Implantation in human tissue of products made of artificial materials (implants) is one of the topical issues of modern dentistry. This technique was first applied about 6 thousand years ago, when, according to archeology, precious metals, mainly gold, platinum and silver, were first used for implantation.
At the beginning of the 20th century, cobalt and molybdenum alloys were replaced. In its modern form, dental implantation was introduced by the Swedish scientist P.I. Brenemark, who in 1952 described the phenomenon of long-term presence of a foreign body in the jawbone and called this phenomenon "osseointegration"; (integration into the bone tissue of a titanium implant), which is still used in dentistry.
Read in this article on estet-portal.com what progressive techniques are used in modern dentistry for dental implantation.
Metals for dental implants
Aluminium, titanium, zirconium and other materials can be used for implantation. Titanium (Ti) and its alloys have good mechanical and anti-corrosion properties, biological compatibility, due to which they are actively used in modern dentistry as a material for dental implantation. Under the action of the environment, a thin, dense protective biologically inert oxidative layer (mainly TiO2) is instantly formed on the Ti surface.
Follow us on Instagram!
This explains the good anti-corrosion and biocompatible properties. When Ti implants are introduced into human tissues, the tissues come into contact with the titanium oxidizing layer on the metal surface, so the biocompatibility of titanium implants depends on the properties of this outer oxidizing layer, such as microstructure and chemical composition. Although titanium is widely used in dentistry for implantation, however, problems remain: the protective film of TiO2 dioxide on the metal surface can be destroyed by fluorine ions; Patients may experience allergic reactions and discoloration of the fabric at the points of contact with the titanium surface.
Some unsuccessful cases of dental implantation are related precisely to the characteristics of the surface of the implant.
Processing of materials for implantation
Therefore, appropriate surface treatment of the latter can play an important role in obtaining an effective dental implant system, especially when the implant is loaded into bone, which has histological disadvantages and certain risks in surgical dentistry.
In an attempt to improve the reactions between biological tissue and the implant, various techniques are used, for example, increasing the adhesion surface of the tissue to the surface of the implant. In particular, to improve the response of cells to an implant, methods are used to treat the surface of titanium implants and modify its relief.
Pulpless tooth: 5 rules for caring for a tooth without a nerve
Applying an appropriate porous structure to the surface of a titanium implant, in terms of biocompatibility, is a major issue in dentistry, so many researchers have studied the creation of appropriate pores on the surface of a titanium implant in order to achieve a better biological response to it.
One approach has been to immerse the titanium in an alkaline solution at 60°C for 24 hours, followed by heat treatment at 600°C. C for 1 hour. This procedure creates a layer of sodium titanate on the surface of the porous titanium. Sodium titanate induces the formation of bone-like apatite, which is formed in bone tissue.

This method allows for the formation of a surface layer of biologically active micropores on the titanium substrate for implantation. Later, titanium pores in implants were created by the electrochemical method, formed by delicately formed and strictly organized TiO2 nanotubes on the surface of titanium in a fluorine solution.
Subsequently, under artificial conditions of cellular compatibility, it was proved that much more accumulations of fibroblast cells are collected on the nanostructured titanium surface.
The main directions of modern implantation in dentistry
Based on the foregoing, we can conclude that an important direction is the creation and improvement of the surface of the intraosseous part of dental implants of a new generation, which must meet a number of requirements: increasing biochemical and biomechanical compatibility with body tissues, improving functional characteristics, using energy-saving and environmentally friendly technological processes in production.
Research is underway on biological processes in bone tissue in order to use certain materials with unique properties to target the processes of reparative osteogenesis.
Why do you need dental floss: rules of use
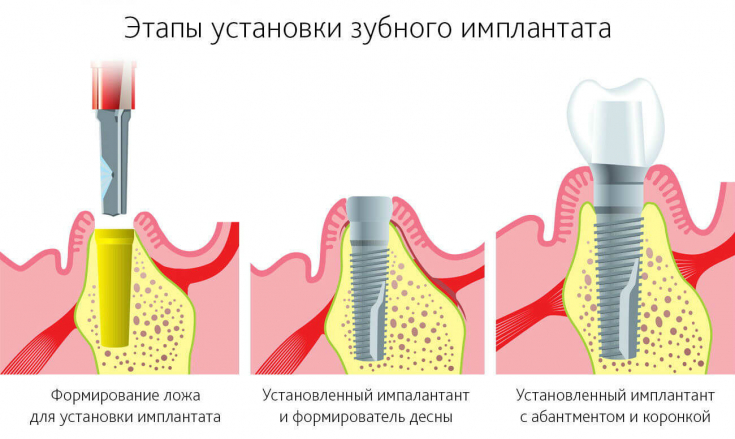
External beauty is a natural gift that a person tries to keep as long as possible, throughout his life. Unfortunately, there are congenital and acquired defects of the maxillofacial area, other congenital malformations that lead to a significant deterioration in the aesthetics of appearance. Congenital functional and anatomically significant defects are corrected in early childhood and usually do not leave significant aesthetic defects. And acquired disorders always bring a person internal discomfort. Modern dental implantation is developing quite progressively and helps people regain both external beauty and internal comfort.
The biggest mistakes in dental care







Add a comment