Symmetrical symbol of beauty and youth – oval face – more than just a detail. Correction and rejuvenation of the facial contour with the help of surgical intervention or non-surgical methods – daily request of patients of aesthetic clinics.
To meet the expectations of the patient, the doctor must be well versed in the anatomy and physiology of the aging process, be fluent in the necessary techniques and keep abreast of new products in the aesthetic medicine market. Doctors Lakhdar Belhaouari, Pierre Quinodoz, Camille Belhaouari and Ignacio Garrido talk about injectable facial rejuvenation techniques using a system of dividing the face into vertical sectors.
Vertical division of the face: important anatomical and physiological factors
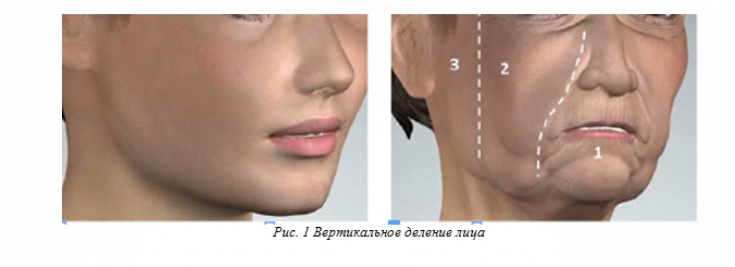
Traditionally, the cervicofacial region is divided into the upper, middle and lower thirds of the face. In this case, the upper part of the neck is often referred to as the lower third of the face. In the context of rejuvenation and correction of facial contours with the help of HA preparations, the authors present an approach based on the division of the face into three vertical parts (Fig. 1):
1. Central sector (proface).
2. Middle sector (mesoface).
3. Side sector (metaface).
The article focuses on the correction of the middle sector of the face, since it is this sector that is subject to gravitational ptosis and leads to deformation of the young face oval.
Follow us on Facebook!
Features of the middle sector of the face (mesoface)
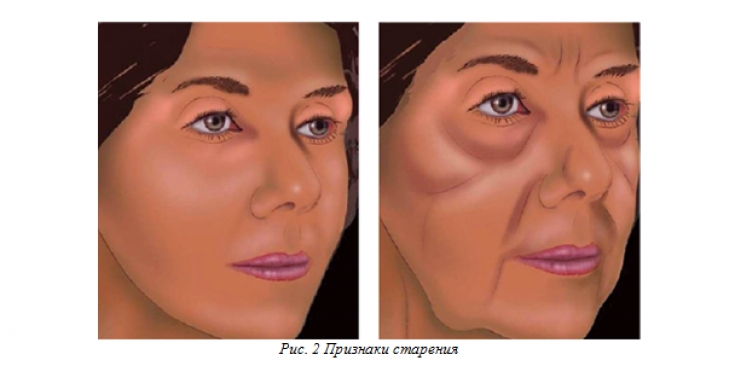
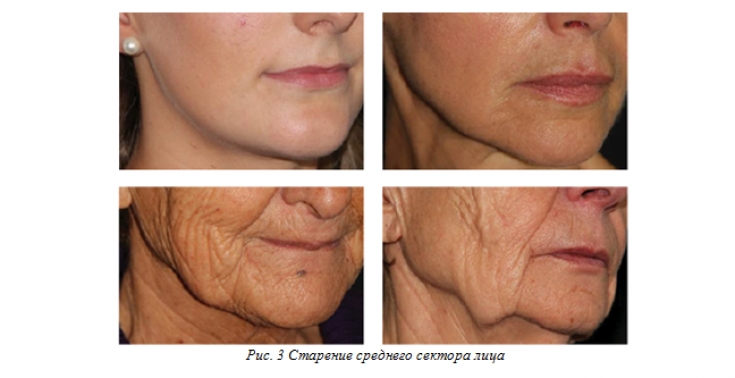
According to the authors, the division of the middle sector of the face into the middle and lower thirds is inappropriate, since they are interconnected. Age-related ptosis is observed throughout the entire vertical zone, therefore, in the context of correction, it is necessary to consider changes along the entire height of this sector (Fig. 3).
In the upper part of the midface, the main movable element is the orbicular muscle of the eye, which lifts the superficial zygomatic fat pack, while the deep fat pack remains immobile because it is attached to the underlying bone. Age-related sagging is observed exclusively in the mobile area, resulting in the formation of three main furrows in the middle part of the face:
1. Palpebromalar and nasolacrimal grooves.
2. Mid-buccal sulcus.
3. Nasolabial sulcus (Fig. 3).
In the lower third of the face, sagging of the oval is observed only in the middle sector. Uneven ptosis leads to the appearance of irregularities in the lower part of the face oval, "blurring" while its contours. The task of the esthetician – eliminate these changes.
Correction of the middle third of the face: what to choose - fillers, lifting or blepharoplasty
Features of the lateral sector of the face (metaface)
Due to anatomical features, the lateral sector of the face is not subject to ptosis. However, sagging in the middle sector creates a disproportion that breaks the contour line along the jawbone and leads to a deformity of the face oval.
The thickness of the masticatory muscle – about 3–8 mm. Its fibers pass from below and attach to the first 3-4 cm of the back of the horizontal branch of the jawbone (corner) – and 1 cm of the vertical ramus of the jawbone.
Deep injection of HA at the level of attachment of the masseter muscle to the horizontal ramus of the jaw does not involve a high risk of damage to nearby important structures. To do this, before the administration of the drug, it is necessary to ask the patient to clench his teeth, and then mark the anterior border of the masticatory muscle.
Superficial HA filler injection using a fan technique is also safe, provided that the drug is injected into the subcutaneous layer. Despite this, there is a risk of ecchymosis.
Features of the central sector of the face (proface)
The central sector of the face also covers the chin. Sagging tissues are not typical for the chin, in contrast to the cheek area. However, this zone is mobile due to the work of the chin muscle, as well as the muscles that lower the corner of the mouth and lower lip.
Since cheek ptosis is not accompanied by chin ptosis, the transition between them has the appearance of a depression in the premaxillary region. As a result, the oval of the face is deformed, its lower part becomes uneven.
There may be differences in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat between the chin and cheeks – in the cheek area, its thickness is greater than in the chin area. With sagging, this difference increases the severity of the premaxillary sulcus.
See also Instagram!
The role of the neck in facial deformity
The aging process also affects the neck: the skin loses elasticity due to a decrease in the number of collagen and elastin fibers. Following the ptosis of the lower zygomatic zone, sagging occurs in the neck. The skin, subcutaneous fatty tissue and subcutaneous muscle of the neck are involved in this process. As a result, the neck, cervico-chin angle and jaw line become "blurred". The young oval of the face and a clear cervico-chin angle are replaced by a double chin, flares and sagging skin in the front of the neck (“turkey neck”).
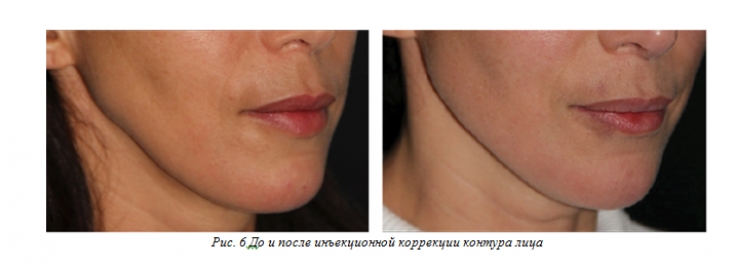
Injection restoration of the contour and lower part of the face oval
Today, the most popular technique for correcting the oval of the face is a surgical lift. Non-surgical technique – implantation of fillers, in particular hyaluronic acid, is also effective. The purpose of injections of fillers – smooth out discrepancies between the chin and cheeks. Hyaluronic acid, especially products with a volumizing effect, is considered the gold standard for the correction of this area.
When correcting the premaxillary sulcus, two main anatomical structures must be taken into account:
• facial artery, which runs behind the target zone and above, along the posterior edge of the muscle that depresses the angle of the mouth;
• mental nerve, which runs above the target area and more medially as it emerges from the mental foramen; it is important not to hit this nerve with a cannula or needle.
The purpose of HA injections – smooth or completely eliminate the irregularities of the contour, deformed due to ptosis of the central vertical sector of the face.
The authors' approach to correcting the oval of the face and premaxillary region is to use one or both techniques:
• deep HA injection at the jawbone margin to provide stable support;
• superficial administration of HA.
Deep HA injection technique for face oval correction
Drug properties:
• volumizing ability;
• cohesiveness;
• high elasticity (G’) for projection;
• moderate viscosity (G”) to avoid spreading.
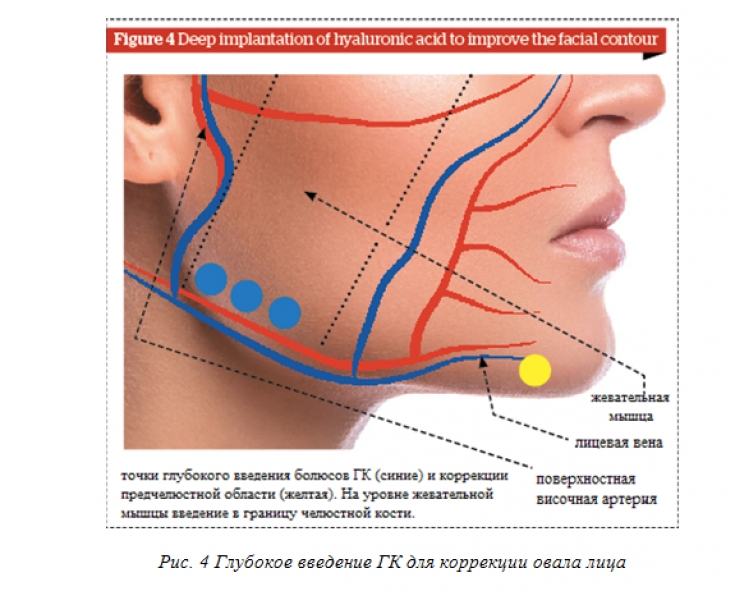
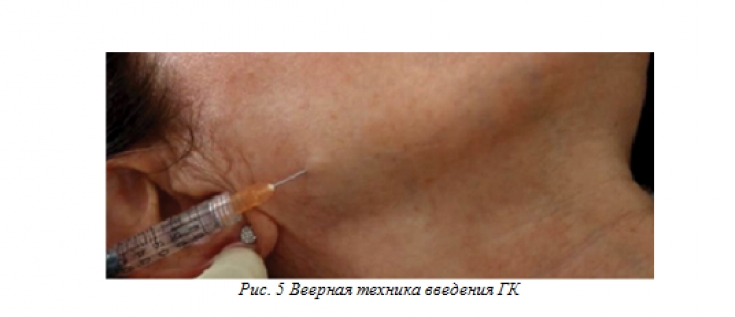
Running:
• ask the patient to clench their teeth and mark the posterior and anterior borders of the masticatory muscle;
• mark the angle of the maxillary bone (between its vertical and horizontal branches);
•
• inject 2 or 3 boluses (0.1-0.3 ml each) perpendicular to the thickened area of the muscle near its insertion (Fig. 4); aspiration must be performed before insertion to avoid vascular damage; thus the drug is injected deeply, slowly and in small amounts, averaging 0.2 ml per bolus;
• you can perform a light massage;
• The amount of product injected may vary and averages 0.6 ml per side.
This insertion carries little or no risk of damage to important structures. The facial vein runs in front of the anterior border of the masseter muscle. The mandibular branch of the facial nerve passes under the horizontal branch of the jawbone, it passes under the subcutaneous muscle of the neck, 1 or 2 cm below the jawbone. Only the parotid salivary gland is located near the posterior bolus, as it partially encloses the angle of the jawbone.
This deep and fixed implantation provides stable support. The function of the chewing muscle is not disturbed.
Follow us on Telegram!
In many cases, the deep insertion technique is sufficient to achieve satisfactory results in facial reshaping. If necessary, they can be improved by superficial injections.
Superficial injection of HA: fan technique for facial contouring
This technique may be sufficient to obtain a satisfactory result of facial contouring. However, authors often combine it with deep HA injections. The drug is administered subcutaneously, therefore it must be remembered that the subcutaneous tissue of the lateral sector of the face is relatively thin. Due to the superficial injection, there is no risk of damage to important structures, since they are located deeper than the subcutaneous muscle of the neck.
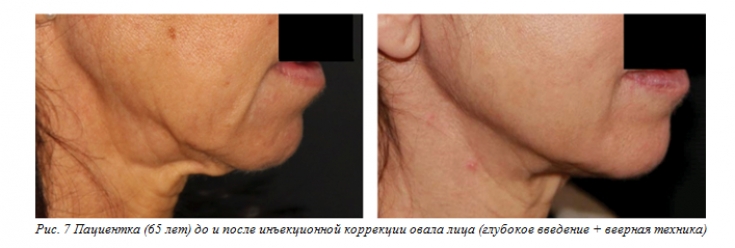
If the purpose of such an injection – to smooth out the differences between the lateral and middle sectors of the face, it must be performed in the posterior part of the jaw line. However, in order to restructure the entire lateral sector of the face (Fig. 7), the insertion area can be expanded towards the ear, beyond the chewing muscle, or anteriorly – to restore the entire oval. To improve trophism, hydration and radiance of the skin, you can work on the entire cheek area.
Drug properties:
• cohesiveness;
• moderate elasticity (G’);
• high modulus of viscosity (G”) for good distribution;
• short HA chains for better integration and penetration into tissues.
Running:
• mark the target area;
• evenly inject the drug subcutaneously, using a fan technique; the authors prefer to use a non-flexible 25 or 23 gauge cannula to reduce ecchymosis, stimulate fibroblasts, and improve skin trophism (skin booster effect); the authors do not use flexible cannulas, since in this case it is difficult to control the trajectory of the drug and increases the risk of implant displacement;
• inject the drug slowly and carefully, after which it is necessary to distribute it well over the marked area;
• to facilitate the penetration and integration of HA into the surrounding tissues, you can perform a light massage;
• The amount of product injected depends on the surface and the severity of the imperfection.
This technique provides immediate results, but comes with the risk of temporary ecchymosis. Improvement in trophism and hydration of the skin, provided by the rheological properties of the product, as well as stimulation of fibroblasts, is noticeable approximately 2 weeks after correction.
Restoration of the oval by smoothing out the differences between the middle and lateral sectors of the face, as well as restoration of the contour of the lower part of the oval of the face, by providing better support and skin tension, also provide a rejuvenating and lifting effect.
Skin texture improvement with superficial fan technique and skin boosting effect enhances the anti-aging effect.
Middle face correction and complications after injections
Premaxillary sulcus correction with HA fillers
The correction of this area is carried out using the techniques described above for deep and superficial injection of fillers based on hyaluronic acid.
Deep Injections
Deep injections performed in contact with the periosteum provide a filling and projecting effect that eliminates level mismatches around the jowls. The technique proposed by the authors involves the administration of 1 or 2 deep boluses of HA.
Product properties:
• cohesiveness;
• volumizing ability;
• high elasticity (G’).
Running:
• mark the premaxillary sulcus;
• mark 1 or 2 points in the premaxillary sulcus, located 5-10 mm above the bone boundary;
• inject the bolus prependicularly, avoiding contact with the bone (slightly remove the needle if it is in contact with the bone); the tip of the needle should be located directly above the insertion of the depressor lip depressor and the depressor angle of the mouth (this point is often located in the muscular abdomen);
• in order to avoid intravascular administration of the drug, it is necessary to aspirate; HA should be injected deeply, in small amounts (average 0.1 ml) and slowly;
• The amount of product injected into each side varies and is about 0.2 ml.
The facial artery passes behind the posterior border of the descent angle of the mouth muscle, but an aspiration test should always be performed before injection to avoid damage to its mental branches.
This deep implantation, which includes contact with the bone, provides a fixed immovable filling that does not sag and provides stable support, which is often sufficient for a satisfactory result. As a result, the recess is eliminated, as well as the level difference. Optionally, a superficial HA injection can be performed.
Surface insertion (fan technique)
Also can be combined with deep infusion.
Aesthetic correction of the middle third of the face: doctor's recommendations
HA is injected subcutaneously, into the space between the skin and the muscles that lower the corner of the mouth and the lower lip. Aspiration must be performed prior to injection.
Product properties:
• high cohesiveness;
• small volumizing effect;
• moderate elasticity (G’);
• moderate modulus of viscosity (G”);
• short GC chains.
Running:
• mark the zone to be restructured;
• using a cannula (for this zone – 25 or 27 gauge) and a fan technique, inject the product subcutaneously;
• Introduction should be neat and the product should be well distributed over the target area;
• shaping and even light massage can be done to distribute and integrate HA into tissues;
• vector covers the entire zone and even slightly goes beyond it in the direction of the labiomental folds;
• don't forget about the mental artery, which is the terminal branch of the inferior alveolar artery – it can be touched with a cannula during the correction of the premaxillary sulcus or marionette wrinkles.
Good knowledge of anatomy and physiology and the use of the "right product in the right place" qualified and experienced professionals – determining factors in successful injectable facial contouring.
Face oval modeling: harmony and beauty with the help of injection technologies
According to Prime magazine







Add a comment