Pathological hyperprolactinemia in women is one of the most common causes of menstrual dysfunction and infertility. Excessive production of the hormone prolactin by the pituitary gland, which is physiological during pregnancy and lactation, at other times can lead to serious disturbances in the functioning of the female reproductive system. Given the diversity of the etiological factors of the disease and the peculiarities of its clinical picture, the diagnostic process of hyperprolactinemia should include a whole range of different studies, after which an adequate selection of a therapeutic regimen is possible.
Hyperprolactinemia in women: methods of diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of pathological hyperprolactinemia in women consists in the study of functions, primarily of the endocrine system of the body. The pathology of the structures of the brain and endocrine organs can serve as a trigger for a malfunction in the hypothalamic-pituitary system. The selection of treatment is carried out in accordance with the detected pathology: in some cases, conservative treatment is sufficient to restore reproductive function, in some cases it is impossible to do without surgical intervention.
Pathological hyperprolactinemia in women:
- Testing hormone levels will help diagnose hyperprolactinemia in women;
- instrumental methods for diagnosing pathological hyperprolactinemia;
- Conservative and surgical treatments for hyperprolactinemia in women.
Studying hormone levels will help diagnose hyperprolactinemia in women
Diagnosis of pathological hyperprolactinemia in women begins, first of all, with the collection of anamnesis, analysis of the patient's complaints and an objective examination. Information about previous injuries or brain exposure, as well as the nature and duration of the symptoms of the disease that have arisen, plays a very important role in the diagnostic process of such a pathology. The results of laboratory studies are of particular importance, as they directly indicate the state of the endocrine system:
- Hormonal panel study helps to determine at what level of endocrine regulation failure has occurred;
- an increase in the level of prolactin in the blood plasma indicates a malfunction of the hypothalamus;
- To assess the state of the reproductive system, it is also important to determine the ratio of gonadotropic and sex hormones.
Instrumental methods for diagnosing pathological hyperprolactinemia
To determine the cause of pathological hyperprolactinemia in women, instrumental diagnostic methods are used, which can determine, first of all, the anatomical cause of the pathology. X-ray examination of the skull may reveal changes in the sella turcica, indicating a neoplasm in the pituitary gland. The pathology is indicated by an increase or expansion of the Turkish saddle, signs of its sclerosis or violation of the integrity of the contours of the entrance to the saddle. Such changes are most characteristic of pituitary macroadenoma. An important role in the diagnosis is played by computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, since they can be used to obtain maximum information about the nature, size and localization of the formation.
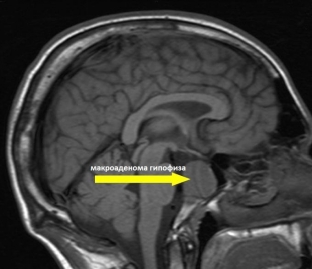
Conservative and surgical treatment of hyperprolactinemia in women
Treatment of pathological hyperprolactinemia in women depends on the etiological factor and may be conservative or surgical. Elimination of the root cause of hormonal imbalance is considered the basis for successful treatment of hyperprolactinemia. For conservative therapy of the disease, dopamine agonists are widely used to help restore reproductive function. Long-term use of drugs that suppress the production of prolactin often leads to a decrease in the size of the neoplasm that has arisen up to its complete disappearance. But often a confirmed pituitary macroadenoma is a direct indication for surgical intervention in order to completely remove the tumor. Currently, high-energy ionizing radiation is also used to treat pituitary adenomas.






Add a comment