Skin itch − a frequent symptom of many diseases in medical practice. According to population studies, one in five in the general population has experienced chronic pruritus at least once in their lifetime. A clinically proven symptom of itchy skin is diagnosed within a year in 7% of the population.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com about dermatological and non-dermatological causes of itching skin, as well as modern approaches to the diagnosis and treatment of this pathology.
- Prevalence and causes of itchy skin
- Basic approaches to the treatment of itchy skin
- Clinical picture of itchy skin
- Modern clinical classification of skin pruritusand
Prevalence and causes of itchy skin
The prevalence of such a symptom as itching of the skin varies significantly and is primarily due to the underlying pathology, accounting for approximately 25% among patients on hemodialysis, and 100% − in patients with skin diseases such as urticaria or atopic dermatitis.
Follow us on Instagram!
Thus, itching of the skin by etiology can be a consequence of both a dermatological disease and a manifestation of another somatic disorder, while usually there are no pathological changes of the skin. Itching of the skin is a frequent companion of systemic diseases, pathologies of the nervous system or mental disorders, as well as a consequence of side effects of drugs.
International guidelines for topical acne treatment
The multimodality of the etiopathogenesis of skin pruritus as a clinical disorder requires a thorough and scrupulous approach to diagnostic measures, since the effectiveness of treatment depends on its quality. And most importantly, without finding out the main cause that prompted the development of chronic itching, all modern therapeutic measures can be useless and even harmfuland.
Basic approaches to the treatment of itchy skin
Today, the treatment algorithm in case of chronic itching of the skin provides for mandatory therapy aimed at the underlying disease, with an additional course of local treatment, namely: symptomatic use of antiallergic drugs, phototherapy using ultraviolet skin irradiation and systemic treatment to relieve itching. Treatment in the presence of chronic itching should be persistent, provide multifactorial influence with the possible step-by-step achievement of improvement in the general condition of the patient, thus requiring a mandatory interdisciplinary approacha.
Updated guidelines for the treatment of moderate to severe psoriasis
Clinical picture of skin itching
Clinically, itching of the skin is accompanied by a sensation that provokes a mechanical effect on the skin. Depending on the duration, itching of the skin can be acute and chronic. According to the IFSI (International Forum for Pruritus Research) definition, chronic is skin itching that continues ≥ 6 weeks. This provision should make it easier for the doctor to determine the state of the course of the disease and choose the direction of the diagnostic search to identify the etiological factor of the diseaseI.
In some cases, itching of the skin may precede the development of the underlying disease for years and be almost the only complaint, in others − may be an early manifestation of a neoplastic disease such as Hodgkin's lymphoma.
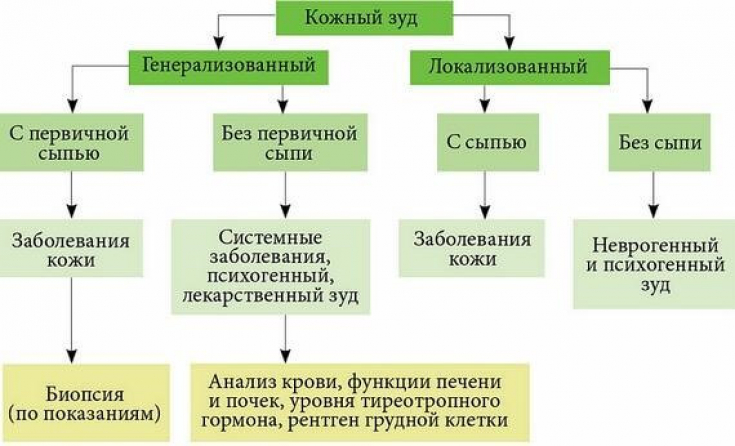
Modern clinical classification of skin pruritus
It is noted that the term "skin pruritus of unknown etiology or origin" should be avoided, as well as most clinically defined conditions that are accompanied by pruritus and are defined as "associated pruritus", which is also not rational for use. Instead, IFSI offers this clinical classification:

Morpho-etiological classification of chronic itching of the skin:
1 Group - patients with primary skin lesions (inflamed skin);
2 Group - patients with the status "normal" or healthy skin;
3 Group - patients with secondary chronic skin lesions.
According to etiology, they are distinguished:
- skin itching in dermatological diseases;
- skin itching in neurological pathology;
- itching in systemic diseases;
- itching of somatoform and mixed origin.
A revolutionary multifunctional treatment for all types of wounds at all stages of healing
Chronic itching of the skin can occur as a common symptom in patients with dermatosis with primary skin lesions on the background of systemic diseases, as well as in neurological and mental / psychosomatic diseases without initial skin lesions. In the last three cases, the skin may appear normal or may be caused by minor lesions. Prolonged underlying disease with a chronic course can lead to the development of a state of chronic itching with the formation of a chronic focus in the skin. In such cases, a thorough search for the cause of itchy skin is necessary.

In a multivariate analysis of the causes that are likely to cause the development of chronic skin pruritus, the following factors were identified:
- eczema;
- dry skin;
- asthma;
- liver disease;
- overweight;
- alarm condition.
Despite the paucity of comprehensive data on the prevalence of chronic pruritus in the population, it can still be argued that about 8-9% of the population noted prolonged pruritus, which was the dominant symptom in all age groups. About 60% of older people (> 65 years) complain of lung symptoms, and sometimes > and a severe bout of itching of the skin for a week.
Skin acidity speaks volumes: the importance of pH







Add a comment