It is known that among infectious diseases of the genitourinary system in women, in particular of childbearing age, bacterial vaginosis (BV) is the most common today.
Bacterial vaginosis − an infectious syndrome associated with vaginal dysbiosis, which is characterized by a high concentration of obligate anaerobic microorganisms and a sharp decrease in the content of lactobacilli or their absence.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about the main approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of bacterial vaginosis.
- Microorganisms that play a role in the development of bacterial vaginosis
- Development of the pathological process in bacterial vaginosis
- Bacterial vaginosis in sexual partnersov
Microorganisms that play a role in the development of bacterial vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis is a non-inflammatory disease, but it can significantly aggravate the course of STIs.
To date, more than 40 microbial agents have been identified that play a role in the development of bacterial vaginosis.
Follow us on Instagram!
Among them, the most important are:
- Gardnerella vaginalis;
- Mycoplasma hominis;
- Mycoplasma genitalium;
- Ureaplasma urealiticum;
- Bacteroides;
- Prevotella;
- Porphyromonas;
- Peptostreptococcus;
- Fusobacterium nuclearum;
- Enterococcus;
- Candida spp.;
- Listeria monocytogenes;
- Mobiluncus;
- Leptotrichia;
- Streptococcus viridens and others
What should be considered when prescribing hormone replacement therapy?
Severe inflammatory reaction from the vaginal epithelium in bacterial vaginosis is usually absent.
Massive growth of mixed flora is associated with the loss of "normal" Lactobacillus spp.
Thanks to the development of laboratory diagnostic methods, in particular the method of nucleic acid amplification with the detection of microorganisms that are difficult to cultivate, a high detection rate in bacterial vaginosis of Atopobium vaginae (A. vaginae) (77-96%) along with G. vaginalis (35 -79%.
But in recurrent bacterial vaginosis, A. vaginae is found in 75%, and G. vaginalis − in 100% of cases, which allows us to speak about the undoubtedly great responsibility of the latter for the recurrence of the disease.
The peculiarity that A. vaginae is almost never a monoinfection, without accompanying G. vaginalis, has been clarified.
When these pathogens are associated, recurrent bacterial vaginosis is diagnosed in 83% of patientsapprox.
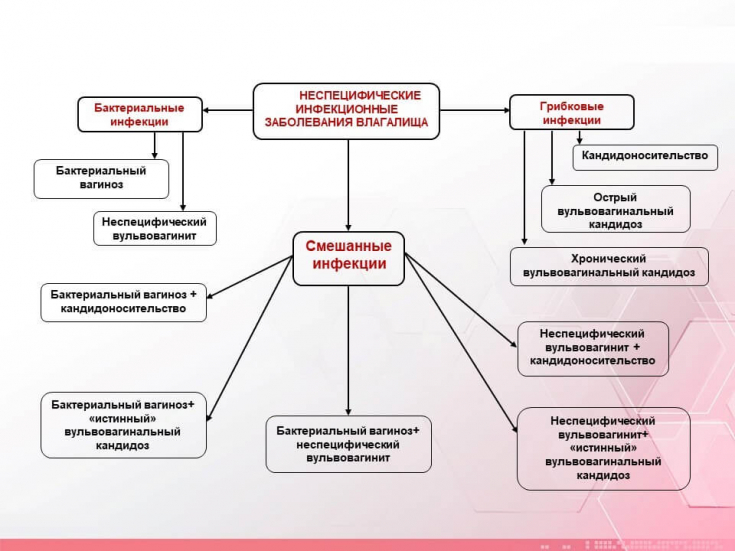
Development of the pathological process in bacterial vaginosis
The main reasons for the development of the pathological process in the vagina should be considered:
- endocrine disorders;
- changes in the state of local immunity (decrease in immunoglobulin A, circulating immune complexes, complement C3 component, increase in immunoglobulin G);
- indiscriminate antibiotic therapy;
- past or concomitant inflammatory diseases of the female genital organs;
- use of contraceptives (oral, intrauterine, spermicides);
- surgical and diagnostic interventions.
Gynecological infections. A new approach in the treatment of trichomoniasis
In women with complaints of long-term, treatment-resistant pathological discharge, bacterial vaginosis was diagnosed in 95% of cases.
After the introduction of reagent kits into laboratory diagnostic practice that allow the detection of anaerobic and microaerobic microflora (using the PCR method), it became known that these microorganisms can cause dysbacteriosis of the genitourinary system in men as well.
Such conditions have been described relatively recently, and therefore they do not yet have a generally recognized nameia.
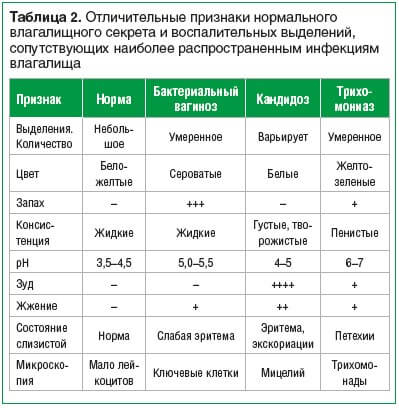
Bacterial vaginosis in sexual partners
The study of protozoal invasions of the genitourinary system occurring in combination with lesions caused by microorganisms associated with bacterial vaginosis in women of childbearing age and their male sexual partners is a promising area of modern medicine, the development of which can contribute to a significant increase in the level of diagnostic examination of patients with STIs and, as a result, increase the effectiveness of their treatment.
First of all, by justifying specific antibacterial therapy for the respective patients, as well as measures to prevent their reinfection.
Vulvovaginal atrophy CO2 laser therapy
For the successful treatment of bacterial vaginosis, it is advisable to make an individual etiological diagnosis of the components of this disease in order to identify exactly those factors that should be subject to medical correction.
Moreover, it is important that the appropriate diagnosis is not only qualitative, but also quantitative, since it is possible to determine which components of this polyetiological pathology are the causative agents of the disease and are subject to correction only by their ratio to the total bacterial mass in the test sample.
Anovulatory cycle: temporary phenomenon or cause of infertility
Today, antibiotics of the nitroimidazole and fluoroquinolone groups are used for the etiotropic treatment of bacterial vaginosis.
It is the substances of these chemical groups that have the ability to influence most of the pathogens of bacterial vaginosis.
Therefore, the combination of nitroimidazoles and fluoroquinolones is most often used in the empirical selection of specific therapy for BV.







Add a comment