The Primary Care Dermatology Society − PCDC, UK, has revised clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis.
The development of modern technologies and research methods require continuous improvement of current treatment regimens for atopic dermatitis.Find out in the article on estet-portal.com
leading recommendations in the diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis.
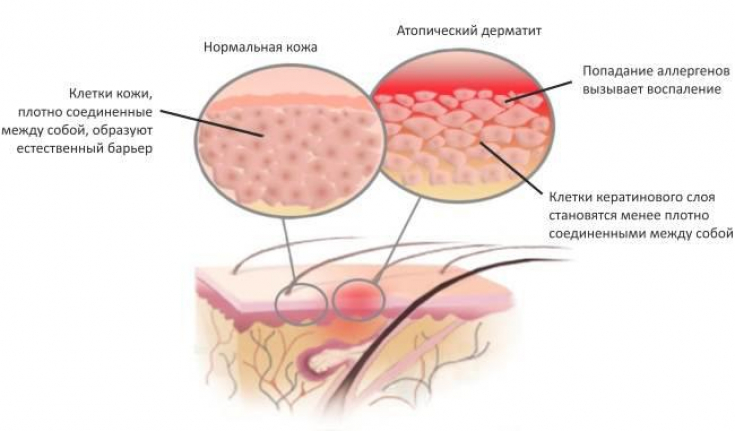
Etiology of atopic dermatitisAtopic dermatitis − an inflammatory skin disease that is histologically characterized by spongy changes with varying degrees of acanthosis and superficial perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrates.
Follow us on Instagram!
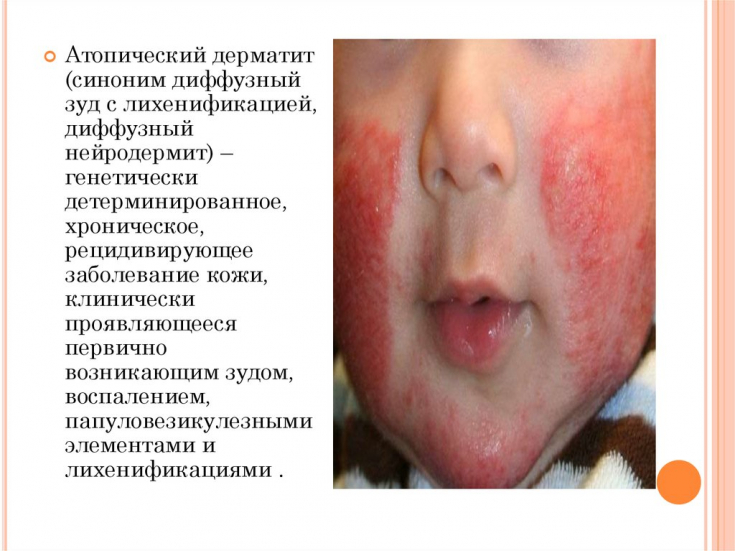
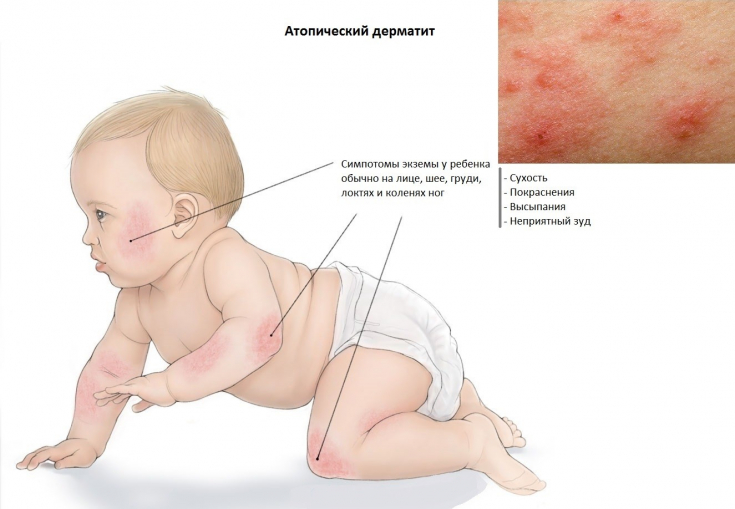
Clinical signs may include itching, flushing, scaling, and clusters of papulovesicles. The condition can be caused by the action of individual or a combination of the influence of external or internal factors. The terms "eczema" and "dermatitis" are considered synonyms.
Methods for preventing atopic dermatitis in children
The development of atopic dermatitis is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Typically, atopic dermatitis occurs in individuals with an “atopic predisposition,” which means that they may develop any or each of the three interrelated conditions & minus; atopic dermatitis, bronchial asthma and hay fever (allergic rhinitis). Often, such diseases are detected in individuals with a burdened family history.
The relevance of this finding is to confirm the importance of the regular use of emollients in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Factors to be minimized in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
Spontaneous manifestation of the manifestations of the disease may be the result of the influence of certain triggers, among which:
1. application of soap and detergents;
2. overheating combined with coarse clothing;
3. skin infections;
4. animal hair & saliva − symptoms that usually disappear when the person spends time in a different environment for a few days;
5. aeroallergens (pollen) − reactions to airborne allergens can cause symptoms to worsen in early spring or summer in sensitized individuals and are most commonly seen in older children and adults;
6. food − more common in newborns and young children;
7. house dust mites − sensitized patients report worsening symptoms of facial eczema after sleep;
Discoveries in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis
Although atopic dermatitis is most often seen for the first time in children, onset can occur at any age. In particular, 1/3 of new cases of atopic dermatitis are registered in adults. It has been established that about 65% of children with preliminary manifestations of atopic dermatitis observe their regression at the age of 7 years, and 74% of children − until they reach the age of 16.
Approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of atopic dermatitis
The clinical manifestations of eczematous lesions are varied, which is associated with the addition or absence of infectious factors, the age of the patient, ethnic origin, and the type of treatment for atopic dermatitis. These changes include: the localization of the lesions changes with age, the localization of the atopic process with lesions of the skin of the face is typical for children, the involvement of the flexor articular surfaces is typical, in some patients the lesions spread over time, which is important to consider in the treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Specific immunotherapy makes it possible to forget about atopic dermatitis
The main approaches in the treatment of atopic dermatitis:
1) The complex use of skin emollients involves the rational use of moisturizers and soap substitutes.
2) GCS-based creams or ointments should be applied in a thin layer to the affected areas of hyperemic skin.
3) "Weekend steroid regimen" − for patients with frequent exacerbations of the process, steroid creams or ointments are prescribed for 2 days a week for exacerbation of the manifestations of eczema.
4) Creams or ointments containing immunomodulators should be used on areas of thin skin (for example, on the face) in conditions of intensive use of creams based on steroid drugs.
Filaggrin gene mutations as a cause of atopic dermatitis









Add a comment