Gonorrhea – an anthroponotic infectious disease caused by the Gram-negative diplococcus Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
Recently, there has been an increase in the incidence of gonorrhea, including in the environment of developed countries.
In 2018, strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were reported to be resistant to most antibiotics used in the treatment of the disease. This once again reminded doctors of the fraughtness of inappropriate prescription of antibacterial drugs and the urgency of the problem of antibiotic resistance in the world.
For more details about the clinical picture, laboratory diagnostics about the principles of treatment of gonorrhea read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Features of the etiological causative agent of gonorrhea - Neisseria gonorrhoeae
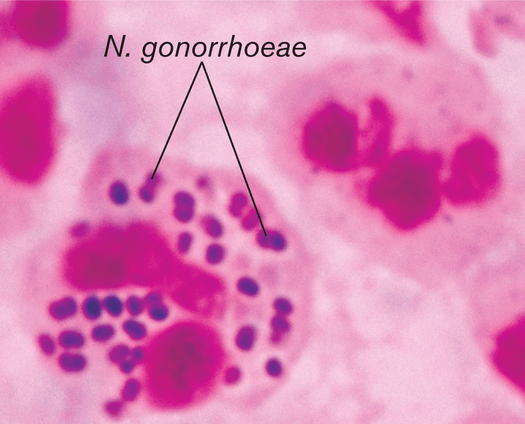
The etiological cause of gonorrhea is Neisseria gonorrhoeae – Gram-negative bacteria arranged in pairs and somewhat resembling coffee beans.
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted disease. Infection is possible both during classical sexual contact, and during anal and oral sex. In the latter case, the disease may resemble a sore throat.
There is an intrapartum mechanism of transmission of gonorrhea, leading to the development of blennorrhea in newborns. Today, blennorea has practically lost its relevance due to the active prevention of the disease in maternity hospitals.
Typical and atypical signs of syphilis: how to recognize the disease in time
Clinical symptoms of gonorrhea and possible complications of the disease
The clinical symptoms of gonorrhea develop 2-5 days after infection in men and slightly later in women.
In our time, the wide spread of erased and asymptomatic forms of gonorrhea is of great danger.
Manifest acute course of gonorrhea is characterized by the presence of purulent vaginal discharge, pain when urinating in women, symptoms of urethritis in men.
The infection tends to spread and affect the testicles, ureters, and bladder.
In many cases, gonorrhea is the cause of infertility.
Follow us on Facebook
Diagnosis of gonorrhea: polymerase chain reaction and culture
The most sensitive and specific method for diagnosing gonorrhea is PCR (polymerase chain reaction). The material for the study can be urine (first portion), as well as pathological discharge from the urethra, cervix, pharynx and rectum.
Given the widespread prevalence of mixed infection of chlamydial and gonococcal etiology, all patients with suspected gonorrhea are also recommended to undergo a specific diagnosis of chlamydia.
To determine the sensitivity of gonococci to antibacterial drugs, a culture test is an obligatory diagnostic method. Material sampling must be carried out before the appointment of empirical antibiotic therapy.
Chancre: causative agent, symptoms, treatment measures
Treatment of gonorrhea: international therapeutic guidelines
In accordance with international recommendations, the empiric antibiotic regimen for gonorrhea includes the appointment of a single intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone at a dose of 500 mg and oral azithromycin at a dose of 2g.
Treatment of gonorrhea consists of a single intramuscular injection of ceftriaxone 500mg and oral azithromycin 2g.
Complicated gonorrhea requires ceftriaxone at a dose of 1 g once a day, the duration of treatment is from 3 to 5 days.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae nucleic acid test should be repeated 3 weeks after treatment. It is important to treat both partners at the same time.
Treatment of gonorrhea with antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone group is not currently recommended due to the widespread prevalence of antibiotic-resistant strains of bacteria.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Infectology" section. You may also be interested in The invisible enemy: the subtleties of the treatment of chlamydia







Add a comment