Many people dream of a thick head of hair. But, in addition to the genetic predisposition to hair density, there are also diseases of the hair and scalp, which contribute to the loss and / or lack of hair growth in the hair follicles.
One of these diseases is alopecia areata. This is an organ-specific genetically determined inflammatory disease with a chronic course.
Alopecia areata is based on damage to the hair follicles, manifested by non-scarring hair loss, which can be both temporary and permanent, as well as changes in the nail plates (up to 65% of cases ). Read on estet-portal.com more about alopecia areata.
- What can be the trigger in the development of alopecia areata
- Are alopecia areata related to other diseases
- Classification of alopecia areata. Appearance of baldness
- What is important to pay attention to when diagnosing alopecia areatai
What can be the trigger in the development of alopecia areata
The main reason for the development of alopecia areata is damage to the hair follicle of an autoimmune nature, against which the immune tolerance of the cells from which the follicle is formed develops, as well as the suspension of specific reception from its hair papilla.
A fifth of patients with alopecia areata have familial cases, suggesting a genetic predisposition to the disease.
Read also: Congenital forms of diseases of the hair follicle and hair structure
Factors that can contribute to the activation of autoimmune processes caused by genetics - anesthesia, infectious diseases, vaccination, stress, antibiotic therapy.
The incidence has ethnic and geographical differences and depends on the immunogenetic background of the patientsta.
Is there an association of alopecia areata with other diseases
Among all cases of visits to dermatologists, cases of alopecia areata account for up to 4%.
The lifetime risk of developing the disease fluctuates around 1.7%. It is noted that alopecia areata is more common in patients who have some diseases.
Alopecia areata associated conditions:
- Atopic dermatitis is registered 2 times more often in patients who have alopecia areata;
- Vitiligo occurs in 3-8% of patients with alopecia areata;
- occur in 8-28% of patients with alopecia areata. The presence and amount of thyroid antibodies in the blood does not affect the severity of alopecia areata. Blood relatives of patients with alopecia areata have been found to have a high risk of developing type 1 diabetes
- ; Often among patients with alopecia areata, there are cases of mental disorders,
- are represented by anxiety disorders and depressive states. The first focus of
Facebook! The disease occurs with the same frequency in both sexes
s. Classification of alopecia areata. Appearance of baldness
Depending on the volume and type of baldness, the following clinical forms of alopecia areata are distinguished:
- Universal
- – absence of hair on the head, in the area of eyelashes, eyebrows and on the skin of the body;
Total – complete loss of terminal hair on the scalp; - Subtotal - characterized by the absence of more than 40% of the hair on the head;
- Limited - one or more areas of alopecia that have clear boundaries;
- Ophiasis – alopecia foci have a ribbon-like shape, covering the marginal zone of hair growth in the temporal and occipital region;
- Inverse ophiasis – areas of baldness have a ribbon-like shape and are localized in the temporal and fronto-parietal zone.
- Diffuse form – complete and partial thinning of hair on the head;
- You may also be interested in:
Alopecia treatment: focus on biofiber
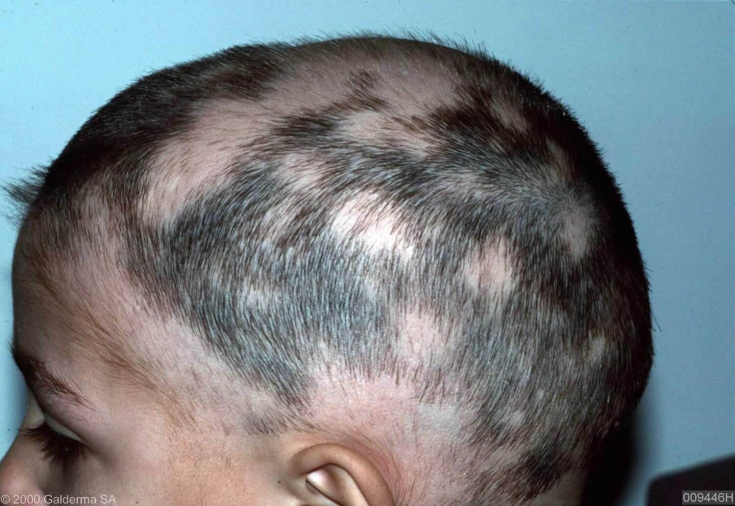
os and burning, the scalp is hyperemic.
What is important to pay attention to when diagnosing alopecia areata During the examination, the dermatologist pays attention to the
number ofalopecia lesions, their shape, quantity and localization. It also evaluates the
presence of hair stumpsin the lesion to determine the activity of the phase. In the course of microscopic examination, the presence in the foci of dystrophic proximal ends of the hair in the form of a “broken cord” is assessed. It is also important to assess the presence of vellus hair in the focus, which indicates the stage of regression of alopecia areata.
nail plates are inspected without fail.microscopic examination of hair and skin is carried out to exclude pathogenic fungi. Based on these signs, the doctor evaluates the type of alopecia areata, duration, severity and stage of the disease. After that, treatment regimen.
is selected individually.Read also:
Alopecia Areata Case Study Treatment of alopecia areata







Add a comment