The skin is an important strategic barrier between the environment and internal homeostasis. However, it also undergoes damage and degeneration, showing signs of aging and reflecting the result of pathological processes. Melatonin is a neutralizer of active free radicals, with powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, maintains mitochondrial homeostasis, thereby slowing down aging. The biochemical action of melatonin at the level of the skin can provide an effective anti-aging strategy, as well as a therapeutic effect on vitiligo, atopic dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis.
- Melatonin as a skin protection factor against damage
- Melatonin in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
- Topical melatonin: results
Melatonin as a factor in protecting the skin from damage
Tissue regenerative potential decreases with age due to changes in stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Damage caused by oxidative stress and inflammation at the molecular level leads to a decrease in collagen production, while the epidermis becomes thinner and less resistant to external aggressors.
Read also: Slowdown of mitochondrial cell apoptosis
Follow us on Instagram!
Melatonin levels in skin cells are significantly higher than in plasma.
The melatonin molecule is able to pass through the lipid protective barrier of the skin, reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, influence mitochondrial functions and affect the expression of certain genes.
Melatonin in the treatment of atopic dermatitis
The course of atopic dermatitis is often accompanied by sleep disturbances and nighttime itching. It has been reported that increased nighttime melatonin levels may be associated with milder disease and less severe symptoms.
Melatonin contributes to the normalization of the level of C-reactive protein in blood plasma, as well as the level of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-4 and IFN-γ.
It has been found that melatonin given orally can influence the course of atopic dermatitis by decreasing nighttime wakefulness, reducing scratching and modulating certain parameters of the immune system. reductions in
Circadian rhythms: impact on the immune response Due to its
degradationwhen first passing through the liver, its access to the skin is limited. Thus, in clinical dermatology, topically melatonin should be applied to achieve the effect. In the course of the studies, it turned out that melatonin is able to accumulate
in the stratum corneumdue to the long-term release from the skin integuments into the circulatory system. Topical application of melatonin
One of the factors in the severity of the signs of aging is
estrogen deficiency:reduction in the thickness of the epidermis and dermis, a decrease in the production of collagen and elastin.
Read also:Melatonin as an anti-aging factor
According to animal studies, topical application of melatonin to the skin increased the thickness of the epidermis and also increased collagen and elastin production. An increase in fibroblast growth factor -.beta. (FGF-.beta.), collagen type I and fibronectin was observed.
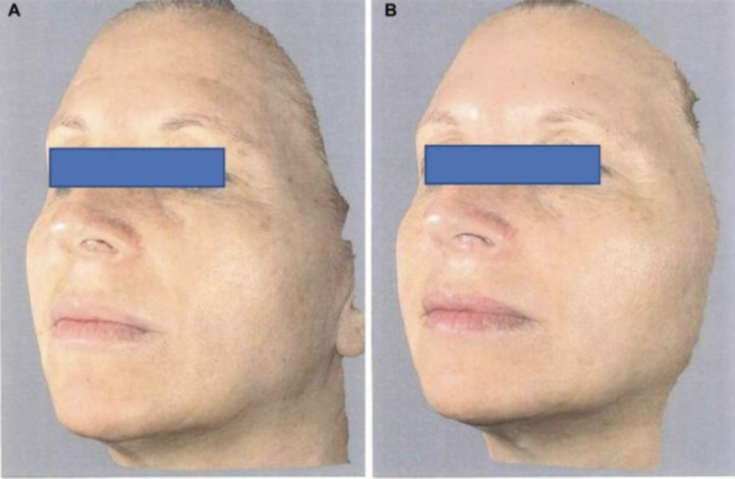
effectiveness of melatonin on the skin, researchers used day and night creams containing melatonin. As a result, these formulations improved hydration and toneof aged skin, and reduced creases and wrinkles compared to placebo control group. Topical application of melatonin can also be used to treat
alopecia. Melatonin in combination with nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) shows high capture efficiency and antioxidant potential in addition to sustained release. During the application of this complex in patients with adrogenetic alopecia hair loss decreased and their density and thickness increased.
Follow us on Trans-epidermalmelatonin delivery is an effective strategy to maintain health and protect skin from damage, to slow the aging process and reduce its clinical signs. At the mitochondrial level, melatonin is able to increase ATP production, regulate michondrial homeostasis, inhibit apoptosis, repair the epidermis and accelerate hair follicle growth. Topically applied melatonin is also considered a UV protection factor.
More interesting stuff on our







Add a comment