Dyskeratosis follicularis or Darier-White disease – an autosomal dominant genetic disease that manifests itself as abnormal keratinization of the epidermis, acantholysis, pathological changes in the nails.
The first symptoms appear in childhood or adolescence, in adulthood, a significant progression of the disease is characteristic. It occurs equally in men and women with a frequency of 1:40,000 of the population. There is evidence of an association of the disease with mental disorders, in particular with schizophrenia, epilepsy and bipolar disorders.
For more information about the typical manifestations of follicular dyskeratosis, as well as the treatment of this disease, read on estet-portal.com in this article.
Characteristic nail changes in Darya's dyskeratosis
Darieu-White dyskeratosis debuts with characteristic nail changes. Longitudinal lines of white (leukonychia), gray or red color appear on the nail plate. The distal part of the nail undergoes a V-shaped destruction with the formation of a defect up to the splitting of the nail in half.
Read more about how nail color helps to diagnose many diseases in time
These changes are the result of a mutation in the DNA segment (12g23-g24), which is responsible for the synthesis of the protein components of calcium pumps, which provide a strong connection between the cells of the nail plate and the epidermis.
The maturation of epidermal cells is disrupted. Representatives of the pathogenic flora enter the expanded intercellular spaces, infection develops, which aggravates the destruction of the nail, and contributes to infectious complications on the skin.
The pathology was described in 1889 by the French dermatologist J. Darier. It was a treatise on psorospermia, special microorganisms – lumps of protoplasm, which the researcher regarded as the cause of the disease.
Follow us on Telegram
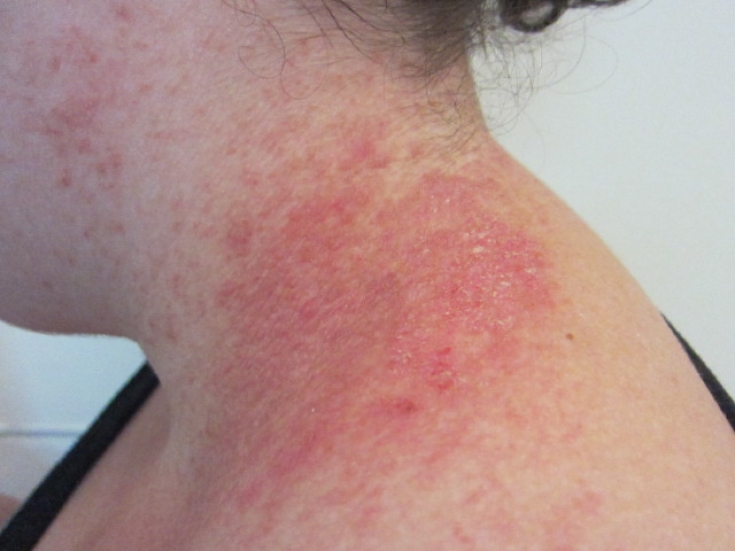
Skin changes in follicular dyskeratosis
In classic follicular dyskeratosis, which occurs in 90% of cases, skin manifestations begin with the formation of small papules 2-4 mm flesh or pinkish in color. They tend to merge, resulting in a brown hyperkeratosis plaque covered with greasy scales and crusts. The secondary element of the – pigmentation and erosion. Localization: chest, upper back, neck, head, armpits and groin.
Localized (linear) dyskeratosis – an abortive form of Darier's disease with linear foci of papules that turn into pigmentation and erosion.
Hypertrophic dyskeratosis is characterized by the appearance of nodules and papules resembling papillomas with a tendency to plaque formation. Localized on the back of the foot and hand. The palm and plantar surface of the foot is covered with punctate keratosis.
Vesicular bullous dyskeratosis is characterized by the formation of nodules that turn into vesicles prone to maceration. Similar elements of the rash can be found in large folds, on the mucous membranes.
Treatment of Darier-White's follicular dyskeratosis
An effective treatment for dyskeratosis is the use of retinol acetate at 200 IU/day. In the presence of a secondary infection, antibiotic therapy is necessary. In the case of a severe course of the disease, prednisolone is used at a dose of 30 mg / day for a week with gradual withdrawal. The use of systemic retinoids is limited due to the toxicity of the drug, but the acceptable dose is 10-20 mg / day for a week.
Risk factors for the development of Darier dyskeratosis are vitamin A deficiency, impaired metabolism of unsaturated fatty acids, and discoordination of the work of stimulants and protease inhibitors.
As a local therapy, fucorcin is used, preparations with keratolytic properties: salicylic ointment, cream with urea 3-10%. With a warty form, diathermocoagulation and surgical treatment are used.
Prognosis for Darier's follicular dyskeratosis
Thus, the diagnostic criteria for follicular dyskeratosis are: hyperkeratotic papules in seborrheic areas, wedge-shaped destruction of the nail plate, white and red longitudinal lines on the nails.
Darier-White disease occurs with constant periods of exacerbation and partial remissions. The prognosis for recovery is poor. To prolong remission, provoking factors should be avoided: insolation, exposure to high temperatures, factors that increase sweating. Modern methods of therapy can improve the condition of the skin and the quality of life of the patient.
Thank you for staying with estet-portal.com. Read other interesting articles in the "Dermatology" section. You may also be interested in Changes in the skin and its appendages in anhydrotic ectodermal dysplasia
British Association of Dermatologists







Add a comment