Chlamydia – it is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. Basically, it manifests itself as urethritis in men and endocervicitis in women.
Most women with chlamydia are asymptomatic carriers, but this infection is dangerous due to ectopic pregnancy, infertility, salpingitis and endometritis. The same chlamydia increases the risk of cervical carcinoma.
of infected individuals is essential to prevent the uncontrolled spread of the disease. Read more about effective treatment methods on estet-portal.com in this article. The main difficulties in diagnosing and treating chlamydia
Chlamydia – These are intracellular parasites with powerful immunogenic properties. However, these pathogens are able to form L-forms, and for a long time remain out of sight of human immunity.
Intracellular localization of chlamydia is the reason for their high resistance to treatment.
The problem that doctors face in the fight against chlamydial infection is that 70-80% of women and up to 50% of men are asymptomatic carriers of the infection. As a result, a large number of infected people, unaware of chlamydia, continue to spread it.
Why Chlamydia is called a New Generation Disease Main features of the diagnosis of chlamydial infection
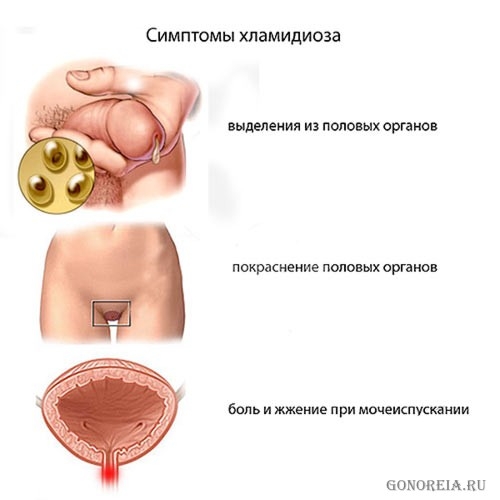
Clinically, chlamydia is most often asymptomatic. If the urethra is affected, there may be some pain during urination.
• cell culture method;
• direct fluorescent test;
• enzyme immunoassay;
• PCR.
Prophylactic testing for chlamydia is recommended for sexually active patients. This infection, in addition to its negative impact on the reproductive system, increases the risk of contracting other sexually transmitted diseases.
Read also:Chlamydia diagnostic methods: advantages and disadvantages The main details of effective treatment of chlamydia
Treatment for chlamydial infection depends on whether it is a first time infection or if it is a recurrence of the disease.
Uncomplicated infectionFor uncomplicated chlamydia, a single dose of azithromycin 1 g or doxycycline 100 mg twice a day for a week is prescribed.
For successful treatment of chlamydial infection, patients should avoid sexual intercourse for a week after starting therapy.
Oral ofloxacin or levofloxacin once a day, plus metronidazole if needed, for two weeks.
Most antibiotics are contraindicated during pregnancy. Azithromycin and amoxicillin are considered the safest treatments for chlamydia in pregnant women.
Chlamydia – it is an insidious infection prone to recurrence, so its treatment requires special attention from both the doctor and the patient.
Read the latest articles in







Add a comment