Literature data show that in 17.5-65% of cases after aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast in the late postoperative period, the effect of the operation is significantly reduced.
Criteria for assessing the caudal displacement of the gland and guidelines for an aesthetically favorable location of the inframammary fold (IMF) have not yet been developed. Therefore, modern methods of breast mammoplasty are not focused on refixation of the mammary glands in case of displacement of the inframammary fold and its prevention in the postoperative period.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com the main causes of cosmetic defects after aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast and what are the approaches to the prevention of this condition.
The role of the inframammary fold in aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast
Modern surgeries to correct glandular ptosis of the breast during aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast are based on the movement of large volumes of soft tissues, which are accompanied by damage to such an important fixation structure as the inframammary fold.
Follow us on Instagram!
Methods of restoring and strengthening the inframammary folds during breast mammoplasty are not given due attention. This is partly due to the lack of studies on the relationship between the thickness of the posterior sheet of the superficial fascia of the mammary gland and the caudal displacement of the inframammary fold in patients with breast ptosis, both before mammoplasty and in the case of its development after traditional surgery.
This is due to the lack of methodology for assessing the level of location of the caudal displacement of the inframammary fold, the uncertainty of the aesthetic norm of its location and the assessment of the degree of displacement.
Norms of proportions for aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast
The location of the inframammary fold in relation to such landmarks as the jugular notch and the umbilicus has individual fluctuations. The most aesthetic is its location, in which the line drawn between the indicated landmarks is divided by the line drawn through the inframammary fold into segments, the lower of which is 85% of the length of the upper.
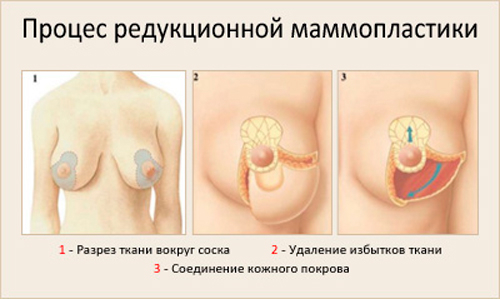
A decrease in this proportion of less than 75% goes beyond the limit of the aesthetic norm interval and indicates a caudal shift of the inframammary fold:
− I degree − 74.9-66.6% (1.1-2 cm),
− II degree - 66.5-59.1 (2.1-3 cm),
− III degree - 3.1 cm).
Perfect breast implants: what is the secret
Along with common etiological factors and pathophysiological mechanisms, patients with caudal displacement of the inframammary fold differ from patients with breast ptosis by a larger average gland mass, a lower average age; and a significantly smaller proportion of women with a history of lactation, as well as the strength of correlations with these parameters. These data indicate that the caudal displacement of the inframammary fold and ptosis of the mammary gland can be considered as independent conditions of the mammary gland, which must be taken into account in aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast.
The average thickness of the deep layer of the Scarpa fascia in the zone of the inframammary fold is significantly less than the superficial one (0.171 ± 0.008) versus (0.297 ± 0.012) mm and significantly inversely correlates with the mass of the mammary gland and lactation in history. In patients with breast ptosis II − III, the mean value of the deep sheet is significantly less than (0.143 ± 0.003) mm.
Practical anatomy of the ligamentous apparatus of the breast: fighting myths
The incidence of complications after aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast
Three years after traditional breast mammoplasty, the frequency of caudal displacement of the inframammary fold significantly increases from 22.7 to 35.3% and the degree of its severity. The recurrence rate of ptosis is 55.9% (including grade II − 26.7%, grade III − 9.6%), while it is combined with caudal displacement of the inframammary fold in 43.2% of patients.
In the development of secondary ptosis of the mammary gland, the mass of the mammary gland and the ratio of the width of the base of the mammary gland to its projection, in the occurrence or progression of the caudal displacement of the inframammary fold − reduction in the thickness of the inner layer of the Scarpa fascia, which is important to consider in aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast.
Dangerous breast implants: the main risks of mammoplasty
Treatment and prevention of caudal displacement of the inframammary fold is an important condition for improving the long-term results of surgical treatment of breast ptosis. The developed pathogenetically substantiated surgical interventions provide for cranial refixation of the inframammary fold, taking into account the aesthetic norm of its location, strengthening the structures of the inframammary fold with the help of Scarpa's fascia duplication and prolene mesh, as well as the formation of the slightest postoperative scar.
Following these techniques, you can significantly improve the results in the long-term postoperative period after aesthetic mammoplasty of the breast.
"Fat Transplantation" as a third breast reconstruction option







Add a comment