Acne (acne vulgaris) − a chronic inflammatory skin disease that occurs as a result of inflammation and blockage of the sebaceous glands and is characterized by the development of acne, mainly on the skin of the face, back and chest. Acne treatment should be aimed at correcting the factors that cause the development of acne: increased proliferation of follicular keratinocytes, hyperproduction of sebum, the presence of the microorganism Cutibacterium acnes (formerly known as Propionibacterium acnes) and combating the inflammatory process.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com modern recommendations, treatment regimens and features of drugs for topical acne therapy.
- Modern approaches to acne treatment
- Topical acne treatment: topical retinoids
- Antibacterial drugs for topical treatment of acnee
Modern approaches to acne treatment
According to current international guidelines, the use of a combination of topical retinoids and antimicrobial therapy should be considered in all patients with acne as first-line treatment for acne. It is the combination of drugs, and not monotherapy, that is effective due to the implementation of complementary mechanisms of action of drugs aimed at various pathogenic factors.
Follow us on Instagram!
In particular, retinoids reduce abnormal desquamation, have comedonolytic and anti-inflammatory properties. At the same time, benzoyl peroxide has antimicrobial activity and to some extent − keratolytic action, while antibiotics − anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effect.
Investigation of the role of the leading causes of acne in the development of the diseasei
Topical acne treatment: topical retinoids
Topical retonoids − comedolytic agents with anti-inflammatory effect, normalizing follicular hyperproliferation and hyperkeratinization. These preparations reduce the number of microcomedones and comedones. Topical retinoids for acne treatment should be started as first line therapy and continued as maintenance treatment to suppress further comedone formation.
The most commonly used topical retinoids for acne are adapalene, tazarotene, and tretinoin.
Topical retinoids are used once a day (at bedtime) and applied to clean, dry skin. The use of topical retinoids may be accompanied by irritation (flaking, redness) of the skin, but these phenomena usually disappear within a few weeks. Moisturizing creams can be used to reduce skin irritation and the interval between topical retinoid applications can be extended.
Modern approaches to acne treatment
The use of topical retinoids leads to a decrease in the thickness of the stratum corneum and is therefore associated with the development of photosensitivity. It is important to inform patients about the need for photoprotection, in particular the use of sunscreenc.
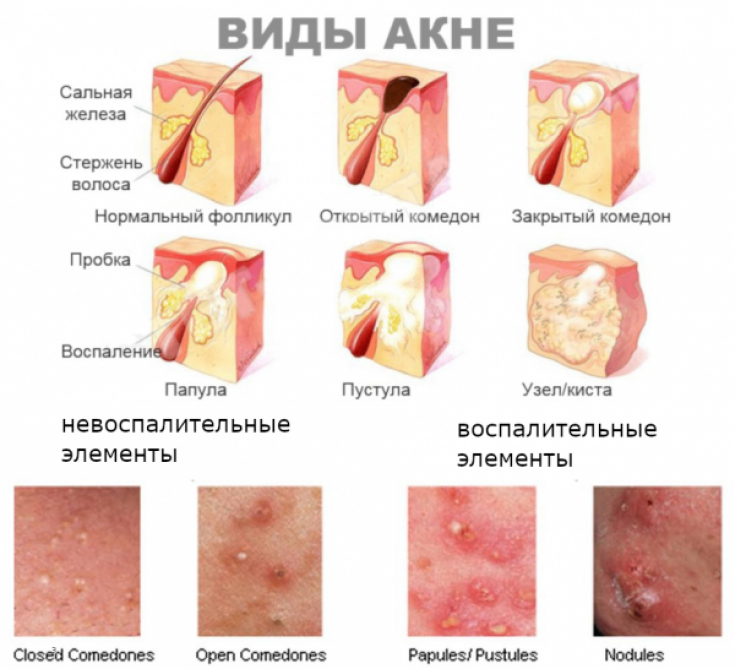
Antibacterial drugs for topical acne treatment
The use of topical antibacterial drugs for the treatment of acne aims to eradicate Cutibacterium acnes. These drugs also cause an anti-inflammatory effect, but are not comedolytic. Bacterial resistance may develop to any of the antibacterial agents. The most commonly used drugs for acne are clindamycin, erythromycin and, more recently, − dapsone. Clindamycin (1% gel, foam, lotion or solution) and erythromycin (2% solution) are applied twice a day.
Antibacterial therapy for acne: to be or not to be
Dapson for topical treatment of acne − a new sulfonic antibacterial drug with anti-inflammatory properties that has been shown to be effective in mild to moderate acne. The drug is well tolerated, side effects are usually represented by local tingling, redness and dryness of the skin. Unlike clindamycin and erythromycin, dapsone 7.5% gel must be applied to the skin once a day, which contributes to the formation of higher compliance. Dapsone is also available in the form of a 5% gel that must be applied twice a day, however both forms of the drug have shown efficacy and safety separately in different studies.

Formation of antibiotic resistance Cutibacterium acnes − frequent occurrence, which greatly complicates therapy. The addition of benzoyl peroxide to the local treatment regimen reduces the risk of developing antibiotic resistance. The simultaneous use of systemic and local antibiotics, as well as antibiotic monotherapy, should be avoided. In case of recurrence of acne, it is necessary to use the antibacterial drug that was effective before. It may also be useful in the treatment of acne, the use of benzoyl peroxide for 5-7 days between courses of antibiotic therapy.
Approaches to the treatment of severe acne
Cutibacterium acnes resistance to benzoyl peroxide has not yet been reported. The drug exists in various forms, including as soap, lotion, cream, and gel. Means containing benzoyl peroxide are used 1-2 times a day. In some cases, the use of benzoyl peroxide can lead to the development of contact dermatitis, especially when the drug is used in conjunction with tretinoin.
Acne pathogenesis depending on the age period of the patient







Add a comment