection.
Suggested filler – YVOIRE Volume.
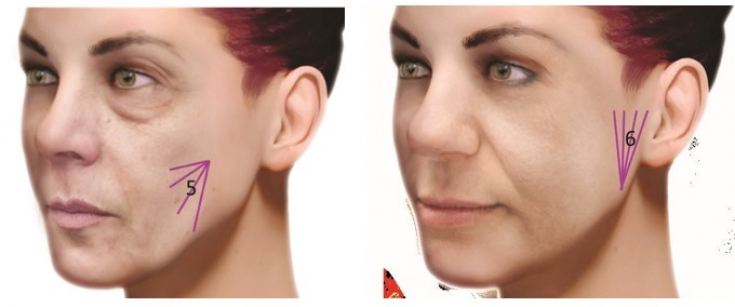 In 2, 3 and 4 patients
In 2, 3 and 4 patients
In this case, YVOIRE Volume
or Contour must be injected with a cannula to restore LTCF buccal volume (Zone 6) . How a chin, cheekbone and mandible correction improves the contour of a patient's face







Add a comment