Laparoscopy is a modern and highly effective surgical method for performing diagnostic and surgical manipulations on the abdominal organs, with minimal incisions. In gynecology, laparoscopy is widely used for the purpose of diagnostic examination of the organs of the reproductive system, since in many pathological conditions non-invasive diagnostic methods do not provide sufficient information. Given the invasiveness of the procedure and possible complications, there are clear criteria for performing laparoscopy.
The essence and sequence of the laparoscopic intervention
Laparoscopy is performed as follows: several small incisions are made on the abdominal wall, through which special instruments for manipulation are inserted into the abdominal cavity.
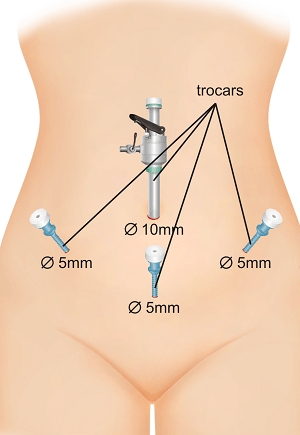 The manipulators are equipped with a clarification system, cameras and directly surgical micro-instruments. Air is pumped into the abdominal cavity to create a pneumoperitoneum, which greatly facilitates the procedure and improves visualization. During surgery, the image is displayed on the screen in front of the surgeon's eyes. The operation is performed under intravenous general anesthesia.
The manipulators are equipped with a clarification system, cameras and directly surgical micro-instruments. Air is pumped into the abdominal cavity to create a pneumoperitoneum, which greatly facilitates the procedure and improves visualization. During surgery, the image is displayed on the screen in front of the surgeon's eyes. The operation is performed under intravenous general anesthesia.
Indications for elective laparoscopic intervention
Elective laparoscopy is performed primarily for diagnostic purposes, bearing in mind that after diagnosis, surgical intervention for therapeutic purposes may be necessary. Elective laparoscopy is performed in such cases:
- tumors and neoplasms of the ovaries;
- abdominal pain of unknown etiology;
- tubal infertility;
- uterine fibroids;
- prolapse and prolapse of the internal genital organs;
- stress urinary incontinence;
- anomalies of the internal genital organs;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- sterilization.
Indications for emergency laparoscopic intervention
Emergency laparoscopy is performed in the case of an urgent condition that has arisen in a patient in which an accurate diagnosis has not been established. Laparoscopy in this case is performed to clarify the diagnosis and immediate surgical intervention. Indications for emergency laparoscopy are as follows:
- ovarian apoplexy;
- acute inflammatory processes of the uterine appendages;
- ectopic pregnancy;
- suspicion of rupture or torsion of the stem of the neoplasm;
- torsion of the stalk of subserous fibroids.
Absolute and relative contraindications for laparoscopy
Given that laparoscopy is an invasive surgical intervention, there are certain contraindications to its performance.
Absolute contraindications for laparoscopy
- decompensated diseases of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems;
- hemorrhagic shock;
- coagulopathy that cannot be corrected;
- liver failure;
- ovarian and fallopian tube cancer (operation performed only with laparotomy).
Relative contraindications for laparoscopy
- presence of confirmed diffuse peritonitis;
- adhesions of the abdominal cavity and small pelvis;
- polyvalent allergy;
- gestational age more than 16 weeks;
- large uterine fibroids;
- ovarian tumor with a diameter of more than 14 cm;
- suspicion of a malignant process of the uterine appendages.

Possible complications during laparoscopic surgery
Complications during and after a surgical intervention such as laparoscopy is directly related to the qualifications and experience of the endoscopist surgeon performing it. Before performing laparoscopy, it is necessary to make sure that there are no absolute and relative contraindications to the procedure, that the patient responds adequately to the medications used during anesthesia, and that all possible risks must be taken into account. The most dangerous complications after laparoscopy can be perforation of the abdominal organs, gas embolism, traumatic damage to the vessels and organs of the gastrointestinal tract and organs of the urinary system, which can lead to peritonitis, as well as emphysema of the omentum and mediastinum.






Add a comment