Sulfonylurea drugs have been used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes for a long time.
These are the most commonsecond-line drugs in the US, and their proportional share of all antidiabetic medicines has been stable over the years.
In our time, new classes ofantidiabetic drugs. are becoming increasingly popular.
Find out in the article onestet-portal.com which drugs and their combinations are most effective and safe for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
- Modern drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
- Clinical trials of drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
- European and American guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetes a
Inhibitors of sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter-2 (iNGCT-2) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (aGLP-1) agonists are gaining increasing popularity for the treatment of
type 2 diabetes, the benefits of which in patients with cardiovascular diseases are widely known.
Follow us on However, it should be understood that the treatment of type 2 diabetes should be based not only on the prevention of cardiovascular diseases and other complications, but also onglycemic control and diabetes compensation.
If a patient'sglycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels are above the target values, no innovative drugs will work properly.
It is HbA1c that is a powerful predictor of the development of both macrovascular and microvascular complications of diabetes mellitus.In particular, if HbA1c rises, the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke definitely increases.
In turn, a 1% decrease in HbA1c levels is accompanied by a 37% decrease in the risk of
microvascular complicationsth.
Foot ulcer in diabetes mellitus: rational antibiotic therapy
Clinical trials of drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetesThe problematic of this topic lies in the fact that almost all studies in which the benefits of
innovative antidiabetic drugs were reported were conducted in patients with HbA1c values close to normal.
That is, it must be understood that new classes of drugs have their cardioprotective effect only against the background ofcompensated type 2 diabetes with the help of "older" drugs. medicines.
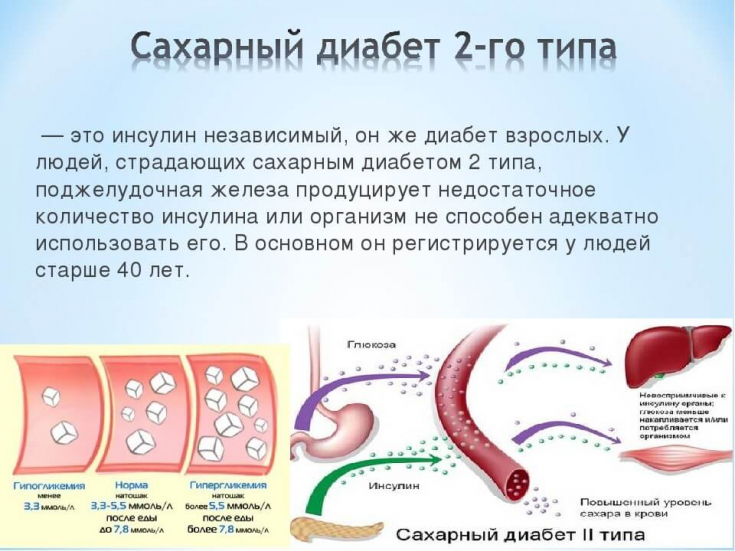
The patient should therefore be given medication that effectively
normalizes the level of HbA1c, and only then (or, if possible, simultaneously) − drugs that will prevent cardiovascular complicationsi.
Discovery of a specific immunotherapy for the treatment of type 1 diabetes. Part 2
European and American guidelines for the treatment of type 2 diabetesAccording to the
Consensus on Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes adopted by the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes, the goals of treating type 2 diabetes mellitus − prevent or delay complications and preserve the patient's quality of life.
This requires glycemic control and management of cardiovascular risk factors, regular follow-up and, importantly, a patient-centered approach to increase patient involvement in their own care.
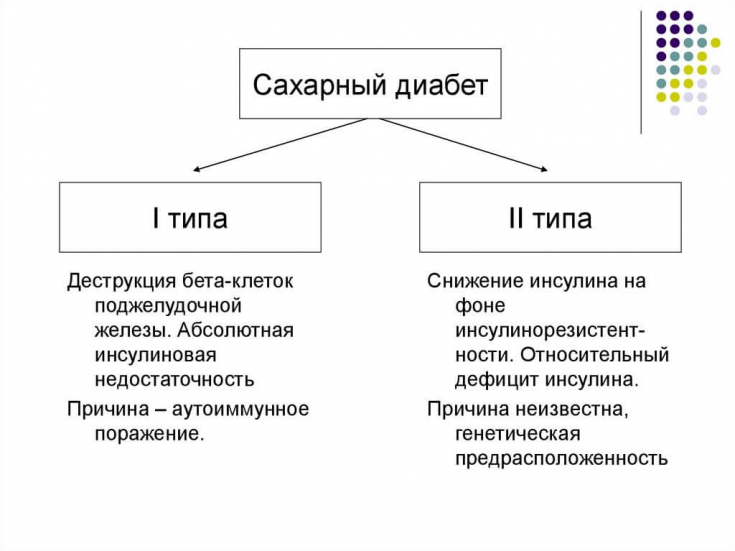
Sulfonylurea drugs are more effective in lowering HbA1c than dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (iDPP-4) and iNCTG-2 inhibitors.
So,PSS are characterized by high efficiency (reduce HbA1c by 1.0-2.0%), iDPP-4 - medium (by 0.5-1.5% ), and iNCTG-2 - medium / high efficiency, depending on the glomerular filtration rate.
It should be noted that this aspect does not discussmetformin, which is the base drug. We are talking about medicines that should be added to the intake of metformin.
The already mentioned American Diabetes Association and European Association for the Study of Diabetes consensus states that both NCTG-2 and GLP-1 agonists have demonstrated benefits in reducingthe risk of cardiovascular complications only for patients with cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the anamnesis, while in patients without CVD, these drugs did not show any benefit in lowering glucose levels.
Hyperglycemia and myocardial infarction: is there a link
Consensus recommends thatsulfonylureas be given to patients with no or low established risk of CVD (according to worldwide statistics, such patients represent about 20% of patients with type 2 diabetes) or for those for whom cost is a concern treatment.
Undoubtedly, the latter aspect is important for the vast majority of patients.In order to minimize the
risk of hypoglycaemia, it is recommended to choose third-generation sulfonylureas (gliclazide).







Add a comment