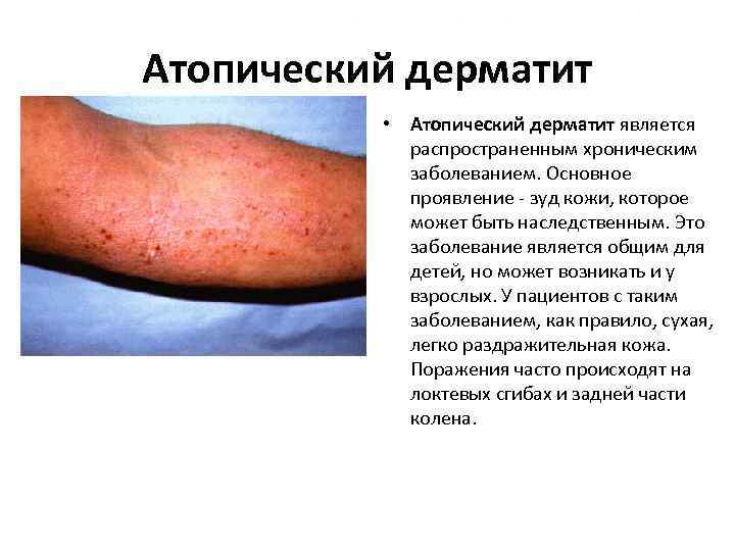
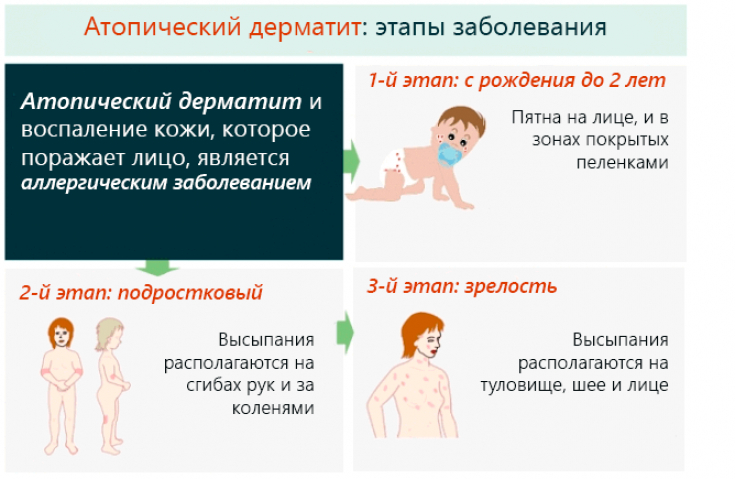
Despite significant advances in dermatologyand the treatment of atopic dermatitis is not an easy task.
There are significant difficulties in the case of primary diagnosis of the patient's condition, severe course of the eczematous process, partial effectiveness of the applied therapy, the development of steroid atrophy in the patient, or uncertainty about the advisability of prescribing a certain amount of local steroids or immunomodulators.
Find out in the article on estet-portal.com the recommendations of the Primary Dermatological Care Society for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, which significantly increase the effectiveness of therapy.
Initial treatment of atopic dermatitis during exacerbation
In children and adults, an intensive regimen of atopic dermatitis over several days is considered effective, compared with less effective treatments over a long period.
Follow us on Instagram!
To eliminate the exacerbation of the pathological process, the use of local steroid combined preparations based on betamethasone, as well as mometasone, is recommended for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. In case of severe sleep disturbances, a short use of a sedative antihistamine at night is recommended, for example, for adults − hydroxyzine 25-50 mg and for children − chlorpheniramine 5-15 mg.
It is recommended that swabs be taken from lesions in the outpatient treatment of atopic dermatitis.
Discoveries in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis
Long-term treatment of atopic dermatitis
Use of emollients − the basis of long-term treatment of atopic dermatitis, which reduces the burden of the use of corticosteroids. Use of Moisturizing Creams and Gels: The use of ointments, unlike gels and creams, generally reduces the likelihood of allergic contact dermatitis due to the absence of preservatives in their composition.
Prescribing order: If steroids and moisturizers are used simultaneously, the patient should be warned to apply moisturizers first, and only 15-20 minutes after that, apply a topical steroid preparation.
Topical steroids for the treatment of atopic dermatitis
It is recommended to use low doses and apply topical preparations only to areas of inflamed skin. It is also important to apply steroid medications 20 minutes after using moisturizers. Regular use of steroid-antibacterial combinations should be avoided to prevent the risk of developing antibiotic resistance.
The choice of a steroid drug for the treatment of atopic dermatitis is determined by the age of the patient, the localization of the lesion and the severity of the inflammation:
1. lesion of the face in a child, the average severity of the course of the disease − hydrocortisone 1%;
2. damage to the trunk and limbs in a child, the average severity of the disease − clobetasone butyrate 0.05% or betamethasone valerate 0.025%;
3. facial lesion in an adult, minimal or moderate severity of the course of the disease − clobetasone butyrate 0.05%;
4. damage to the trunk and limbs in an adult, severe − betamethasone valerate 0.1%, mometasone;
5. palms and soles, severe or extremely severe − clobetasol propionate 0.05%.
Methods for preventing atopic dermatitis in children
The correct use of local steroid preparations eliminates the risk of developing atrophic skin changes. However, special care should be taken when using these drugs in such localizations of skin lesions: periorbital areas (a regular regimen of topical corticosteroids should be avoided due to the risk of developing glaucoma); face (avoid regular use of topical corticosteroids); distal lower limbs in elderly patients and others at risk of developing ulcerative lesions (avoid regular use of topical corticosteroids).
Treatment of atopic dermatitis between exacerbations
In case of frequent exacerbations of the inflammatory process, it is necessary to consider the regimen of prescribing local corticosteroids combined preparations based on betamethasone or mometasone in a thin layer on the affected areas of the skin for 2 weeks. Then alternate days of application for another 2 weeks.
After the acute inflammatory process has resolved, switch the patient to a steroid regimen for 2 consecutive days (eg Saturday and Sunday) weekly on the affected skin. Treatment of atopic dermatitis should be continued even if there are no signs of skin inflammation. Target − reduction in the frequency of exacerbations of the process.
Specific immunotherapy makes it possible to forget about atopic dermatitis
In the absence of positive changes in the patient's condition, it is necessary to consider the possibility of developing allergic contact dermatitis, which can sometimes be caused by topical therapy. In this case, the reaction to topical preparations can be checked on small areas of unaffected skin, for example, on the outer surface of the arm, to monitor skin reactions.
If the result is positive − change treatment tactics. It should be noted that the topical steroid based on fluocinolone acetonide is highly likely to cause the development of contact allergic reactions.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis with immunomodulators
Topical immunomodulators tacrolimus and pimecrolimus are calcineurin inhibitors. Tacrolimus ointment 0.03% and pimecrolimus cream are licensed for patients ≥2 years of age. Tacrolimus ointment 0.1% is approved for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in patients 16 years of age.
Consideration should be given to the use of immunomodulators for the treatment of atopic dermatitis in the following cases: development of eczema of the skin of the eyelids and periorbital area; regular use of steroid drugs in areas of the face; regular use of steroid drugs in the areas of the legs in elderly patients and other individuals at risk of developing ulcerative complications; detection of any signs of the development of atrophy of the skin.
In mild cases, pimecrolimus cream is preferred, otherwise − ointment based on tacrolimus. Like topical steroids, immunomodulators are preferably used at night.









Add a comment