Xanthelasmas are localized accumulations of lipid deposits on the eyelids.
Lesions are usually asymptomatic and treatment is required more for cosmetic purposes.
Standard treatments include topical trichloroacetic acid, liquid nitrogen cryotherapy, and various lasers. Traditional surgical removal of xanthelasmas is also used.
The prevalence of the disease is 4%. Age of onset can range from 15 to 73 years.
In about half of the cases, the appearance of xanthelasma may be associated with hyperlipidemia.
On estet-portal.com read about the causes of these formations, and about effective methods of treating xanthelasma.
- The pathogenesis of xanthelasma is hyperlipidemia
- Systemic therapy for xanthelasma
- Topical xanthelas therapywe
The pathogenesis of xanthelasma is hyperlipidemia
Although the exact pathogenesis of xanthelasma is not fully understood, it is a deposition of fibroproliferative connective tissue associated with histiocytes that are loaded with lipids, also known as foam cells.
Thus, it becomes clear that conditions that are accompanied by hyperlipidemia can lead to the formation of xanthelasma palpebrarum, namely:
- pregnancy;
- obesity;
- diabetes mellitus;
- hypothyroidism;
- nephrotic syndrome;
- cholestasis;
- taking estrogens, tamoxifen, prednisolone, oral retinoids, cyclosporine and protease inhibitors.
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids present as soft, symmetrical, bilateral, yellow, thin, polygonal papules and plaques, usually in the periorbital region.
Other areas that may be affected include the neck, torso, shoulders, and armpits.
It is important to consider that the presence of xanthelasmas is a predictor of risk of myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, severe atherosclerosis, and death in the general population.
Xanthelasmas of the eyelids must be differentiated from:
- chalazion;
- sebaceous gland hyperplasia;
- syringomas, nodular basal cell carcinoma;
- necrobiotic xanthogranulomaoh.
The appearance of xanthoma may be due to excess cholesterol
Systemic therapy for xanthelasma
There are reports in the literature of successful treatment with oral probucol.
Probucol, as an antioxidant, is thought to act by potentially inhibiting atherogenesis by limiting the oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol required for foam cell formation.
Alirocumab, a monoclonal antibody that belongs to a new class of anticholesterol therapy, is primarily used to treat hypercholesterolemia.
However, there was evidence that the use of alirocumab was associated with regression of xanthelsm.
The appearance of xanthomas on the skin: a harmless symptom or a serious threat to the body
Topical xanthelasma therapy
Chemical trichloroacetic acid peel is a form of destructive therapy for xanthelasma. Applied topically in concentrations ranging from 50% to 100%.
The peel is applied in a circular fashion, making sure that the largest amount of TCA is at the edge of the lesion. The treated area is then neutralized with sodium bicarbonate.
The most effective in the treatment of xanthelasma was taken 70% concentration of trichloroacetic acid.
Liquid Nitrogen Cryotherapy – it is a simple and effective treatment option for xanthelasma.
The mechanism of action of cryotherapy is thought to be related to vasoconstriction and the formation of microthrombi caused by cryoinduced cell death. This leads to tissue ischemia and cell death.
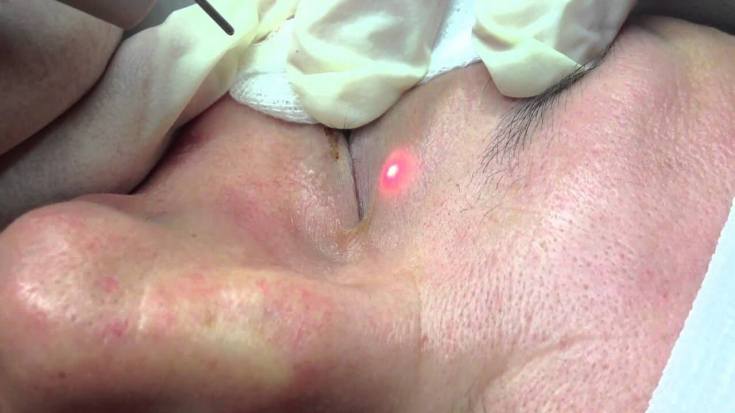
Radiofrequency and laser ablation are also considered effective treatments for xanthelasma.
In laser ablation, perivascular foam cells are destroyed by thermal energy damage and coagulate dermal vessels, blocking further lipid leakage into the tissue.
Classic blepharoplasty can be used to excise xanthelasma in a sequential stepwise approach.
Read the most interesting articles in Telegram!







Add a comment