Reversible contraception long-acting is a good choice for those who are planning a pregnancy, however, are not in a hurry with a joyful event. It provides reliable protection, while requiring virtually no hassle. These methods include intrauterine systems, birth control implants, and injections.
Choosing a contraceptive method is not always easy, however, having weighed all the pros and cons, the doctor will easily prescribe the most optimal method of protection against unwanted pregnancy for a particular patient. On estet-portal.com read more about the advantages and disadvantages of long-acting reversible contraception.
Contraceptive methods: mechanisms of action
Different types of birth control work differently.
Contraceptive methods can:
• prevent sperm from entering the egg;
• inactivate or damage spermatozoa;
• prevent ovulation;
• change the lining of the uterus so that the fertilized egg does not attach to it;
• thicken the cervical mucus so that sperm cannot easily pass through it.
Today, there are a huge number of methods of contraception. The selection of the most optimal means of protection is carried out by a doctor, depending on the needs and individual characteristics of the patient.
Reversible long-acting contraception is one of the most convenient and reliable methods of protection against unwanted pregnancy.
Long-acting reversible contraception includes hormonal and non-hormonal intrauterine systems, contraceptive implants, and injections. In addition to being effective and easy to use, long-acting reversible contraception also provides a quick return to fertility, especially when it comes to IUDs or contraceptive implants.
On the brink of fantasy: the contraception of our future
Contraceptive implants: safe and effective
A contraceptive implant is a small, flexible plastic rod that a doctor places under the skin on the inside of your upper arm. It releases progestogen, makes the cervical mucus thicker, making it difficult for sperm to pass through the cervix. The implant also makes the lining of the uterus thinner, thereby reducing the risk of egg implantation.
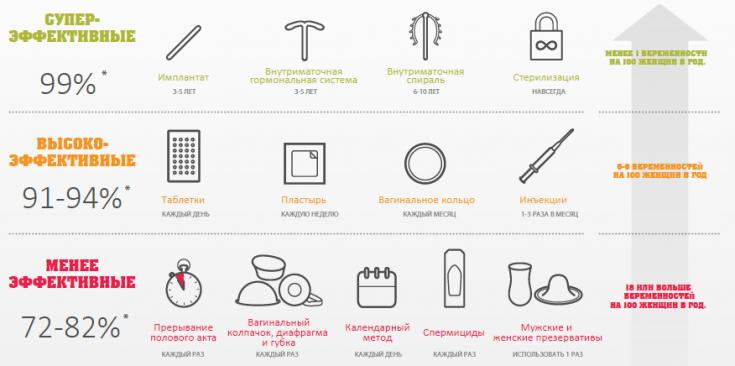
Implant is valid for 3 years. It can be removed at any time with rapid return of fertility.
Side effects of the contraceptive implant include amenorrhea and dysmenorrhea. Headaches, nausea, breast tenderness, and mood swings may also occur during the first few months after implant placement.
Read the latest articles in Telegram!
Contraceptive injections: advantages and disadvantages
The contraceptive effect of contraceptive injections is based on the release of progestogen.
This method of contraception is contraindicated if:
• unexplained bleeding;
• diseases of the cardiovascular system;
• liver diseases;
• risk of osteoporosis.
The duration of one injection lasts an average of 8 to 13 weeks, depending on the drug. Recovery of reproductive function after the withdrawal of injectable contraceptives may require about 1 year.
Female condoms, diaphragms and other methods of contraception
Pros and cons of intrauterine systems

Intrauterine systems (IUDs) are small, T-shaped plastic devices that are inserted into the uterus.
Hormonal IUDs release the hormone progestogen, while metal-containing or non-hormonal IUDs, when oxidized, create unfavorable conditions for egg implantation.
Installation of the coil takes no more than 5 minutes, while it is inserted through the cervix into the uterine cavity.
Hormonal IUD Benefits:
• work from 3 to 5 years;
• this is one of the best methods of contraception;
• quick restoration of fertility;
• The IUD does not affect weight or increase the risk of cancer.
Defects:
• periods may become irregular or stop completely;
• may cause headache, soreness of the mammary glands;
• may experience a slight decrease in libido;
• The IUD may be rejected (expelled) by the uterus or may be displaced.
Thus, reversible methods of long-term contraception are the optimal choice for the modern woman, as they provide long-term reliable protection, do not require regular use, and allow you to quickly restore fertility.
New era of contraception: transdermal patches







Add a comment