Vulvovaginitis is one of the most common reasons for patients to visit antenatal clinics and gynecological hospitals. Despite the fact that this pathology does not pose an immediate threat to health, it can cause inflammatory diseases, increase the risk of intrauterine infections, and significantly worsen the quality of life.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com what are the current approaches to the study of the microbiome of the female genital tract, as well as management of the treatment of patients with vulvovaginitis, including fungal etiology.
- Key Factors for Disrupting the Vaginal Microbiome
- Causes of vulvovaginal candidiasis
- Approaches to the treatment of vulvovaginal candidofor
Key Factors for Disrupting the Vaginal Microbiome
It is known that normal vaginal biocenosis − this is a natural defense mechanism against colonization of the vagina by opportunistic microflora. The composition of the microbial flora of the vagina can change not only depending on the cycle, but also on the regime of the day, therefore it is often quite difficult to establish the initial nature.
Follow us on Instagram!
The microbiome is usually based on lactobacilli, which have a protective effect, in particular prevent the growth of opportunistic vaginal flora. The microbiome can be influenced by both exogenous and endogenous trigger factors. In turn, disruption of the microbiome can lead to the development of vaginal dysbiosis.
Bacterial vaginosis: current evidence on the causes of the disease
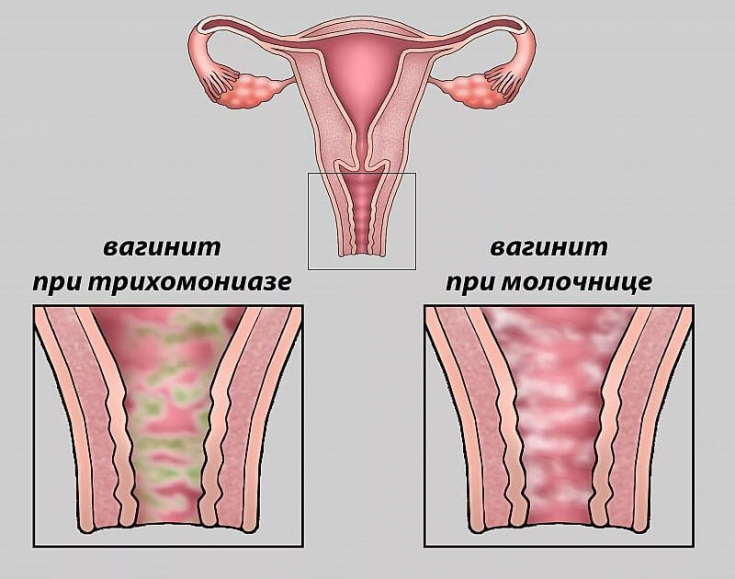
Violation of the normal microbiome of the vagina is the key pathogenetic mechanism for the developmentof both nonspecific vaginitis and bacterial vaginosis. A distinctive feature of these two nosological forms − these are clinical signs of inflammation in vulvovaginitisand their absence inand bacterial vaginosis (obligate markers are Atopoblum vaginae and Gardnerella vaginalis).
Causes of vulvovaginal candidiasis
Vulvovaginal candidiasis − an infectious lesion of the mucous membrane of the vulva and vagina caused by fungi of the genus Candida (in 90% of Candida albicans, in 10% of other types of fungi). Typically, 75% of women experience at least one episode of uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis at some point in their lives.
Modern approaches to the prevention of preterm birth
The causes of this disease are various:
- stress;
- genetic predisposition;
- zinc deficiency;
- anemia, etc.
Complicated vulvovaginal candidiasis can occur with relapse of the disease, severe forms of pathology, infection with Candida non-albicans, as well as with concomitant diseases (uncompensated diabetes mellitus, immunosuppression, etc.).
When diagnosing vulvovaginal candidiasis , the patient's complaints and the clinical picture of the disease must be taken into account, it is necessary to identify the background and concomitant pathology.

Colposcopy is of no definite value in establishing the diagnosis, but may be an additional method for screening for other pathologies. Chronic recurrent candidiasis of the genitals necessarily requiresno species identification of the pathogen, phase contrast microscopy.
Approaches to the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis
According to international guidelines, the gold standard of treatment for vulvovaginal candidiasis is fluconazole 150 mg once or itraconazole 200 mg twice daily for one day . preparations for intravaginal administration (clotrimazole, miconazole, econazole) are also recommended.
When choosing a drug, preference must be given to means:
- with a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity that do not suppress the normal physiological microflora of the vagina;
- effective and safe;
- with complex action.
Combined drug ciprofloxacin + ornidazole meets these requirements, which affects:
- gram-negative and gram-positive aerobic bacteria;
- anaerobic bacteria;
- protozoal infections;
- intracellular pathogens;
- has a bactericidal effect.
Urinary tract infections during pregnancy: evidence-based medicine
Complicated vulvovaginal candidiasis is caused by Candida non-albicans and is recurrent (more than 4 times a year), accompanied by severe symptoms of candidiasis with acute inflammatory erythema, edema, ulcers, cracks in the mucous membranes and skin of the perianal region.
It is more often observed in patients who have risk factors for the development of this pathology, accompanied by suppression of the body's immune reactivity (diabetes mellitus, the use of cytostatics, glucocorticosteroids, etc.).
More useful information on our YouTube channel:







Add a comment