Inflammatory processes in the female genital organs remain an urgent problem in modern obstetrics and gynecology. Despite a large number of scientific studies, as well as the invention of new antibacterial drugs, the frequency of gynecological infections does not tend to decrease.
Over the last decade in the world there has been an increase in the frequency of gynecological infections, which are sexually transmitted. Read more on estet-portal.com about new approaches to the treatment of certain gynecological infections.
- Pathogens of gynecological infections and causes of recurrence of diseases
- What are the features of the course of trichomonas infection
- Medicines for the treatment of gynecological infections caused by Trichomonas
- What is the mechanism of action of effective antitrichomonas drugsin
Pathogens of gynecological infections and causes of recurrence of diseases
The main spectrum of microorganisms that are capable of provoking gynecological infections and inflammatory processes in the genitals are, in most cases, microbial-protozoal-viral associations that are sexually transmitted. They are characterized by qualitatively new abilities and features of the clinical course, and are not the sum of the pathological components of individual infectious components.
Incorrectly selected drugs for gynecological infections, their dose, regimen and duration of administration, or a frivolous attitude towards the treatment of the patient herself lead to the transition of the process to a chronic state with periodic exacerbations.
This leads to the search for ways to improve the effectiveness of the treatment of inflammatory processes. In such cases, it is necessary to use the most effective drugs for the treatment of gynecological diseases.
This requires the doctor to invent a new treatment strategy and tactics.
Gonorrheal, trichomonas, chlamydial, candidal, mycoureaplasma and viral gynecological infections can persist in a woman's body until the end of her life and cause periodic exacerbation of adnexitisin, colpitis, bartholinites, etc.
Genital herpes: the main drugs for the treatment of the disease
What are the features of the course of trichomonas infection
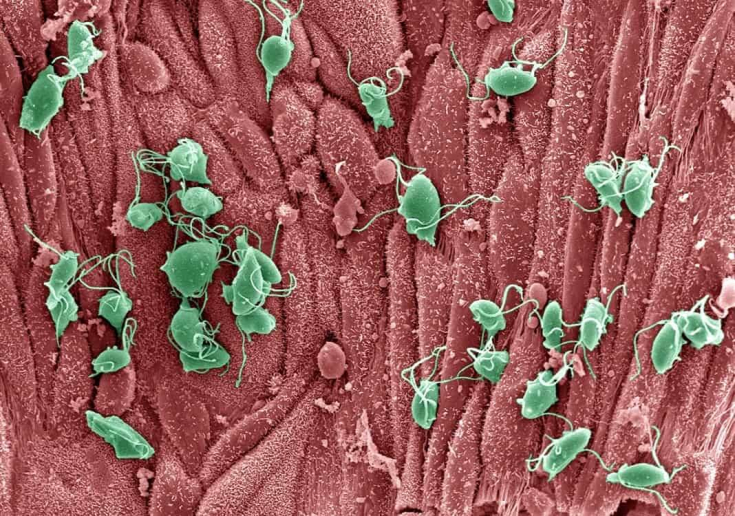
Undiagnosed Trichomonas often results in failure to treat gynecological infections, and is perceived as a reinfection.
Morphological studies have shown that 3-4 weeks after infection with trichomoniasis, the inflammatory process becomes chronic.
With the help of special research methods, 80% of cases of gynecological infections with chronic recurrent forms of inflammatory diseases of the internal genital organs were diagnosed with latent Trichomonas infection.
A feature of the persistence of Trichomonas is that they phagocytize and keep microorganisms alive.
There is a biological phenomenon: the ability of vaginal Trichomonas to capture and reserve various pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms. This phenomenon explains the occurrence of recurrences of gynecological infections even after massive antibacterial courses, but in the absence ofand antitrichomonas treatment.
Read more of our articles on Facebook !
Drugs for the treatment of gynecological infections caused by Trichomonas
The first step in the treatment of gynecological infections, especially mixed infections, is sanitation from trichomonas infection.
To do this, drugs widely known in medical practice trichopolum, tinidazole, metronidazole.
But, over several years of their use, genetic modeling of new strains of Trichomonas has occurred, which have developed protective mechanisms against antiprotozoal therapy. This prompted the search and development of new effective drugs.
A feature of new generation of ornidazoles is the presence of an active radical in them, due to which the drug penetrates into the cell by active and passive transport, selectively accumulating. Preparations from this group have an active radical with a chlorine atom.
Under the influence of nitroreductases of anaerobic microorganisms, which are absent in aerobes, the nitro group is renewed in the composition of the ornidazole molecule with the simultaneous appearance of free radicalsv.
Candidiasis (Thrush): Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment
What is the mechanism of action of effective antitrichomonas drugs
Ornidazole renewal products interact with microbial cell DNA and promote its degradation. Thus, the process of transcription and DNA replication is disturbed, which leads to the death of the microbial cell.
In addition, the reduced products of ornidazole and free radicals are toxic to the process of cellular respiration of anaerobes.
The course dose of drugs of this group for the treatment of gynecological infections should be prescribed taking into account the duration of the life cycle of Trichomonas, that is, at least 7-10 days. Mandatory is the simultaneous treatment of the sexual partner.
It is interesting that the quantitative and qualitative composition of the spermogram after such a course of treatment improves by 10-15%.
In second place in terms of prevalence and presence in microbial associations are chlamydia, mycoplasma and ureaplasma.
Therefore, among the drugs for the treatment of such gynecological infections, there should be a drug with a wide spectrum of antibacterial action. That is, active against chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, as well as against staphylococcus, Escherichia coli, pneumococcus, Proteus and other gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms.
At the end of treatment, it is necessary to carry out sanation of candida-mycosis infection and conduct antiviral therapy. However, this stage of treatment should be started after negative control of trichomoniasis, gonorrhea and chlamydial infection.
Trichomoniasis: symptoms, treatment, complications







Add a comment