Using systemic retinoid therapy for the treatment of acne in patients with severe forms, we are increasingly convinced that in recent years, significant, almost revolutionary changes have occurred in the treatment of this chronic dermatosis, which allow achieving a therapeutic effect in those individuals young people who despaired of the possibility of getting rid of this disease.
For how to use the modern arsenal of drugs for the effective treatment of acne, read on estet-portal.com
- Approaches to the treatment of severe acne
- Acne treatment tactics depending on severity of the disease
Approaches to the treatment of severe acne
The problem of severe forms of acne, which include both conglobate and fulminant acne, requires special attention. Severe forms, leading to severe cosmetic deficiencies in the form of hypo- and hypertrophic scars, account for 5-15% of all cases of acne.
Follow us on Instagram! Fulminant acne
is a severe ulcerative form of the disease with an acute onset and the presence of systemic symptoms, which is mainly observed in young men aged 13-16. For the first time this form is described by RE Burns, JM Colville (1959) as conglobate acne with septicemia. PA Kelly, RE Burns proposed the term "acute febrile ulcerative acne conglobate with polyarthralgia", characterizing such signs as acute onset, severe lesions with cyst formation, fever, polyarthralgia, inadequate response to conventional antibiotic therapy. G. Plewig, AM Kligman (1975) separated this disease from acne conglobata and proposed the term "acne fulminans".
The etiology of fulminant acne
remains unknown, but infectious, genetic, and immunological factors are suspected. Already the first clinical signs include the presence of inflammatory and hemorrhagic painful areas on the face, upper back and chest. The following symptoms may also join: fever, weakness, musculoskeletal pain.
Previously, these patients had typical moderate acne during 1 year of illness. This highlights the need for sound acne treatment to prevent
severe complications.
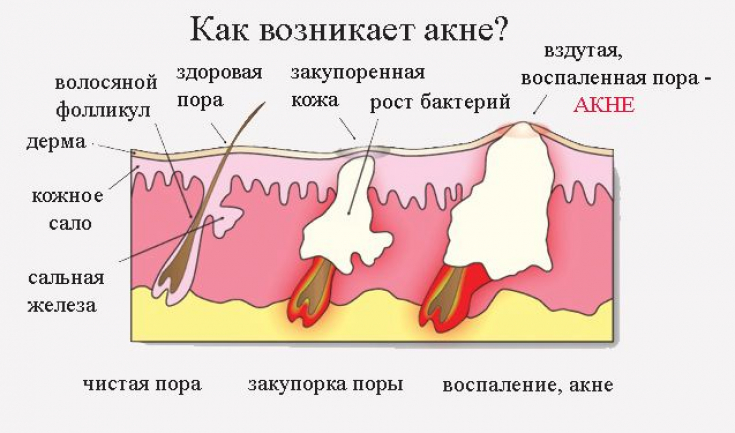
The choice of a specific acne treatment strategy is influenced by: the age and sex of the patient, the severity of clinical manifestations, the presence of concomitant pathology:
1. For mild acne, only topical therapy (topical retinoids, antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs) is used in combination with basic care.
3. In severe forms of the disease, systemic retinoids (isotretinoin) are indicated for the treatment of acne. They are divided into natural (retinol, retinal, retinoic acid) and synthetic or aromatic (etretinate, acitretin, adapalene, tazarotene).
Isotretinoin
- the stereoisomer of transretinoic acid (tritenoin) differs significantly from its predecessor in a minimum number of side effects. The systemic use of isotretinoin over the past decades has allowed a significant impact on the treatment of acne, in particular, severe acne. Systemic isotretinoin is indicated for severe forms of nodular and fulminant acne,
Systemic isotretinoin,
, unlike topical, has a sebosuppressive effect in the treatment of acne. Such an effect of the drug has been proven in a number of works with histological confirmation of a decrease in the size of the sebaceous gland and inhibition of the proliferation of sebocytes in the excretory duct of the sebaceous-hair follicle. Such changes help to reduce the colonization of P. acnes against the background of the normalized functioning of the sebaceous glands, which significantly affects the effectiveness of acne treatment.
There is a known strong correlation between blood levels of vitamin A derivatives and immune system function. There are such immunomodulatory functions of retinol: participation in antibody formation; decrease in the immunosuppressive effect of glucocorticoid hormones; stimulation of cell populations in the reaction of blast transformation of lymphocytes; stimulation of phagocytic activity of macrophages; increase in lysosomal and complementary activity of blood plasma; stimulation of phagocytic activity of neutrophils.
If acne treatmentwith systemic isotretinoin is successful, it is not rational to use antibiotic therapy. It should be remembered that it is impossible to combine systemic and topical acne treatment with retinoids. Isotretinoin should be used with monthly measurements of liver enzymes, cholesterol, triglycerides, alkaline phosphatase, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase. In the event of a tendency for biochemical parameters to increase, the dose of isotretinoin is reduced.
When evaluating the results of therapy, it must be remembered that often the effect of the drug continues even after discontinuation of treatment. In this regard, a second course should be prescribed no earlier than 8 weeks later. In most cases, one course is enough to treat acne.<
Watch us on YouTube:







Add a comment